【SVM回归预测】基于matlab布谷鸟搜索算法优化SVM回归预测【含Matlab源码 1525期】
一、布谷鸟算法简介
布谷鸟算法,英文叫做Cuckoo search (CS algorithm)。首先还是同样,介绍一下这个算法的英文含义, Cuckoo是布谷鸟的意思,啥是布谷鸟呢,是一种叫做布谷的鸟,o(∩_∩)o ,这种鸟她妈很懒,自己生蛋自己不养,一般把它的宝宝扔到别的种类鸟的鸟巢去。但是呢,当孵化后,遇到聪明的鸟妈妈,一看就知道不是亲生的,直接就被鸟妈妈给杀了。于是这群布谷鸟宝宝为了保命,它们就模仿别的种类的鸟叫,让智商或者情商极低的鸟妈妈误认为是自己的亲宝宝,这样它就活下来了。
布谷鸟搜索算法(Cuckoo Search, CS)是2009年Xin-She Yang 与Suash Deb在《Cuckoo Search via Levy Flights》一文中提出的一种优化算法。布谷鸟算法是一种集合了布谷鸟巢寄生性和莱维飞行(Levy Flights)模式的群体智能搜索技术,通过随机游走的方式搜索得到一个最优的鸟巢来孵化自己的鸟蛋。这种方式可以达到一种高效的寻优模式。
1 布谷鸟的巢寄生性

2 莱维飞行
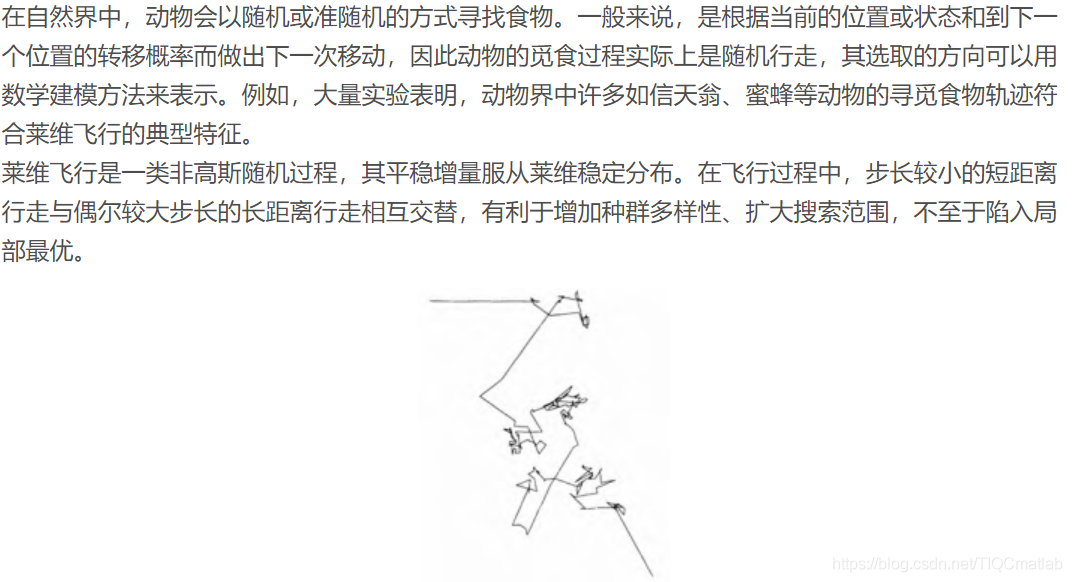
图1.模拟莱维飞行轨迹示意图
3 布谷鸟搜索算法的实现过程

二、部分源代码
clear; clc; close all;
%% 数据导入
data = csvread ('输入输出数据集/VMD_Brent_Total.csv');
IMF = data(:,14);
%% 划分训练集和测试集
x = 5; % sliding window length
z = 1; % output length
[train_input,train_output,test_input,test_output] = Split(IMF,x,z); % 默认按照 8:2 的比例划分训练集和测试集
%% 预处理
%归一化
%% CS-SVR
time= 50;
n=20; % n为巢穴数量
pa=0.20; % 被宿主发现的概率
dim = 2; % 需要寻优的参数个数
% 随机初始化巢穴
nest=zeros(n,dim);
for i=1:n % 遍历每个巢穴
nest(i,:)=Lb+(Ub-Lb).*rand(size(Lb)); % 对每个巢穴,随机初始化参数
end
fitness=ones(1,n); % 目标函数值初始化
[fmin,bestnest,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,nest,fitness,input_train,output_train,input_test,output_test); % 找出当前最佳巢穴和参数
%% 迭代开始
for t=1:time
new_nest=get_cuckoos(nest,bestnest,Lb,Ub); % 保留当前最优解,寻找新巢穴
[~,~,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,new_nest,fitness,input_train,output_train,inpu
% 找出当前最佳巢穴和参数
[fnew,best,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,new_nest,fitness,input_train,output_train,input_test,output_test);
if fnew<fmin
fmin=fnew;
bestnest=best ;
end
end
%% 打印参数选择结果
bestobjfun=fmin;
bestc=bestnest(1);
bestg=bestnest(2);
disp('打印参数选择结果');
str=sprintf('Best c = %g,Best g = %g',bestc,bestg);
disp(str)
%% 利用回归预测分析最佳的参数进行SVM网络训练
cmd_cs_svr=['-s 3 -t 2',' -c ',num2str(bestnest(1)),' -g ',num2str(bestnest(2))];
model_cs_svr = svmtrain(output_train',input_train',cmd_cs_svr); % SVM模型训练
%% SVM网络回归预测
[output_test_pre,acc,decision_values]=svmpredict(output_test',input_test',model_cs_svr); % SVM模型预测及其精度
test_pre=mapminmax('reverse',output_test_pre',rule2);
test_pre = test_pre';
figure('Name','原始-预测图')
plot(test_pre,'r-');hold on;plot((test_output),'b-');
legend('预测','原始')
set(gcf,'unit','centimeters','position',[15,13,20,13])
result=[test_output',test_pre];
MAE = mymae(test_output',test_pre)
MSE = mymse(test_output',test_pre)
MAPE = mymape(test_output',test_pre)
%% 显示程序运行时间
% toc
function [bestsol,fval]=cuckoo_ori_with_chinese_note(time)
% 由CS算法源码添加中文注释,Genlovy Hoo,2016.09.05
clear
clc
close all
format long
if nargin<1
% Number of iteraions 迭代次数
time=2000;
end
disp('Computing ... it may take a few minutes.');
% Number of nests (or different solutions)
n=25; % n为巢穴数量
% Discovery rate of alien eggs/solutions
pa=0.25; % 被宿主发现的概率
% Simple bounds of the search domain
% Lower bounds and upper bounds
dim = 3; % 需要寻优的参数个数
Lb=[0.05,0.25,2.0]; % 设置参数下界
Ub=[2.0,1.3,15.0]; % 设置参数上界
% Random initial solutions
nest=zeros(n,dim);
for i=1:n % 遍历每个巢穴
