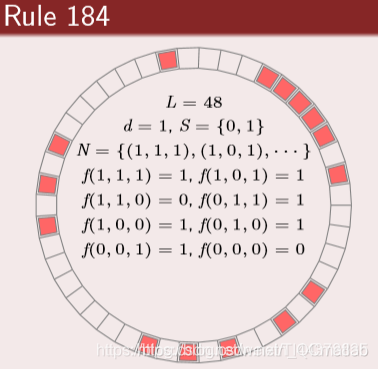
【元胞自动机】基于matlab元胞自动机交通事故通行【含Matlab源码 1345期】
一、元胞自动机简介
1 元胞自动机发展历程
最初的元胞自动机是由冯 · 诺依曼在 1950 年代为模拟生物 细胞的自我复制而提出的. 但是并未受到学术界重视.
1970 年, 剑桥大学的约翰 · 何顿 · 康威设计了一个电脑游戏 “生命游戏” 后, 元胞自动机才吸引了科学家们的注意.
1983 年 S.Wolfram 发表了一系列论文. 对初等元胞机 256 种 规则所产生的模型进行了深入研究, 并用熵来描述其演化行 为, 将细胞自动机分为平稳型, 周期型, 混沌型和复杂型.
2 对元胞自动机的初步认识
元胞自动机(CA)是一种用来仿真局部规则和局部联系的方法。典型的元胞自动机是定义在网格上的,每一个点上的网格代表一个元胞与一种有限的状态。变化规则适用于每一个元胞并且同时进行。典型的变化规则,决定于元胞的状态,以及其( 4 或 8 )邻居的状态。
3 元胞的变化规则&元胞状态
典型的变化规则,决定于元胞的状态,以及其( 4 或 8 )邻居的状态。
4 元胞自动机的应用
元胞自动机已被应用于物理模拟,生物模拟等领域。
5 元胞自动机的matlab编程
结合以上,我们可以理解元胞自动机仿真需要理解三点。一是元胞,在matlab中可以理解为矩阵中的一点或多点组成的方形块,一般我们用矩阵中的一点代表一个元胞。二是变化规则,元胞的变化规则决定元胞下一刻的状态。三是元胞的状态,元胞的状态是自定义的,通常是对立的状态,比如生物的存活状态或死亡状态,红灯或绿灯,该点有障碍物或者没有障碍物等等。
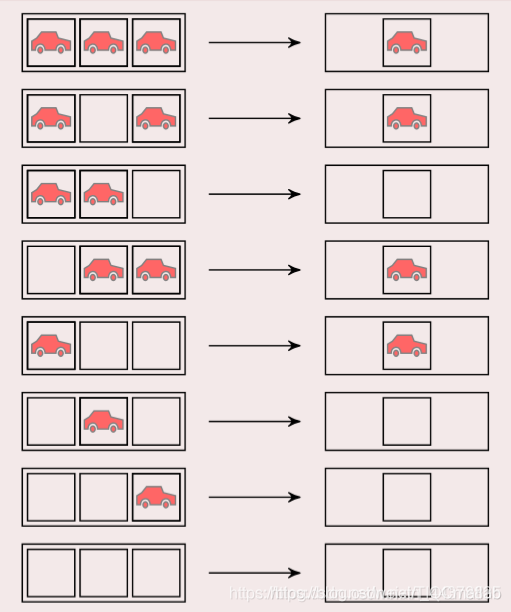
6 一维元胞自动机——交通规则
定义:
6.1 元胞分布于一维线性网格上.
6.2 元胞仅具有车和空两种状态.
7 二维元胞自动机——生命游戏
定义:
7.1 元胞分布于二维方型网格上.
7.2 元胞仅具有生和死两种状态.
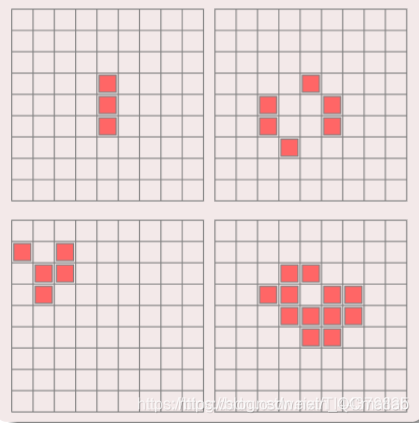
元胞状态由周围八邻居决定.
