【语音处理】基于matlab Fxlms算法有源噪声控制系统【含Matlab源码 1394期】
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
通过订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可获得此代码。
获取代码方式2:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【基础处理】基于matlab Fxlms算法有源噪声控制系统【含Matlab源码 1394期】
备注:
订阅紫极神光博客付费专栏,可免费获得1份代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
二、FxLMS算法简介
滤波x-LMS算法,即FxLMS算法,是在LMS算法的基础上,考虑了次级声通道对主动噪声控制系统的影响而进行的改进,其算法原理框图如图1所示。

图1 反馈FxLMS自适应算法原理框图
其中,x(n)为估计的参考信号,W(Z)为横向滤波器,S(Z)为次级扬声器到误差传声器之间的声学路径,yw(n)表示滤波器的输出,Sh(Z)为S(Z)的估计,理论上,Sh(Z)与S(Z)相等,e(n)为残余噪声。
FxLMS算法的计算过程如下:
1)计算滤波器输出yw(n)

式中 wL=[w0(n),w1(n),w2(n),…,wL-1(n)]为滤波抽头权系数;x(n-L)=[x(n),x(n-1),…,(n-L+1)]为滤波器对应的输入向量,L为滤波器的长度。
2)计算传递到误差传声器的声波ys(n)
ys(n)=yw(n)S(n) (2)
式中 “”为线性卷积运算,S(n)为S(Z)的脉冲响应。
3)计算LMS算法的输入信号xh(n)
xh(n)=x(n)*Sh(n) (3)
式中 Sh(n)为Sh(Z)的脉冲响应。
4)计算残余噪声e(n)
e(n)=d(n)+ys(n) (4)
5)计算抽头权系数向量w(n)的更新
w(n+1)=w(n)+2μe(n)·xh(n) (5)
式中 μ为固定步长因子,其收敛范围如下式所示
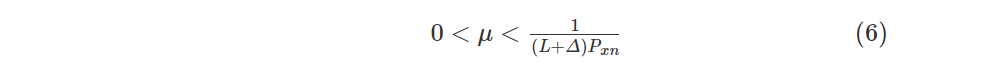
式中 Δ为考虑次级路径存在的延迟,Pxn为滤波输入信号的功率。
三、部分源代码
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Set simulation duration (normalized)
clear
T=1000;
% We do not know P(z) and S(z) in reality. So we have to make dummy paths
Pw=[0.01 0.25 0.5 1 0.5 0.25 0.01];
Sw=Pw*0.25;
% Remember that the first task is to estimate S(z). So, we can generate a
% white noise signal,
% send it to the actuator, and measure it at the sensor position,
% Then, start the identification process
Shx=zeros(1,16); % the state of Sh(z)
Shw=zeros(1,16); % the weight of Sh(z)
e_iden=zeros(1,T); % data buffer for the identification error
% and apply least mean square algorithm
mu=0.1; % learning rate
for k=1:T, % discrete time k
Shy=sum(Shx.*Shw); % calculate output of Sh(z)
e_iden(k)=y_iden(k)-Shy; % calculate error
Shw=Shw+mu*e_iden(k)*Shx; % adjust the weight
