【语音识别】基于matlab GUI MFCC+VQ说话人识别系统【含Matlab源码 1153期】
一、MFCC+VQ简介
1 引言
在人类生活的这样一个信息高度交互的社会里, 判定人的身份是一个十分重要的问题。传统的身份鉴别方法 (如钥匙、证件、口令等等) 已经不能满足社会的需要, 基于生物特征的身份鉴别技术为我们提供了一种更加方便和可靠的方法, 已经引起了国内外学术界和企业界的极大关注。说话人识别技术是一项根据语音波形中反映说话人生理和行为特征的语音参数, 自动识别说话人身份的技术。
属于生物识别技术的一种。从说话人识别系统的职能上看, 可以分为说话人辨认系统和说话人确认系统。从识别基于的对象来看, 又可以分为基于文本的说话人识别系统和文本无关的说话人识别系统两大类。根据待识别的说话人是否在注册的说话人集合内, 说话人识别可以分为开集 (Open-set) 识别和闭集 (Close-set) 识别。说话人识别的关键问题在于特征参数的选择与识别模型的建立, 目前常用的特征参数有LPC、LPCC以及MFCC等, 常用的识别模型有DTW、VQ、HMM等。
2 说话人识别的过程及系统框架
图1中, 建立和应用说话人识别系统分为两个部分:训练 (或注册) 部分和识别部分。

图1 说话人识别系统框图
3 说话人识别中的特征提取
3.1 Mel倒谱参数 (MFCC)
倒谱特征是用于说话人个性特征和说话人识别的最有效的特征之一[4]。实验表明, 大部分情况下, MFCC优于其他倒谱系数。其提取及计算过程如下:
(1) 原始语音信号S (n) 经过预加重、分帧、加窗等处理, 得到每个语音帧的时域信号X (n) 。然后经过离散傅里叶变换 (DFT) 后得到离散频谱X (k) 。设语音信号的DFT为:
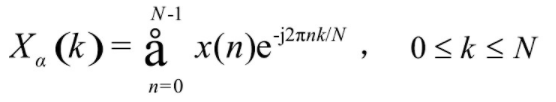
式中x (n) 为输入的语音信号, N表示傅里叶变换的点数。
(2) 将上述离散频谱X (k) 通过Mel频率滤波器组得到Mel频谱并通过对数能量的处理, 得到对数频谱S (m) 。
(3) 计算每个滤波器组输出的对数能量为:
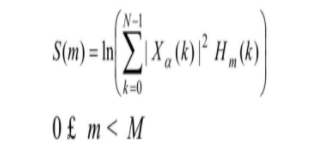
(4) 经离散余弦变换 (DCT) 得到MFCC系数:
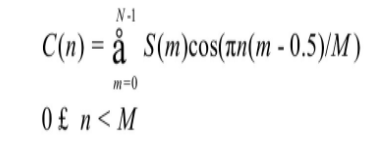
例如, 语音样本为“说话人识别”, 采样率8000kHz, 精度为8bit, 滤波器组数为24, 系数选取了前面的16个 (C0~C15) 提取的MFCC参数如图2, 图中x轴表示语音分析的帧数, y轴表示倒谱系数的维数, z轴表示对应的倒谱值。图2 (a) 带有倒谱C0项, 图2 (b) 不带有倒谱C0项。
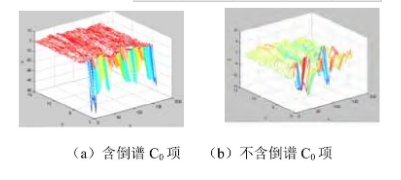
图2 MFCC参数
从图中可以看出, 对于MFCC系数, 它的第一维的值C0的能量很大, 故在一般的识别系统中, 将其称为能量系数, 不作为倒谱系数中的一员。
3.2 不同参数结合特征
表征说话人特征的参数主要有:基音周期、倒谱系数、共振峰频率与带宽、音调轮廓特征等。以上所有的特征参数中, 我们并不能说单独使用哪个参数就能有效可靠地表征说话人特征。一般情况下, 为了更有效地表征说话人特征, 更多地采用几个特征参数的组合使用。当各组合参数间相关性不大时, 会有较好的效果, 因为它们分别反映了语音信号的不同特征。
(1) 基音特征参数与倒谱特征结合, 它们分别描述了说话人声道、声带特征, 可以充分反映说话人特征。
(2) 利用倒谱系数和差值倒谱系数作为描述声道的信息, 利用基音和差值基音来描述激励派。
(3) 采用倒谱系数和相应的差分倒谱参数相结合等。
4 识别模型VQ
对于N个说话人集合的系统, 需要为每个人建立一个码本。训练的时候, 用LBG算法, 由说话人语音的训练样本序列聚类生成码本。识别的时候, 用同样的方法从待识别语音中提取特征序列X1…XN, 然后用系统中建立的N个码本对其进行矢量量化, 用式
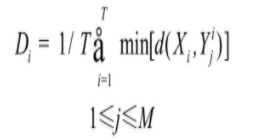
定义的平均量化畸变程度判断该矢量序列与哪一个码本的分布最为接近。其中Yji表示第i个说话人码本的第j个码字, T是特征矢量序列的长度, 也就是待识别语音所包含帧的总数, 式中, d (Xi, Yji) 采用欧式距离测度。最终的识别结果就是Di最小所对应的第i个说话人。
利用矢量量化技术时, 主要有两个问题要解决:
(1) 设计一个好的码本;
(2) 未知矢量的量化。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = untitled(varargin)
% UNTITLED M-file for untitled.fig
% UNTITLED, by itself, creates a new UNTITLED or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = UNTITLED returns the handle to a new UNTITLED or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% UNTITLED('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in UNTITLED.M with the given input arguments.