规则:
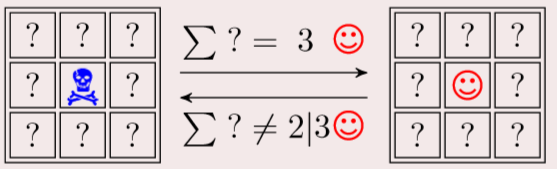
骷髅:死亡;笑脸:生存
周围有三个笑脸,则中间变为笑脸
少于两个笑脸或者多于三个,中间则变死亡。
8 什么是元胞自动机
离散的系统: 元胞是定义在有限的时间和空间上的, 并且元 胞的状态是有限.
动力学系统: 元胞自动机的举止行为具有动力学特征.
简单与复杂: 元胞自动机用简单规则控制相互作用的元胞 模拟复杂世界.
9 构成要素
(1)元胞 (Cell)
元胞是元胞自动机基本单元:
状态: 每一个元胞都有记忆贮存状态的功能.
离散: 简单情况下, 元胞只有两种可能状态; 较复杂情况下, 元胞具有多种状态.
更新: 元胞的状态都安照动力规则不断更新.
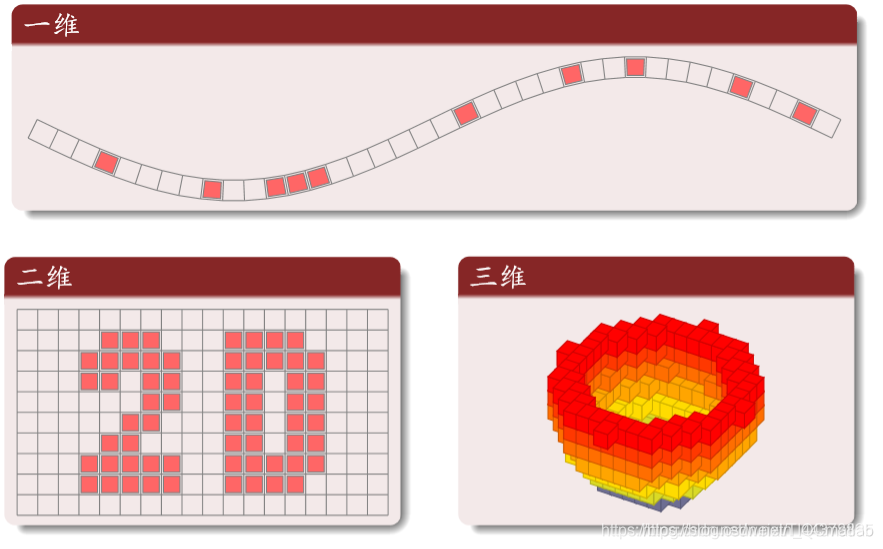
