【水果识别】基于matlab GUI苹果质量检测及分级系统(带面板)【含Matlab源码 1613期】
一、简介
1 案例背景
目前,苹果的分级主要靠人工完成,该方法存在主观误差大、效率低和苹果易造成二次损伤等问题。随着机器视觉技术的快速发展, 图像处理在水果质量检测方面也取得了深入进展。
试验拟通过采集视野内苹果图, 综合特征对苹果进行分级, 通过SVM决策树算法将苹果分为特级果、一级果、二级果和三级果,以增加苹果在线分级的准确度并提高分级效率。
2 背景分割
2.1 图像预处理
系统通过摄像头采集苹果图像,由于苹果表面光滑,光线容易发生反射,所拍摄到的果面可能会因为角度和光照影响出现光照不均现象,故采用同态滤波方式对图像进行增强,采用中值滤波方式消除噪声。同时,为了提高苹果在线分级的效率,仅对感兴趣区域进行背景分割与特征提取;最后综合两幅不同位姿的苹果图像信息对苹果进行分级。
2.2 背景分割
为了从苹果图像中提取出苹果轮廓,一般采用边缘检测、阈值分割、区域提取3种方法。由于光照、拍摄角度等问题,单一的阈值又不利于多峰图像的分割,在复杂背景下容易出现欠分割、过分割等问题,所以采用全局阈值分割效果并不理想。自适应O stu阈值分割算法可以通过自动计算最佳阈值对图像中的苹果进行提取。泛洪填充算法是从一个点开始,将其附近像素点依次填充成新的颜色,直到封闭区域内的所有像素点均被填充成新颜色为止,采用泛洪填充算法将图像中与背景颜色相近的部分填充成黑色, 可以突出背景与前景的差距。故采用泛洪填充+自适应Ostu的算法进行背景分割, 使Ostu自适应分割效果更加显著, 具体步骤如下。
(1)将输入的原图[图2(a)]进行图像预处理。
(2) 对预处理后的图像进行泛洪填充, 计算得到图像高度h和宽度w, 种子点(w-1, h-1) , 填充的颜色RGB新值为(0,0,0),相对于种子点向下的像素值为(10,10,10),向上的像素值为(9,9,9),采用8领域填充法进行填充,结果如图2(d)所示。
(3)假设图2(d)前景与背景分割阈值为t,前景点占图像的比例为Wo,均值为Uo,背景点占图像的比例为W1,均值为U1。那么,整个图像的均值为:
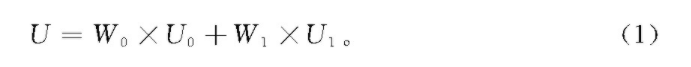
目标函数为:
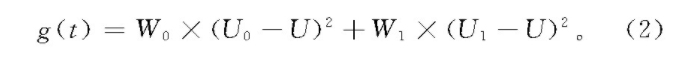
其中g(t) 是分割阈值为t时的类间方差表达式。O stu算法可以使g(t)取得全局最大值,当g(t)达到最大时,所对应的t被称为最佳阈值,处理结果如图2(f)所示。
由图2可知,未进行泛洪填充处理的图像灰度直方图存在两个尖峰,对原图进行O stu分割后的边缘较差, 存在欠分割问题; 经泛洪填充后的图像直方图尖峰明显, 进行O stu分割处理效果很好,证明了试验方法是可行的。
2.4 特征提取
2.4.1果径
根据鲜苹果分级标准可知,苹果果径等于苹果的最大横截面直径。故采用最小外接圆法对苹果上表面的二值化图像进行计算,得到苹果果径,结果如图3所示。
首先按式(3)计算出最小外接圆的质心(Cx,Cy)

式中:
Cx———质心的横坐标;
Cy———质心的纵坐标;
M10———二值图中水平向右的像素个数;
M00———总像素个数;
M01———垂直向下的像素个数。
将图像的质心作为苹果轮廓的圆心,遍历轮廓上所有像素点,计算出目标像素点离质心的最大距离d,即最小外接圆的半径。
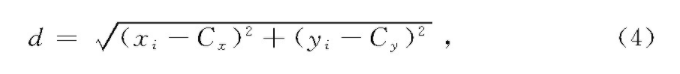
式中:
xi———目标像素点的横坐标;
yi———目标像素点的纵坐标;
d———两点之间的距离。

式中:
R———果径,mm;
2.4.2 着色度
目前,常用的彩色模型包括RGB模型和HSV模型。其中HSV模型更符合人眼对颜色的认知,是面向彩色处理最常用的模型,其中H为色度、S为饱和度、V为明度[8]。故选择在HSV颜色空间上对苹果的着色度、疤痕和果锈特征进行提取。
