【数字信号调制】基于matlab GUI数字信号调制系统【含Matlab源码 1030期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【数字信号调制】基于matlab GUI数字信号调制系统【含Matlab源码 1030期】
获取代码方式2:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、数字信号调制系统简介
二进制数字信号调制原理
数字调制是指用数字基带信号对载波的某些参量进行控制, 使载波的这些参量随基带信号的变化而变化。在通信系统中, 作为载波的正弦波有幅度、频率和相位3个参数, 对应的也就有3种基本的调制方式:调幅、调频和调相。由于数字信号不同与模拟信号的特殊性, 在数字载波通信中, 这3种基本的调制方式分别被称为幅移 (ASK) 、频移键控 (FSK) 和相移键控 (PSK) 。调制信号是二进制数字基带信号时, 这种调制称为二进制数字调制。在二进制数字调制中, 载波的幅度、频率和相位只有两种变化方式。
1 ASK调制
振幅键控是利用载波的幅度变化来传递数字信息, 而其频率和初相位保持不变。二进制幅度键控 (2ASK) 方式是数字调制方式中出现最早也是最简单的一种方法。这种方法最初用于电报系统, 二进制振幅键控常常作为研究其它数字调制方式的基础。2ASK调制信号只有0或1两个电平相乘的, 结果相当于将载频或者关断, 或者接通, 它的实际意义是当调制的数字信号为“1”时, 传输载波;当调制的数字信号为“0”时, 不传输载波。
2ASK信号的一般表达式为:
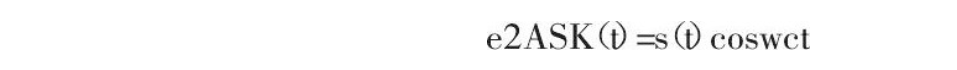
其中

2 FSK调制
频移键控是利用载波的频率变化来传递数字信息。在2FSK中, 载波的频率随二进制基带信号在f1和f0的两个频率点变化。它的实际意义是当调制的数字信号为“1”或“0”时传输f1或f2频率的载波。

其中ω1=2nf1, ω0=2nf0, θn为频率为f1的载波的初始相位, φn为频率为f0的载波的初始相位。令 为Dn的反码, 即

则2FSK信号可表示为:

3 PSK调制
相移键控是利用载波的相位变化来传递数字信息, 而振幅和频率保持不变。PSK调制时, 载波的相位随调制信号状态不同而改变。如果两个频率相同的载波同时开始振荡, 这两个频率同时达到正最大值, 同时达到零值, 同时达到负最大值, 此时它们就处于“同相”状态;如果一个达到正最大值时, 另一个达到负最大值, 则称为“反相”。一般把信号振荡一次 (一周) 作为360度。如果一个波比另一个波相差半个周期, 我们说两个波的相位差180度, 也就是反相。当传输数字信号时, “1”码控制发0度相位, “0”码控制发180度相位。相移键控有很好的抗干扰性, 在有衰落的信道中也能获得很好的效果。
三、部分源代码
function varargout = display_signal(varargin)
% DISPLAY_SIGNAL MATLAB code for display_signal.fig
% DISPLAY_SIGNAL, by itself, creates a new DISPLAY_SIGNAL or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = DISPLAY_SIGNAL returns the handle to a new DISPLAY_SIGNAL or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% DISPLAY_SIGNAL('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in DISPLAY_SIGNAL.M with the given input arguments.
%
% DISPLAY_SIGNAL('Property','Value',...) creates a new DISPLAY_SIGNAL or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before display_signal_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to display_signal_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help display_signal
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 20-Dec-2020 17:01:23
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @display_signal_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @display_signal_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before display_signal is made visible.
function display_signal_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to display_signal (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for display_signal
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes display_signal wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = display_signal_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on selection change in type.
function type_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to type (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = cellstr(get(hObject,'String')) returns type contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from type
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function type_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to type (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function Fb_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Fb (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of Fb as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of Fb as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function Fb_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Fb (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function Fc_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Fc (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of Fc as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of Fc as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function Fc_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Fc (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function Bit_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Bit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of Bit as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of Bit as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function Bit_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to Bit (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
tempobj=findobj(gcbf,'tag','type');
modu_type=get(tempobj,'value');
fc=eval(get(handles.Fc,'String')); %可选参数设置
B=str2double(get(handles.Fb,'String'));
DisBit=str2double(get(handles.Bit,'String'));
switch(modu_type)
case 1
nper=B/fc; %一个码元中所包含的载波周期数
nsamp=128; %过采样率
fs=nsamp*B; %采样率
Ts=1/fs; %采样周期
NumBit=1024; %数据位数
%数字基带信号产生
Data=randint(1,NumBit);
NumSample=NumBit*nsamp; %总采样点数
signal=zeros(1,NumSample);
start=1;
for i=1:NumBit
if(Data(i))
signal(start:start+nsamp-1)=1;
end
start=start+nsamp;
end
t=0:Ts:Ts*(NumSample-1);
ASK_signal=signal.*sin(2*pi*fc*t);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
四、运行结果








五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 沈再阳.精通MATLAB信号处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[2]高宝建,彭进业,王琳,潘建寿.信号与系统——使用MATLAB分析与实现[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[3]王文光,魏少明,任欣.信号处理与系统分析的MATLAB实现[M].电子工业出版社,2018.
[4]曾祥龙,梁清梅,索丽敏.运用MATLAB实现对数字信号调制的仿真[J].黑龙江科技信息. 2009,(32)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118060970
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)