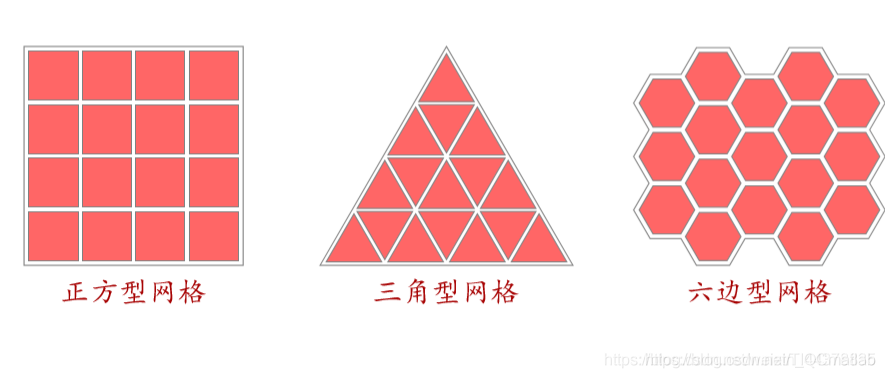
(2)网格 (Lattice)
不同维网格
常用二维网格
(3)邻居 (Neighborhood)
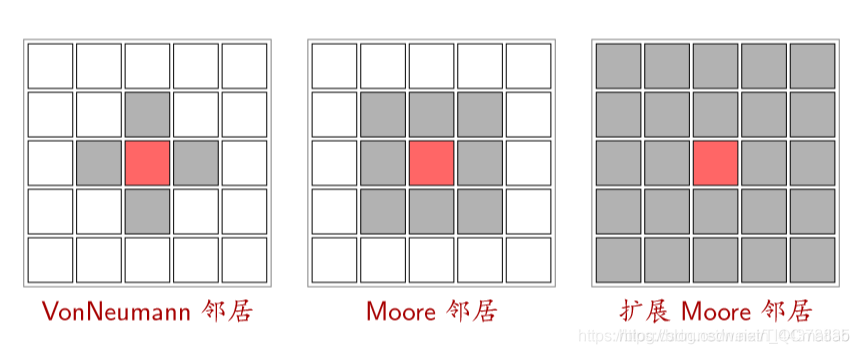
(4)边界 (Boundary)
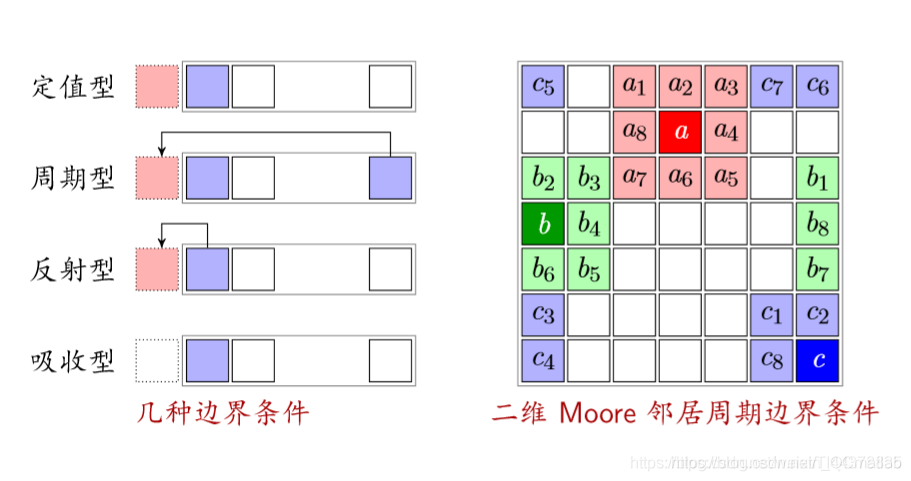
反射型:以自己作为边界的状态
吸收型:不管边界(车开到边界就消失)
(5)规则(状态转移函数)
定义:根据元胞当前状态及其邻居状况确定下一时刻该元胞状态的动力学函数, 简单讲, 就是一个状态转移函数.
分类 :
总和型: 某元胞下时刻的状态取决于且仅取决于它所有邻居 的当前状态以及自身的当前状态.
合法型: 总和型规则属于合法型规则. 但如果把元胞自动机 的规则限制为总和型, 会使元胞自动机具有局限性.