根据红富士苹果分级标准可知,苹果着色度为统计集中着色面,条红或者片红的程度。通过统计两帧图像中红色所占的比例,得出红富士苹果的着色度。
首先将RGB图转换成HSV图,然后选取红色的提取范围H(156~180)、S(43~256)、V(46~255)。经阈值处理后统计图像中白色像素点个数,按式(8)计算苹果的着色度。

式中:
C———着色度;
C1———第一帧苹果的着色度;
C2———第二帧苹果的着色度;
r1———第一帧图像阈值处理后白色像素点个数;
r2———第二帧图像阈值处理后白色像素点个数;
s1———第一帧整个苹果像素点个数;
s2———第二帧整个苹果像素点个数。
2.4.3 苹果缺陷
苹果在生长、采摘和运输过程中受天气、病害、虫害和碰伤等伤害产生疤痕。苹果果锈是一种比较常见的苹果病害,特别是在中小果园种植的红富士苹果中最为常见,故将疤痕和果锈特征参数作为苹果缺陷的判定依据。由于果梗处的颜色较深,比较容易被判定为疤痕,为了消除此影响,将除果梗处的苹果区域视为感兴趣区域。
为了提取苹果疤痕和果锈特征,首先将采集到的苹果图像由RGB空间转换到HSV空间,并且分离出图像的H(色相)、S(饱和度)和V(亮度)通道图像。
由图6、7可知,苹果的疤痕和果锈的亮度较暗,故根据苹果HSV图像的亮度值对苹果的疤痕和果锈进行特征提取。通过分析疤痕和果锈图像特点,将感兴趣区域中像素点在V∈(120~140)的区域视为疤痕区域,V∈(150~180)的区域视为果锈区域。按式(9)计算苹果疤痕和果锈。
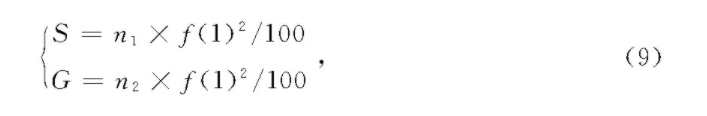
式中:
S———疤痕面积,cm2;
G———果锈面积,cm2;
n1———V∈(120~140)像素点个数;
n2———V∈(150~180)像素点个数。
1.5 苹果分级
由于SVM算法在小样本训练集上的分类效果相比于其他分类算法有较好的表现,可以提高模型的泛化能力,能够处理高维空间的数据,故选择SVM算法对苹果进行分类。但SVM算法最初是针对二分类问题提出的,并不能直接应用于多分类问题,由于试验将苹果分为多个等级,因此选择多分类SVM分类器对苹果进行分级。
SVM分类器的惩罚参数C与核参数σ对最后的分类结果影响非常大,所以需对其进行优化选取。而粒子群算法有着很好的全局寻优能力,可以有效解决非线性问题,收敛速度快,但容易陷入局部最优,故采用基于改进粒子群算法的SVM决策树的分类方法进行苹果分级工作,可以克服决策树本身对门限敏感和错误传递的缺陷。
对苹果样本进行果径、着色度、疤痕和果锈特征的提取,然后将特征参数送入SVM决策树分级模型,通过分级模型将苹果分为特级果、一级果、二级果和三级果。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = appletest(varargin)
% APPLETEST MATLAB code for appletest.fig
% APPLETEST, by itself, creates a new APPLETEST or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = APPLETEST returns the handle to a new APPLETEST or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% APPLETEST('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in APPLETEST.M with the given input arguments.