%
% UNTITLED('Property','Value',...) creates a new UNTITLED or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before untitled_OpeningFunction gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to untitled_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help untitled
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 21-May-2021 13:54:38
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @untitled_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @untitled_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin & isstr(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before untitled is made visible.
function untitled_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to untitled (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for untitled
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% This sets up the initial plot - only do when we are invisible
% so window can get raised using untitled.
if strcmp(get(hObject,'Visible'),'off')
plot(sin(1:0.01:25));
end
axes(handles.axes1);cla;plot(rand(5));
axes(handles.axes3);cla;plot(rand(5));
% UIWAIT makes untitled wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = untitled_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
axes(handles.axes1);
cla;
%plot(rand(5));
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function FileMenu_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to FileMenu (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function OpenMenuItem_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to OpenMenuItem (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
file = uigetfile('*.fig');
if ~isequal(file, 0)
open(file);
end
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function PrintMenuItem_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to PrintMenuItem (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
printdlg(handles.figure1)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function CloseMenuItem_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to CloseMenuItem (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
selection = questdlg(['Close ' get(handles.figure1,'Name') '?'],...
['Close ' get(handles.figure1,'Name') '...'],...
'Yes','No','Yes');
if strcmp(selection,'No')
return;
end
delete(handles.figure1)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
else
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor',get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'));
end
set(hObject, 'String', {'plot(rand(5))', 'plot(sin(1:0.01:25))', 'comet(cos(1:.01:10))', 'bar(1:10)', 'plot(membrane)', 'surf(peaks)'});
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu3.
function popupmenu1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = get(hObject,'String') returns popupmenu3 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu3
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
n=get(handles.popupmenu2, 'Value');
second=1;%录音时长(秒)
framelnc = 100;%length of Frames excursion
framelen = 256;%length of Frames 采样频率12.500kHz ,桢长为020.5ms
Fs =8000;
pause(2);
message={'录音开始!'};
msgbox(message);
x= audiorecord(second*Fs, Fs, 'double');
message={'录音结束!'};
msgbox(message);
pause(1);
audioplay(x, Fs);
[x1,x2,amp,zcr]=vad2(x,framelen,framelnc);
axes(handles.axes1);
cla;
%subplot(3,1,1)
plot(x)
axis([1 length(x) -1 1])
line([x1*framelnc x1*framelnc],[-1 1],'color','red');
line([x2*framelnc x2*framelnc],[-1 1],'color','red');
ylabel('归一化的原始信号')
text(x1*framelnc,0.5,'起始端点 \rightarrow',...
'HorizontalAlignment','right')
text(x2*framelnc,0.5,'\leftarrow 结束端点 ',...
'HorizontalAlignment','left')
axes(handles.axes3);
cla;
plot(amp,'b');
hold on;
plot(zcr,'y');
length(amp)
length(zcr)
pmax=max(max(amp),max(zcr));
pmin=min(min(amp),min(zcr));
axis([1 length(amp) 0 pmax])
line([x1 x1],[pmin,pmax],'color','red');
line([x2 x2],[pmin,pmax],'color','red');
ylabel('短时能量(蓝色),过零率(黄色)')
text(x1,pmax/2,'起始端点 \rightarrow',...
'HorizontalAlignment','right')
text(x2,pmax/2,'\leftarrow 结束端点 ',...
'HorizontalAlignment','left')
file = sprintf('mytrain\\s%d.wav',n);
WAVWRITE(x,Fs,file);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%code=train1('mytrain\',4);
Fm = 100;%length of Frames excursion
Fn = 256;%length of Frames 采样频率12.500kHz ,桢长为020.5ms
k = 16; % number of centroids required
n=8;
traindir='mytrain\';
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/119045794
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)