(6)森林火灾
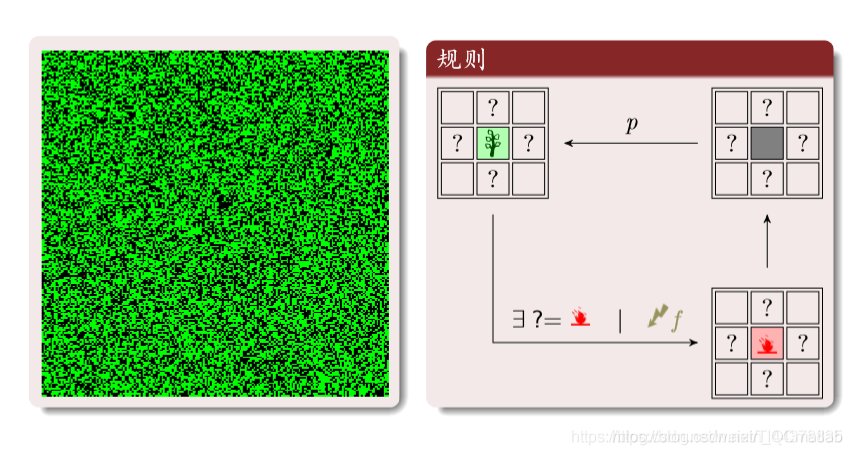
绿色:树木;红色:火;黑色:空地。
三种状态循环转化:
树:周围有火或者被闪电击中就变成火。
空地:以概率p变为树木
理性分析:红为火;灰为空地;绿是树
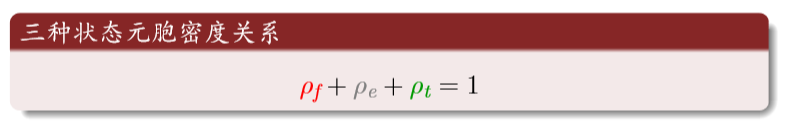
元胞三种状态的密度和为1
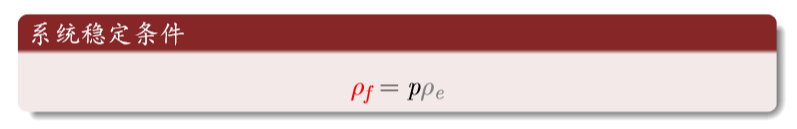
火转化为空地的密度等于空地转换为树的密度(新长出来的树等于烧没的树)

f是闪电的概率:远远小于树生成的概率;T s m a x T_{smax}T smax
是一大群树被火烧的时间尺度
程序实现
周期性边界条件
购进啊
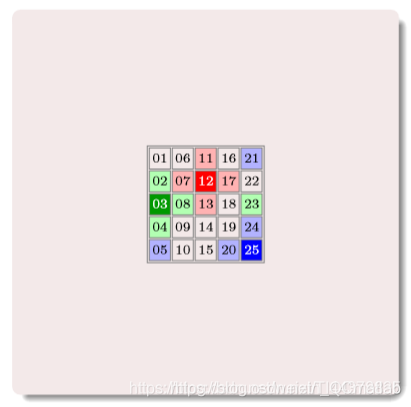
其中的数字为编号
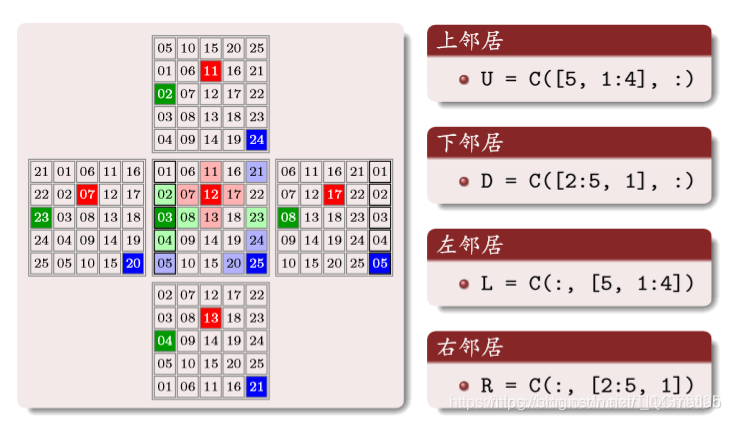
构建邻居矩阵

上面矩阵中的数字编号,对应原矩阵相同位置编号的上邻居编号,一 一对应
同样道理:
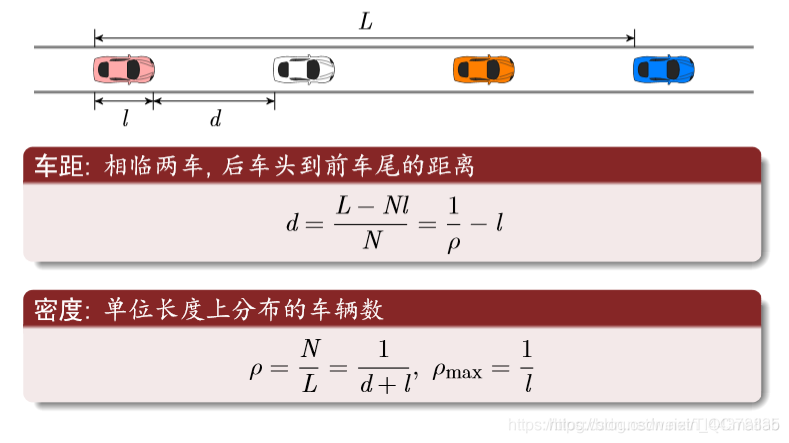
(7)交通概念
车距和密度
流量方程

守恒方程