nest(i,:)=Lb+(Ub-Lb).*rand(size(Lb)); % 对每个巢穴,随机初始化参数
end
% Get the current best
fitness=10^10*ones(n,1); % 目标函数值初始化
[fmin,bestnest,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,nest,fitness); % 找出当前最佳巢穴和参数
N_iter=0; % 迭代计数器
%% Starting iterations
for t=1:time
% Generate new solutions (but keep the current best)
new_nest=get_cuckoos(nest,bestnest,Lb,Ub); % 保留当前最优解,寻找新巢穴
[fnew,best,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,new_nest,fitness); % 找出当前最佳巢穴和参数
% Update the counter
N_iter=N_iter+n; % 更新计数器
% Discovery and randomization
new_nest=empty_nests(nest,Lb,Ub,pa); % 发现并更新劣质巢穴
% Evaluate this solution
[fnew,best,nest,fitness]=get_best_nest(nest,new_nest,fitness); % 找出当前最佳巢穴和参数
% Update the counter again
N_iter=N_iter+n; % 更新计数器
end %% End of iterations
%% Post-optimization processing
%% Display all the nests
disp(strcat('Total number of iterations=',num2str(N_iter)));
fmin
bestnest
%% --------------- All subfunctions are list below ------------------
%% Get cuckoos by ramdom walk 通过随机游走搜寻鸟巢
function nest=get_cuckoos(nest,best,Lb,Ub)
% Levy flights
n=size(nest,1); % 鸟巢个数
% Levy exponent and coefficient
% For details, see equation (2.21), Page 16 (chapter 2) of the book
% X. S. Yang, Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms, 2nd Edition, Luniver Press, (2010).
% Levy flights参数准备
beta=3/2;
sigma=(gamma(1+beta)*sin(pi*beta/2)/(gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*2^((beta-1)/2)))^(1/beta); % gamma(x)求gamma函数值
for j=1:n % 遍历每个巢穴
s=nest(j,:); % 提取当前巢穴的参数
% This is a simple way of implementing Levy flights
% For standard random walks, use step=1;
%% Levy flights by Mantegna's algorithm
u=randn(size(s))*sigma; % 生成服从 N(0,sigma^2) 的随机数u,u为长度为参数个数的向量
v=randn(size(s)); % 生成服从 N(0,1) 的随机数v向量
step=u./abs(v).^(1/beta); % 计算步长
% In the next equation, the difference factor (s-best) means that
% when the solution is the best solution, it remains unchanged.
stepsize=0.01*step.*(s-best); % 巢穴位置变化量,如当前巢穴为最优解,则变化量将为0
% Here the factor 0.01 comes from the fact that L/100 should the typical
% step size of walks/flights where L is the typical lenghtscale;
% otherwise, Levy flights may become too aggresive/efficient,
% which makes new solutions (even) jump out side of the design domain
% (and thus wasting evaluations).
% Now the actual random walks or flights
s=s+stepsize.*randn(size(s)); % 步长调整
% Apply simple bounds/limits
nest(j,:)=simplebounds(s,Lb,Ub); % 更新巢穴
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
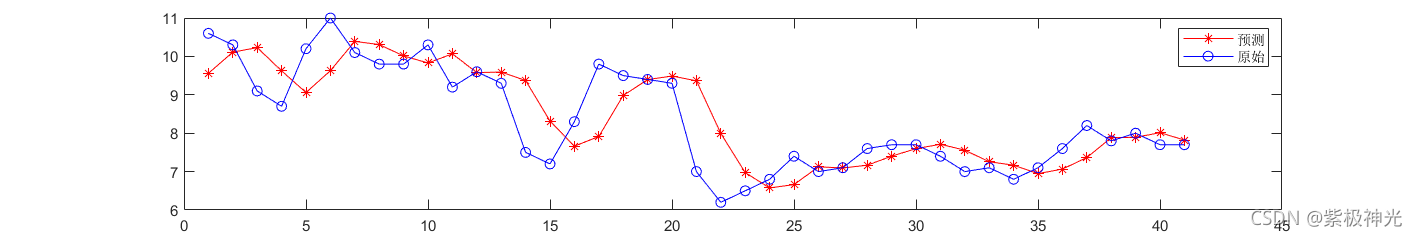
三、运行结果
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业出版社,2016.
[2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017.
[3]周品.MATLAB 神经网络设计与应用[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]陈明.MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[5]方清城.MATLAB R2016a神经网络设计与应用28个案例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2018.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121321419
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)