【优化覆盖】基于matlab萤火虫算法求解无线网络传感覆盖优化问题【含Matlab源码 1275期】
一、萤火虫优化算法(FA)简介
1 介绍
萤火虫(firefly)种类繁多,主要分布在热带地区。大多数萤火虫在短时间内产生有节奏的闪光。这种闪光是由于生物发光的一种化学反应,萤火虫的闪光模式因种类而异。萤火虫算法(FA)是基于萤火虫的闪光行为,它是一种用于全局优化问题的智能随机算法,由Yang Xin-She(2009)[1]提出。萤火虫通过下腹的一种化学反应-生物发(bioluminescence)发光。这种生物发光是萤火虫求偶仪式的重要组成部分,也是雄性萤火虫和雌性萤火虫交流的主要媒介,发出光也可用来引诱配偶或猎物,同时这种闪光也有助于保护萤火虫的领地,并警告捕食者远离栖息地。在FA中,认为所有的萤火虫都是雌雄同体的,无论性别如何,它们都互相吸引。该算法的建立基于两个关键的概念:发出的光的强度和两个萤火虫之间产生的吸引力的程度。
2 天然萤火虫的行为
天然萤火虫在寻找猎物、吸引配偶和保护领地时表现出惊人的闪光行为,萤火虫大多生活在热带环境中。一般来说,它们产生冷光,如绿色、黄色或淡红色。萤火虫的吸引力取决于它的光照强度,对于任何一对萤火虫来说,较亮的萤火虫会吸引另一只萤火虫。所以,亮度较低的个体移向较亮的个体,同时光的亮度随着距离的增加而降低。萤火虫的闪光模式可能因物种而异,在一些萤火虫物种中,雌性会利用这种现象猎食其他物种;有些萤火虫在一大群萤火虫中表现出同步闪光的行为来吸引猎物,雌萤火虫从静止的位置观察雄萤火虫发出的闪光,在发现一个感兴趣趣的闪光后,雌性萤火虫会做出反应,发出闪光,求偶仪式就这样开始了。一些雌性萤火虫会产生其他种类萤火虫的闪光模式,来诱捕雄性萤火虫并吃掉它们。
3 萤火虫算法
萤火虫算法模拟了萤火虫的自然现象。真实的萤火虫自然地呈现出一种离散的闪烁模式,而萤火虫算法假设它们总是在发光。为了模拟萤火虫的这种闪烁行为,Yang Xin-She提出了了三条规则(Yang,2009):
(1)假设所有萤火虫都是雌雄同体的,因此一只萤火虫可能会被其他任何萤火虫吸引。
(2)萤火虫的亮度决定其吸引力的大小,较亮的萤火虫吸引较暗的萤火虫。如果没有萤火虫比被考虑的萤火虫更亮,它就会随机移动。
(3)函数的最优值与萤火虫的亮度成正比。
光强(I)与光源距离(r)服从平方反比定律,因此由于空气的吸收,光的强度(I)随着与光源距离的增加而减小,这种现象将萤火虫的可见性限定在了非常有限的半径内:

萤火虫算法的主要实现步骤如下:

其中I0为距离r=0时的光强(最亮),即自身亮度,与目标函数值有关,目标值越优,亮度越亮;γ为吸收系数,因为荧光会随着距离的增加和传播媒介的吸收逐渐减弱,所以设置光强吸收系数以体现此特性,可设置为常数;r表示两个萤火虫之间的距离。有时也使用单调递减函数,如下式所示。

第二步为种群初始化:

其中t表示代数,xt表示个体的当前位置,β0exp(-γr2)是吸引度,αε是随机项。下一步将会计算萤火虫之间的吸引度:

