【路径规划】基于matlab GUI改进的迪杰斯特拉算法路径规划【含Matlab源码 1031期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
获取代码方式2:
通过紫极神光博客主页开通CSDN会员,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
获取代码方式3:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【路径规划】基于matlab GUI改进的迪杰斯特拉算法路径规划【含Matlab源码 1031期】
备注:开通CSDN会员,仅只能免费获得1份代码(有效期为开通日起,三天内有效);
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得2份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、简介
DWA算法全称为dynamic window approach,其原理主要是在速度空间(v,w)中采样多组速度,并模拟这些速度在一定时间内的运动轨迹,再通过一个评价函数对这些轨迹打分,最优的速度被选择出来发送给下位机。
1 原理分析

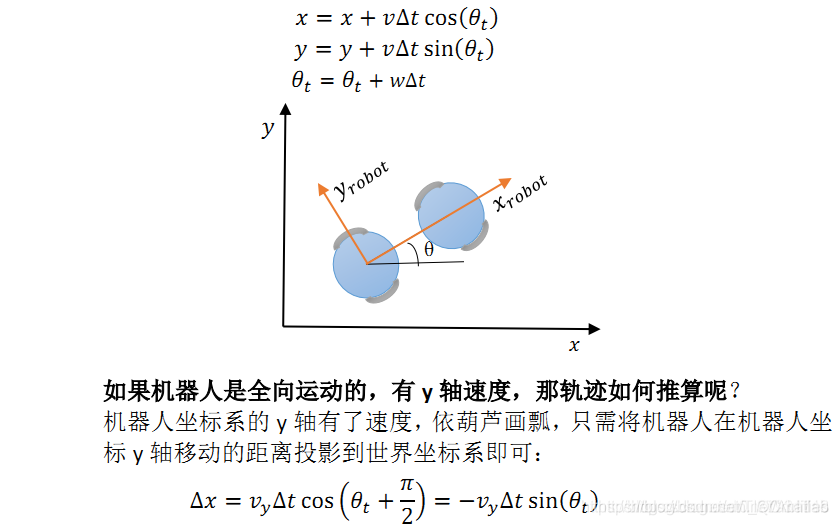

2 速度采样
机器人的轨迹运动模型有了,根据速度就可以推算出轨迹。
因此只需采样很多速度,推算轨迹,然后评价这些轨迹好不好就行了。
(一)移动机器人受自身最大速度最小速度的限制
(二) 移动机器人受电机性能的影响:由于电机力矩有限,存在最大的加減速限制,因此移动机器人軌迹前向模拟的周期sim_period内,存在一个动态窗口,在该窗口内的速度是机器人能够实际达到的速度:
(三) 基于移动机器人安全的考虑:为了能够在碰到障碍物前停下来, 因此在最大减速度条件下, 速度有一个范围。
三、部分源代码
function varargout = main(varargin)
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @main_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @main_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before main is made visible.
function main_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
handles.output = hObject;
%initial values
load('graph.mat');
load('position.mat');
load('labelnodeposition.mat');
load('labeledge.mat');
handles.graph = graph;
handles.graph_backup = graph;
handles.position = position;
handles.labelnodeposition = labelnodeposition;
handles.labeledgeposition = getlabeledgeposition;
handles.labeledge = labeledge;
handles.source = 1;
handles.destination = 1;
handles.street = 'J1 ';
guidata(hObject, handles);
axes(handles.axes1);
hold on;
gplot(handles.graph, handles.position,'-ok');
for i = 1:27
text(handles.labelnodeposition(i,1),handles.labelnodeposition(i,2),int2str(i),'FontSize',7,'Color','k');
end
for i= 1:36
text(handles.labeledgeposition(i,1),handles.labeledgeposition(i,2),handles.labeledge(i,1:3),'FontSize',7,'Color','b');
end
axis off;
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = main_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes when figure1 is resized.
function figure1_ResizeFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu2.
function popupmenu2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
val = get(hObject,'Value');
string_list = get(hObject,'String');
source =char(string_list(val));
handles.source = str2num(source);
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
val = get(hObject,'Value');
string_list = get(hObject,'String');
source = char(string_list(val));
handles.source = str2num(source);
guidata(hObject, handles);
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu3.
function popupmenu3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
val = get(hObject,'Value');
string_list = get(hObject,'String');
destination = char(string_list(val));
handles.destination = str2num(destination);
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
val = get(hObject,'Value');
string_list = get(hObject,'String');
destination = char(string_list(val));
handles.destination = str2num(destination);
guidata(hObject, handles);
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
axes(handles.axes1);
[cost rute] = showShortestPath(handles.graph,handles.position,handles.source,handles.destination);
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu4.
function popupmenu4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
val = get(hObject,'Value');
string_list = get(hObject,'String');
handles.street = char(string_list(val));
guidata(hObject, handles);
function [node1 node2]=street2node(street)
node1=1;
node2=2;
switch street
case 'J1'
node1 = 1;
node2 = 2;
case 'J2'
node1 = 2;
node2 = 3;
case 'J3'
node1 = 3;
node2 = 4;
case 'J4'
node1 = 4;
node2 = 5;
case 'J5'
node1 = 22;
node2 = 26;
case 'J6'
node1 = 26;
node2 = 27;
case 'J7'
node1 = 8;
node2 = 9;
case 'J8'
node1 = 9;
node2 = 10;
case 'J9'
node1 = 10;
node2 = 11;
case 'J10'
node1 = 6;
node2 = 7;
case 'J11'
node1 = 7;
node2 = 12;
case 'J12'
node1 = 12;
node2 = 13;
case 'J13'
node1 = 13;
node2 = 14;
case 'J14'
node1 = 14;
node2 = 15;
case 'J15'
node1 = 15;
node2 = 16;
case 'J16'
node1 = 17;
node2 = 18;
case 'J17'
node1 = 18;
node2 = 19;
case 'J18'
node1 = 19;
node2 = 20;
case 'J19'
node1 = 2;
node2 = 7;
case 'J20'
node1 = 22;
node2 = 8;
case 'J21'
node1 = 8;
node2 = 12;
case 'J22'
node1 = 12;
node2 = 17;
case 'J23'
node1 = 17;
node2 = 23;
case 'J24'
node1 = 9;
node2 = 13;
case 'J25'
node1 = 13;
node2 = 18;
case 'J26'
node1 = 18;
node2 = 24;
case 'J27'
node1 = 3;
node2 = 26;
case 'J28'
node1 = 26;
node2 = 10;
case 'J29'
node1 = 10;
node2 = 14;
case 'J30'
node1 = 14;
node2 = 19;
case 'J31'
node1 = 19;
node2 = 25;
case 'J32'
node1 = 4;
node2 = 27;
case 'J33'
node1 = 27;
node2 = 11;
case 'J34'
node1 = 11;
node2 = 15;
case 'J35'
node1 = 15;
node2 = 20;
case 'J36'
node1 = 20;
node2 = 21;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
四、运行结果


五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118065939
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)