时空轨迹(横轴是空间纵轴为时间)

红线横线与蓝色交点表示每个时间车的位置。
如果是竖线则表示车子在该位置对应的时间
宏观连续模型:
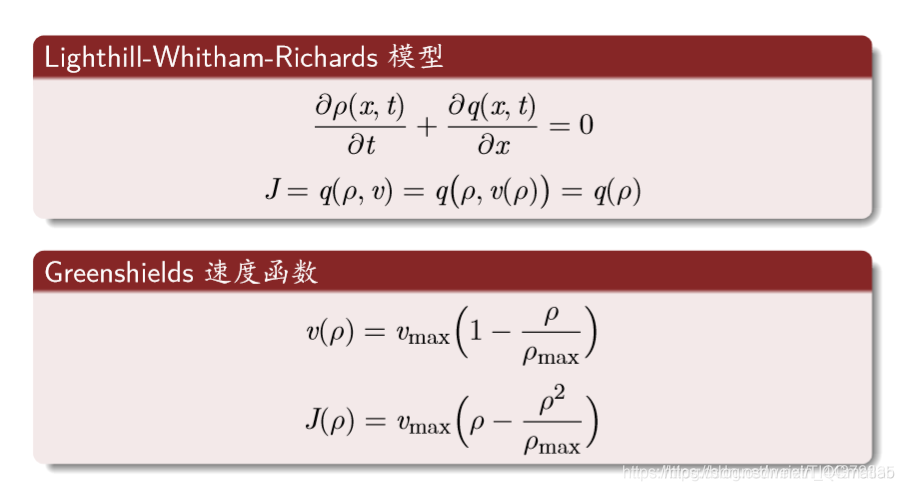
最常用的规则:
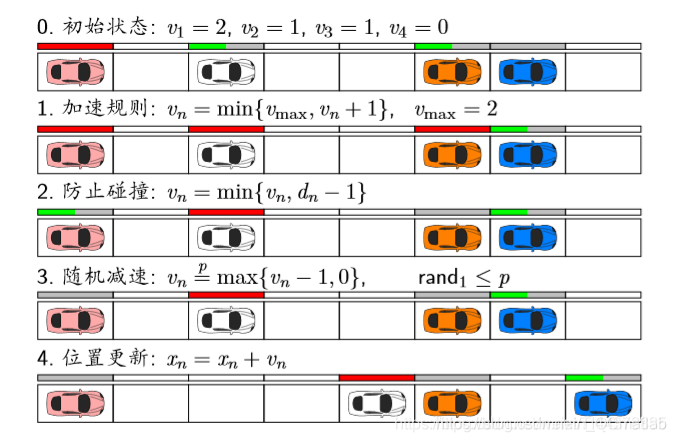
红色条表示速度是满的。
1 加速规则:不能超过v m a x ( 2 格 / s ) v_{max}(2格/s)v
max(2格/s)
2 防止碰撞:不能超过车距
理论分析:
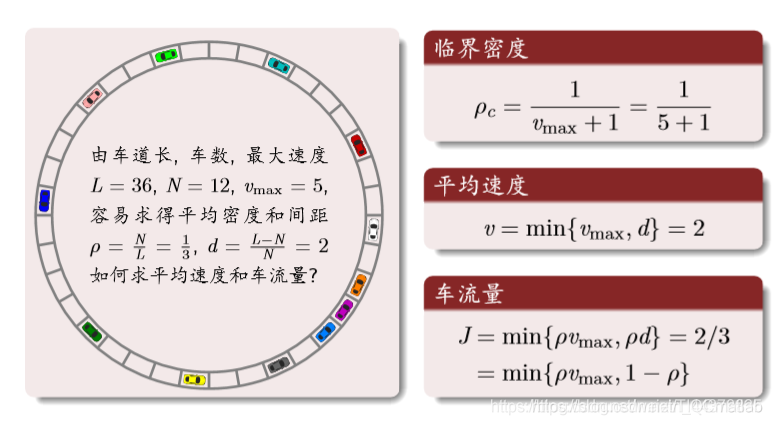
结果分析: 密度与流量
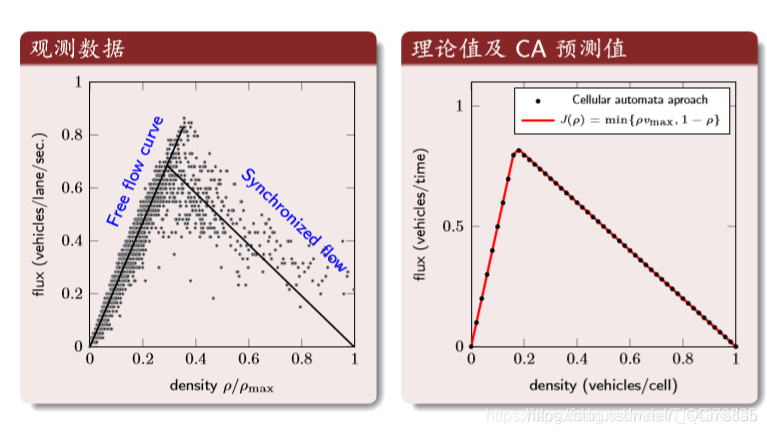
第一个图:横坐标是归一化后的密度,纵坐标是车流量。第二个图:理论值与CA的结果
结果分析: 时空轨迹
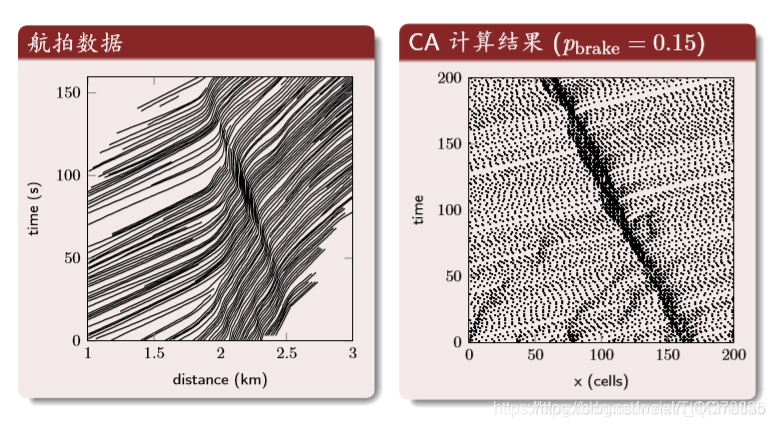
中间的深色区域是交通堵塞的区域。
二、部分源代码
% main.m
%
% This is a main script to simulate the approach, service, and departure of
% vehicles passing through a toll plaza, , as governed by the parameters
% defined below
%
% iterations = the maximal iterations of simulation
% B = number booths
% L = number lanes in highway before and after plaza
% Arrival = the mean total number of cars that arrives
% plazalength = length of the plaza
% Service = Service rate of booth
% plaza = plaza matrix
% 1 = car, 0 = empty, -1 = forbid, -3 = empty&booth
% v = velocity matrix
% vmax = max speed of car
% time = time matrix, to trace the time that the car cost to
% pass the plaza.