其中β0表示r=0时的最大吸引度。
下一步,低亮度萤火虫向较亮萤火虫运动:
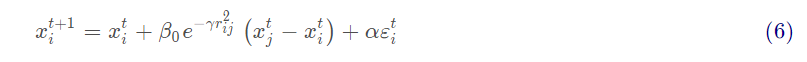
最后一个阶段,更新光照强度,并对所有萤火虫进行排序,以确定当前的最佳解决方案。萤火虫算法的主要步骤如下所示。
Begin
初始化算法基本参数:设置萤火虫数目n,最大吸引度β0,光强吸收系数γ,步长因子α,最大迭代次数MaxGeneration或搜索精度ε;
初始化:随机初始化萤火虫的位置,计算萤火虫的目标函数值作为各自最大荧光亮度I0;
t=1
while(t<=MaxGeneration || 精度>ε)
计算群体中萤火虫的相对亮度I(式2)和吸引度β(式5),根据相对亮度决定萤火虫的移动方向;
更新萤火虫的空间位置,对处在最佳位置的萤火虫进行随机移动(式6);
根据更新后萤火虫的位置,重新计算萤火虫的亮度I0;
t=t+1
end while
输出全局极值点和最优个体值。
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
萤火虫算法与粒子群算法(PSO)和细菌觅食算法(BFA)有相似之处。在位置更新方程中,FA和PSO都有两个主要分量:一个是确定性的,另一个是随机性的。在FA中,吸引力由两个组成部分决定:目标函数和距离,而在BFA中,细菌之间的吸引力也有两个组成部分:适应度和距离。萤火虫算法实现时,整个种群(如n)需要两个内循环,特定迭代需要一个外循环(如I),因此最坏情况下FA的计算复杂度为O(n2I)。
二、部分源代码
%% Main Function
clc;
clear;
%% Parameters Setting
w = 100;
d = 100; % dimensions of each solutions(firefly)
point = d; %the sensor point covered by WSN 100*100
% 选择的探测半径
r = 7; % radius of sensor point coverage region in WSN
q = 0;
% 参数意义
para = [25 5 0.7 0.2 1];% parameters [n N_iteration alpha betamin gamma]
Ub = ones(1,d).*w; %/*upper bounds of the parameters. */
Lb = zeros(1,d); %/*lower bound of the parameters.*/
% Initial random guess
u0=(Lb+Ub)/2;
%% Wireless Sensor Network Deployment using Fireflies Algorithm
% 函数ffa_wsn为萤火虫算法的实质
[ux,uy,fval,NumEval,maxzn]=ffa_wsn(u0,Lb,Ub,para,q);
%% Results Visualization
draw(ux, uy, 100, 7)
bestsolutionx = ux;
bestsolutiony = uy;
bestojb = fval
total_number_of_function_evaluations = NumEval
function [nsx,nsy] = ffa_move(n, nsx, nsy, Lightn, nsxo, nsyo, Lighto, alpha, betamin, gamma, b)
%% Move all fireflies toward brighter ones
% optional extra parameters: (Lb, Ub, nxbest, nybest,Lightbest)
% Note:
% the ways of updating solution are strongly encouraged to overwrite,
% because the original one is time consuming,
% a simple way is to update solution randomly,
% but ensure the new coverage after updated should be better,
% otherwise, do not update
%
% ==================================
%%
% Scaling of the system
% scale=abs(Ub-Lb);
% Updating fireflies
for i = 1:n,
% The attractiveness parameter beta=exp(-gamma*r)
for j = 1:n,
k = randi([1, 100],1,1);
l = randi([1, 100],1,1);
rx = abs(nsx(i,k) - nsx(j,l));
ry = abs(nsy(i,k) - nsy(j,l));
rx1 = abs(nsx(i,l) - nsx(j,k));
ry1 = abs(nsy(i,l) - nsy(j,k));
% r=sqrt(sum((nsx(i,:)-nsx(j,:)).^2)+(nsy(i,:)-nsy(j,:)).^2); %r^2=||xi-xj||^2+||yi-yj||^2
% Update moves
if Lightn(i) < Lighto(j), % Brighter and more attractive
% ================= original ==========================
% beta0 = 1;
% beta = (beta0 - betamin)*exp(-gamma*r.^2) + betamin;
% b = beta0 - betamin
% ====================================================
%% Update Solution
% TODO: NEED TO BE REPLACED WITH OTHER UPDATE METHOD
betax = b*exp(-gamma*rx.^2) + betamin;
betay = b*exp(-gamma*ry.^2) + betamin;
betax1 = b*exp(-gamma*rx1.^2) + betamin;
betay1 = b*exp(-gamma*ry1.^2) + betamin;
tmpf = alpha.*(rand(1,1) - 0.5);%.*scale;
nsx(i,k) = nsx(i,k).*(1-betax) + nsxo(j,l).*betax + tmpf;