end
% Lets check the result
subplot(2,1,1)
plot([1:T], e_iden)
ylabel('Amplitude');
xlabel('Discrete time k');
legend('Identification error');
subplot(2,1,2)
stem(Sw)
hold on
stem(Shw, 'r*')
ylabel('Amplitude');
xlabel('Numbering of filter tap');
legend('Coefficients of S(z)', 'Coefficients of Sh(z)')
% The second task is the active control itself. Again, we need to simulate
% the actual condition. In practice, it should be an iterative process of
% 'measure', 'control', and 'adjust'; sample by sample. Now, let's generate
% the noise:
X=randn(1,T);
% and measure the arriving noise at the sensor position,
% Initiate the system,
Cx=zeros(1,16); % the state of C(z)
Cw=zeros(1,16); % the weight of C(z)
Sx=zeros(size(Sw)); % the dummy state for the secondary path
e_cont=zeros(1,T); % data buffer for the control error
Xhx=zeros(1,16); % the state of the filtered x(k)
% and apply the FxLMS algorithm
mu=0.1; % learning rate
for k=1:T, % discrete time k
Cx=[X(k) Cx(1:15)]; % update the controller state
Cy=sum(Cx.*Cw); % calculate the controller output
Sx=[Cy Sx(1:length(Sx)-1)]; % propagate to secondary path
e_cont(k)=Yd(k)-sum(Sx.*Sw); % measure the residue
end
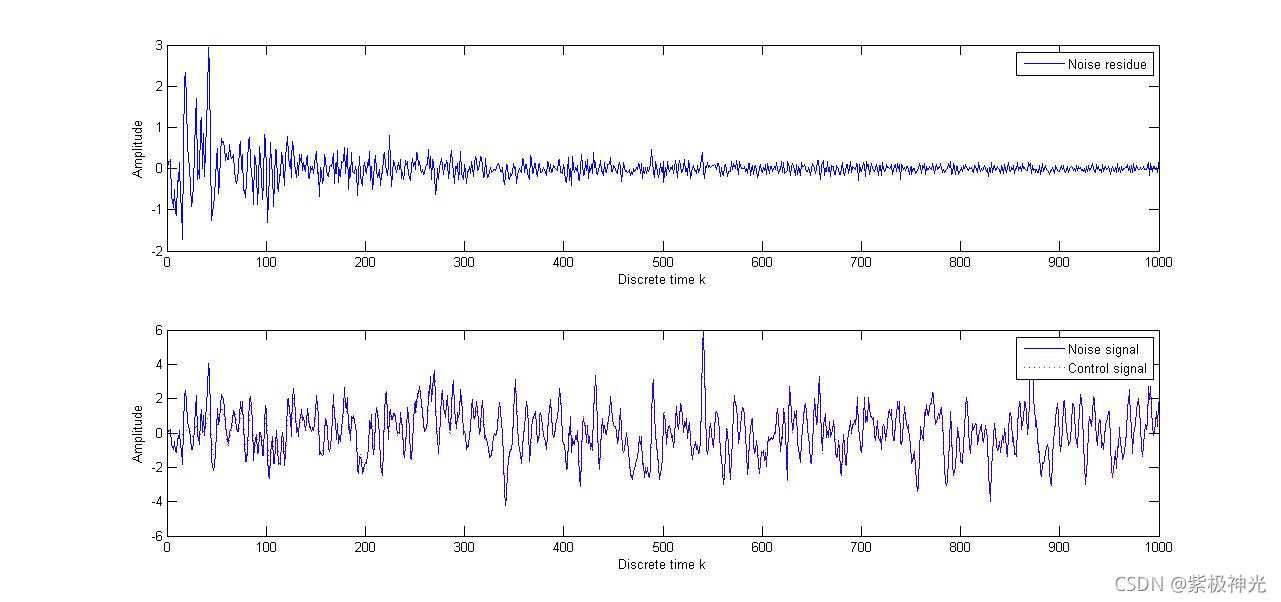
% Report the result
figure
subplot(2,1,1)
plot([1:T], e_cont)
ylabel('Amplitude');
xlabel('Discrete time k');
legend('Noise residue')
subplot(2,1,2)
plot([1:T], Yd)
hold on
plot([1:T], Yd-e_cont, 'r:')
ylabel('Amplitude');
xlabel('Discrete time k');
legend('Noise signal', 'Control signal')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
四、运行结果

五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[3]龚孝平,郭勇,刘强,朱再胜.驾驶室主动降噪的改进FxLMS算法及DSP实现[J].传感器与微系统. 2021,40(09
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120747245
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)