% dt = time step
% t_h = time factor
% departurescount = number of cars that departure the plaza in the step
% departurestime = time cost of the departure cars
% influx = influx vector
% outflux = outflux vector
% timecost = time cost of all car
% h = handle of the graphics
%
% zhou lvwen: zhou.lv.wen@gmail.com
clear;clc
iterations = 1200; % the maximal iterations of simulation
B = 3; % number booths
L = 3; % number lanes in highway before and after plaza
Arrival=3; % the mean total number of cars that arrives
plazalength = 81; % length of the plaza
[plaza, v, time,buspla] = create_plaza(B, L, plazalength);
h = show_plaza(plaza,buspla, NaN, 0.01);
timeblock=5;
dt = 0.2; % time step
t_h = 1; % time factor
vmax = 2; % max speed
vinit=1;%initial speed
busstop=6*ones(plazalength,B+2);
carstop=3*ones(plazalength,B+2);
timecost = [];
sf=0;%switchflag
for i = 1:iterations
if i==14
ss=0;
end
if i==370
ss=0;
end
if i==490
ss=0;
end
if i==550
ss=0;
end
if i==602
ss=0;
end
if i==711
ss=0;
end
% introduce new cars
[plaza, v, arrivalscount] = new_cars(Arrival, dt, plaza, v, vinit,i);
[plaza, v, buspla] = new_bus(plaza, v, vinit, i,buspla);
h = show_plaza(plaza,buspla, h, 0.02);
[timeblock,plaza] = carblock(timeblock,plaza,sf);%转向导致堵车
% update rules for lanes
r=rand();
if(r<0.3)
[plaza, v, time,buspla,busstop,carstop,sf] = switch_lanes(plaza, v, time,buspla,busstop,carstop,sf); % lane changes
[plaza, v, time,buspla] = move_forward(plaza, v, time, vmax,buspla); % move cars forward
else
[plaza, v, time,buspla] = move_forward(plaza, v, time, vmax,buspla); % move cars forward
[plaza, v, time,buspla,busstop,carstop,sf] = switch_lanes(plaza, v, time,buspla,busstop,carstop,sf); % lane changes
end
[plaza,buspla, v, time, departurescount, departurestime] = clear_boundary(plaza,buspla, v, time);
% flux calculations
influx(i) = arrivalscount;
outflux(i) = departurescount;
timecost = [timecost, departurestime];
end
h = show_plaza(plaza, h, 0.01);
xlabel({strcat('B = ',num2str(B)), ...
strcat('mean cost time = ', num2str(round(mean(timecost))))})
function [plaza, v, time,buspla] = create_plaza(B, L, plazalength)
%
% create_plaza create the empty plaza matrix( no car ).
% 1 = car, 0 = empty, -1 = forbid, -3 = empty&booth
%
% USAGE: [plaza, v, time] = create_plaza(B, L, plazalength)
% B = number booths
% L = number lanes in highway before and after plaza
% plazalength = length of the plaza
%
% zhou lvwen: zhou.lv.wen@gmail.com
plaza = zeros(plazalength,B+2); % 1 = car, 0 = empty, -1 = forbid, -3 = empty&booth
v = zeros(plazalength,B+2); % velocity of automata (i,j), if it exists
time = zeros(plazalength,B+2); % cost time of automata (i,j) if it exists
plaza(1:plazalength,[1,2+B]) = -1;
plaza(ceil(plazalength/2),[3:1+B]) =-1;
%left: angle of width decline for boundaries
toptheta = 1.3;
bottomtheta = 1.2;
for col = 2:ceil(B/2-L/2) + 1
for row = 1:(plazalength-1)/2 - floor(tan(toptheta) * (col-1))
plaza(row, col) = -1;
end
for row = 1:(plazalength-1)/2 - floor(tan(bottomtheta) * (col-1))
plaza(plazalength+1-row, col) = -1;
end
end
fac = ceil(B/2-L/2)/floor(B/2-L/2);
%right: angle of width decline for boundaries
toptheta = atan(fac*tan(toptheta));
bottomtheta = atan(fac*tan(bottomtheta));
for col = 2:floor(B/2-L/2) + 1
for row = 1:(plazalength-1)/2 - floor(tan(toptheta) * (col-1))
plaza(row,B+3-col) = -1;
end
for row = 1:(plazalength-1)/2 - floor(tan(bottomtheta) * (col-1))
plaza(plazalength+1-row,B+3-col) = -1;
end
end
buspla=plaza;
function [plaza, v, number_cars] = new_cars(Arrival, dt, plaza, v, vmax, iteration)
%
% new_cars introduce new cars. Cars arrive at the toll plaza uniformly in
% time (the interarrival distribution is exponential with rate Arrival?).
% "rush hour" phenomena can be consider by varying the arrival rate.