nsy(i,k) = nsy(i,k).*(1-betay) + nsyo(j,l).*betay + tmpf;
nsx(i,l) = nsx(i,l).*(1-betax1) + nsxo(j,k).*betax + tmpf;
nsy(i,l) = nsy(i,l).*(1-betay1) + nsyo(j,k).*betay + tmpf;
Solution_temp = [nsx(i,:);nsy(i,:)];
Lightn_temp = coverage(Solution_temp,100,7);
if Lightn_temp < Lightn(i) %lightness didn't be improved
nsx(i,:) = nsxo(i,:);
nsy(i,:) = nsyo(i,:);
else Lightn(i) = Lightn_temp;
Lighto(i) = Lightn(i);
end
end
end % end for j
end % end for i
function [nxbest,nybest,fbest,NumEval,maxzn]...
= ffa_wsn(u0, Lb, Ub, para,q)
%% Check input parameters (otherwise set as default values)
%if nargin<6,
%para=[20 150 0.25 0.20 1];
%end
%if nargin<5, Ub=[]; end
%if nargin<4, Lb=[]; end
%if nargin<3,
%disp('Usuage: FA_wsn(u0,Lb,Ub,para)');
%end
% n=number of fireflies
% MaxGeneration=number of pseudo time steps
% ------------------------------------------------
% alpha=0.25; % Randomness 0--1 (highly random)
% betamn=0.20; % minimum value of beta
% gamma=1; % Absorption coefficient
% ------------------------------------------------
% @author: Shangru Zhong
% @email: draco.mystack@gmail.com
% @date: 11/01/2013
% ==================================
%% 先前para数组中各个参数的含义
% 萤火虫数目
n = para(1);
% 迭代次数
MaxGeneration = para(2);
% 步长因子
alpha = para(3);
% 待理解
betamin = para(4);
gamma = para(5);
beta0 = 1;
b = beta0-betamin;
NumEval = n*MaxGeneration;% Total number of function evaluations
disp('Simple bounds/limits are improper!');
return
end
% Calcualte dimension
d = length(u0);
% Initial values of an array
zn = ones(n, 1);
% ------------------------------------------------
% generating the initial locations of n fireflies
% 初始化萤火虫位置
[nsx, nsy, Lightn] = init_ffa(n, d, Lb, Ub, u0);
% Iterations or pseudo time marching
for iter = 1:MaxGeneration,
2*100
zn(i) = coverage(Solution,100,7); % WSN coverage of solution i (with points 100 and radius 7)
Lightn(i) = zn(i);
end
maxzn(q) = max(zn);
disp(['coverage of current solution: ', num2str(maxzn(q))])
% minzn(a)=min(zn)
%% Find the current best
nsxo = nsx;
nsyo = nsy;
Lighto = Lightn;
% Move all fireflies to the better locations
[nsx,nsy] = ffa_move(n, nsx, nsy, Lightn, nsxo, nsyo, Lighto, alpha, betamin, gamma, b);%Lb,Ub);
end % end of iterations
% Ranking fireflies by their light intensity/objectives
[Lightn,Index] = sort(zn);
nxbest = nsx(n,:);
nybest = nsy(n,:);
Lightbest = Lightn(n);
fbest = Lightbest;
% Check if the updated solutions/locations are within limits
[nsx, nsy] = findlimits(n, nsx, nsy, Lb, Ub);
function alpha = alpha_new(alpha, NGen)
% alpha_n=alpha_0(1-delta)^NGen=0.005
% alpha_0=0.9
delta=1-(0.005/0.9)^(1/NGen);
alpha=(1-delta)*alpha;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
三、运行结果

四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
[3]群体智能优化算法之萤火虫算法(Firefly Algorithm,FA)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120063674
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)