%
% APPLETEST('Property','Value',...) creates a new APPLETEST or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before appletest_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to appletest_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help appletest
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 19-Oct-2019 20:28:04
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @appletest_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @appletest_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before appletest is made visible.
function appletest_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to appletest (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for appletest
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes appletest wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = appletest_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile({'*.*';'*.bmp';'*.jpg';'*.tif';'*.jpg'},'选择图像');
image=[pathname,filename];%合成路径+文件名
im=imread(image);%读取图像
im=im2double(im);
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(im);%在坐标axes1显示原图像
title('原始图像');
handles.X1=im;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu1.
function popupmenu1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: contents = cellstr(get(hObject,'String')) returns popupmenu1 contents as cell array
% contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu1
Val=get(hObject,'Value')
strl=get(hObject,'string')
switch strl{Val};
case ' 面积'
x1=handles.X1;
w=rgb2gray(x1);
L=medfilt2(w);
level=graythresh(L);
bw=im2bw(L,level);
bw=imfill(~bw,'holes');
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(bw);
title('面积图像');
strNC=[num2str(bwarea(bw))];
set(handles.text9,'string',strNC);
strNC1=('一级果');
strNC2=('二级果');
strNC3=('三级果');
if bwarea(bw)>30000
set(handles.text14,'string',strNC1);
else if bwarea(bw)>1000&&bwarea(bw)<30000
set(handles.text14,'string',strNC2);
else
set(handles.text14 ,'string',strNC3);
end
end