%
% USAGE: [plaza, v, number_cars] = new_cars(Arrival, dt, plaza, v, vmax)
% Arrival = the mean total number of cars that arrives
% dt = time step
% plaza = plaza matrix
% 1 = car, 0 = empty, -1 = forbid, -3 = empty&booth
% v = velocity matrix
% vmax = max speed of car
%
% zhou lvwen: zhou.lv.wen@gmail.com
% Find the empty lanes of the entrance where a new car can be add.
unoccupied = find(plaza(1,:) == 0);
n = length(unoccupied); % number of available lanes
function [time,plaza] = carblock(time,plaza,sf)
if plaza(122)~=1
if sf==1
plaza(122)=-1;
time=5;
elseif time<3
plaza(122)=0;
else
time=time-1;
end
end
% end
end
function [plaza, v, time,buspla,busstop,carstop,sf] = switch_lanes(plaza, v, time,buspla,busstop,carstop,sf)
%
% switch_lanes Merge to avoid obstacles.
%
% The vehicle will attempt to merge if its forward path is obstructed (dn = 0).
% The vehicle then randomly chooses an intended direction, right or left. If
% that intended direction is blocked, the car will move in the other direction
% unless both directions are blocked (the car is surrounded).
%
% USAGE: [plaza, v, time] = switch_lanes(plaza, v, time)
% plaza = plaza matrix
% 1 = car, 0 = empty, -1 = forbid, -3 = empty&booth
% v = velocity matrix
% time = time matrix, to trace the time that the car cost to pass the plaza.
%
% zhou lvwen: zhou.lv.wen@gmail.com
[L, W] = size(plaza);
found = find(plaza==1);
% if ~isempty(found)
% found = found(randperm(length(found)));
% end
sf=0;
for k=1:length(found)
if(buspla(found(k))==0)%car
if (plaza(found(k)+1)~=0)%前方有障碍
if carstop(found(k))<=0 %转向前计时
if plaza(found(k)-L) == 0
plaza(found(k)-L) = 1;
plaza(found(k)) = 0;
v(found(k)-L) = 0;
v(found(k)) = 0;
time(found(k)-L) = time(found(k));
time(found(k)) = 0;
carstop(found(k))=3;
sf=1;
end
else
carstop(found(k))=carstop(found(k))-1;%计时
end
end
else%bus
if buspla(found(k))==1%找到车头
if plaza(found(k)+1)~=0
if busstop(found(k)+1)<=0 %转向前计时
if plaza(found(k)-L)==0 && plaza(found(k)-L-1)==0
plaza(found(k)-L) = 1;
plaza(found(k)-L-1) = 1;
plaza(found(k)) = 0;
plaza(found(k)-1)=0;
buspla(found(k)-L) = 1;
buspla(found(k)-L-1) = 2;
buspla(found(k)) = 0;
buspla(found(k)-1)=0;
v(found(k)-L) = 0;
v(found(k)-L-1)=0;
v(found(k)) = 0;
time(found(k)-L) = time(found(k));
time(found(k)-L-1)=time(found(k)-1);
time(found(k)) = 0;
time(found(k)-1)=0;
busstop(found(k)+1)=6;
sf=1;
end
else
busstop(found(k)+1)=busstop(found(k)+1)-1;
end
end
end
end
end
% elseif plaza(k+L) == 0
% plaza(k+L) = 1;
% plaza(k) = 0;
% v(k+L) = v(k);
% v(k) = 0;
% time(k+L) = time(k);
% time(k) = 0;
% elseif plaza(k-1)==0
% plaza(k-1) = 1;
% plaza(k) = 0;
% v(k-1) = v(k);
% v(k) = 0;
% time(k-1) = time(k);
% time(k) = 0;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[5]孟逸凡,柳益君.基于PCA-SVM的人脸识别方法研究[J].科技视界. 2021,(07)
[6]张娜,刘坤,韩美林,陈晨.一种基于PCA和LDA融合的人脸识别算法研究[J].电子测量技术. 2020,43(13)
[7]陈艳.基于BP神经网络的人脸识别方法分析[J].信息与电脑(理论版). 2020,32(23)
[8]戴骊融,陈万米,郭盛.基于肤色模型和SURF算法的人脸识别研究[J].工业控制计算机. 2014,27(02)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120028426
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)