% strNC1=('无');
% set(handles.text14,'string',strNC1);
case' 颜色'
x1=handles.X1;
hv=rgb2hsv(x1);
H=hv(:,:,1);
S=hv(:,:,2);
V=hv(:,:,3);
axes(handles.axes3);
imshow(H)
title('H分量图像');
level=graythresh(x1);
apple=im2bw(x1,level);
count=length(x1);
for i=1:count
red_ratio=length(find((H>0 & H<1/12) | H>11/12))/length(find(apple==1));
end
r=red_ratio;
strNC=[num2str(red_ratio*100),'%'];
set(handles.text10,'string',strNC);
strNC1=('一级果');
strNC2=('二级果');
strNC3=('三级果');
if r>1
set(handles.text15,'string',strNC1);
else if r>0.8&&r<1
set(handles.text15,'string',strNC2);
else
set(handles.text15 ,'string',strNC3);
end
end
case' 圆形度'
x1=handles.X1;
I2=rgb2gray(x1);
J=im2bw(I2,0.75);
I=~J;
%====形态特征值计算===%
l=bwlabel(I,8);
[l,num]=bwlabel(I,8);
STATS=regionprops(l,'Area');
A=STATS.Area;
STATS=regionprops(l,'Perimeter');
L=STATS.Perimeter
C=(4.*pi.*A)./(L.*L); % 计算圆度
% L为周长,A为面积,C为圆形度
strNC=[num2str(C)];
set(handles.text12,'string',strNC);
strNC1=('一级果');
strNC2=('二级果');
strNC3=('三级果');
if C>0.65
set(handles.text17,'string',strNC1);
else if C>0.55&&C<0.65
set(handles.text17,'string',strNC2);
else
set(handles.text17,'string',strNC3);
end
end
case' 表面缺陷'
x1=handles.X1;
w=rgb2gray(x1);
L=medfilt2(w);
level=graythresh(L);
bw=im2bw(L,level);
X=imclearborder(bw,4); %去除图像与边界相连通,但更高亮的区域
axes(handles.axes4);
imshow(X)
title('缺陷图像');
Q=(bwarea(X)/bwarea(~bw)*100)
q=num2str(bwarea(X)/bwarea(~bw)*100)
strNC=[q,'%'];
set(handles.text11,'string',strNC);
strNC1=('一级果');
strNC2=('二级果');
strNC3=('三级果');
if Q<0.1
set(handles.text16,'string',strNC1);
else if Q>0.1&&Q<0.2
set(handles.text16,'string',strNC2);
else
set(handles.text16,'string',strNC3);
end
end
end
guidata(hObject, handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function popupmenu1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
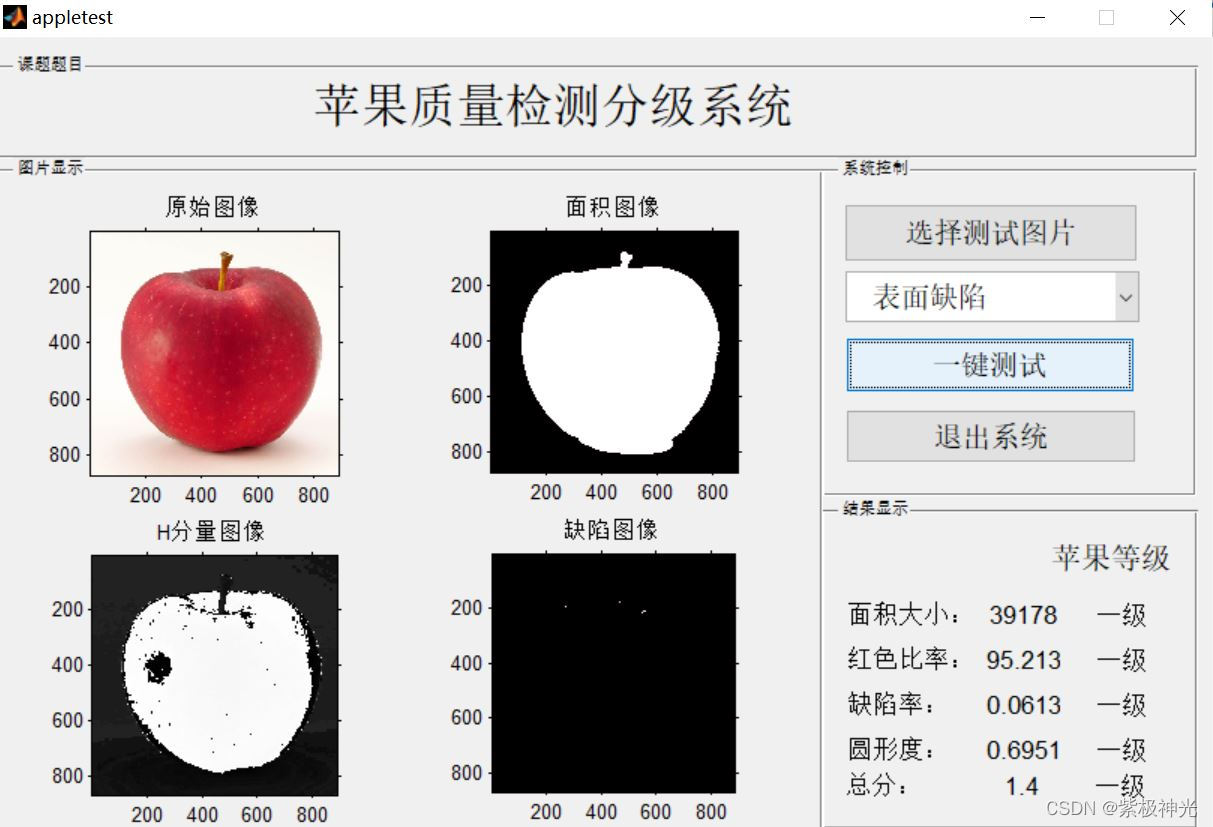
三、运行结果

四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/122266682
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)