【图像检测】基于matlab LSD直线检测【含Matlab源码 1697期】
一、LSD直线提取算法简介
LSD算法由Grompone等2010年在结合Burns所提算法基础上提出,该算法结合图像梯度和方向信息提取直线,主要包括3部分。
1)生成直线支持区域:通过计算每个像素点的梯度,生成对应梯度场,将在一定阈值内且具有相同梯度的像素相连成为直线支持区域,如图1所示。
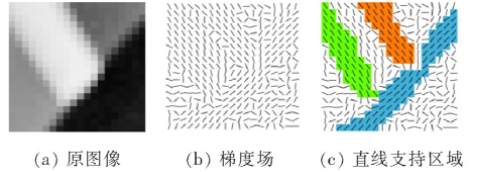
图1 LSD算法梯度场和直线支持域
2)直线支持区域的矩形拟合:对于每个直线支持区域我们可以观察它的最小外接矩形,矩形的主轴表示直线支持域的主轴方向,且矩形要覆盖整个区域,该最小外接矩形表示直线信息,如图2所示。
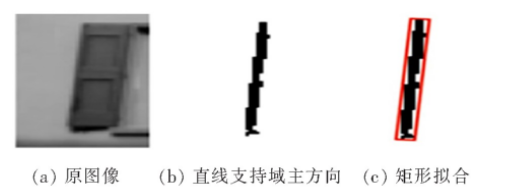
图2 直线支持域矩形拟合
3)直线确认:每个拟合的矩形都需要对应一个直线确认步骤,根据Helmholtz原则对拟合矩形进行判断[20],验证该矩形区域是否可以作为直线提取。Helmholtz原则通过与一个假设的独立分布值为[0,2π]的噪声图相比较,判断是否为直线。在一个分辨率为m×n的图像中,可能出现(nm)5/2种直线支持域,直线支持域中像素总数为n,k为与拟合矩形同方向的像素总数,δ为一个确定的精度,直线区域的错误报警数QNFA定义如下
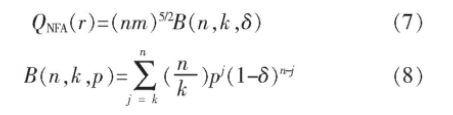
ε为判定阈值,如果QNFA小于ε,则该直线支持域为直线,原算法中ε取1得到了较好效果,本文也取1。
二、部分源代码
img = imread('test.png');
img_gray = rgb2gray(img);
figure;imshow(img_gray);
[~, lineIm, ~, ~, linesInfo] = LineSegmentDetector( img_gray, 0.3, 0.6, 22.5, 0.7, 1024, 255 );
figure;imshow(lineIm);
function linesInfoOut=LineCoalescer(linesInfo,verThre,latThre)
% linesInfo=LineCoalescer(linesInfo,verThre,latThre)对调整好的线段进行必要的
% 融合。
% 输入:
% 输入包含3个必要参数。
% linesInfo为直线段信息<1xK struct>。.k为直线段斜率;.b为直线段与Y轴交点值;
% .dx为倾角的余弦值;.dy为倾角的正弦值;.x1为直线段起点X坐标;.y1为直线段起点Y
% 坐标;.x2为直线段终点X坐标;.y2为直线段终点Y坐标。
% binNum为角度分隔区间个数<1x1 uint8>。
% verThre为垂直方向线段偏差阈值<1x1 double>。
% latThre为水平方向线段分离阈值<1x1 double>。
% 输出:
% 输出包含1个必要参数。
% linesInfoOut为融合更新后的直线信息结构体的胞元数组<1xN struct>。N小于等于M。
% 示例:
% priLinesInfo=LineCoalescer(priLinesInfo,5,10);
iter1=1;
tempLinesInfo=linesInfo;
%% 将需要融合的线段组旋转到水平后进行融合检测
for i=1:length(tempLinesInfo)
curLine=tempLinesInfo(i);
ang=atand(curLine.k);
if (ang<0)
ang=ang+180;
end;
%% 向右旋转
angDif=0-ang;
X1=curLine.x1*cosd(angDif)-curLine.y1*sind(angDif);
X2=curLine.x2*cosd(angDif)-curLine.y2*sind(angDif);
Y1=curLine.x1*sind(angDif)+curLine.y1*cosd(angDif);
Y2=curLine.x2*sind(angDif)+curLine.y2*cosd(angDif);
tempLinesInfo(i).x1=X1;
tempLinesInfo(i).y1=Y1;
tempLinesInfo(i).x2=X2;
tempLinesInfo(i).y2=Y2;
end;
while (iter1<=length(tempLinesInfo))
exLen=length(tempLinesInfo);
iter2=iter1+1;
while (iter2<=length(tempLinesInfo))
line1=tempLinesInfo(iter1);
if (iter1==iter2)
iter2=iter2+1;
continue;
end;
line2=tempLinesInfo(iter2);
%% 按照长短将待判断融合的直线进行区分
if (line1.len<line2.len)
minLine=line1;
maxLine=line2;
else
minLine=line2;
maxLine=line1;
end;
lenSum=maxLine.len+minLine.len;
maxLineY=(maxLine.y1+maxLine.y2)/2;
minLineY=(minLine.y1+minLine.y2)/2;
%% 两条线段垂直之间距离
curLatDist=abs(maxLineY-minLineY);
%% 如果距离过远大于阈值
if (curLatDist>verThre)
iter2=iter2+1;
continue;
end;
coaFlag=0;
%% 判断线段左右端点之间的关系
maxLineXLeft=maxLine.x1;
maxLineXRigh=maxLine.x2;
minLineXLeft=minLine.x1;
minLineXRigh=minLine.x2;
if (maxLineXLeft>maxLineXRigh)
temp=maxLineXLeft;
maxLineXLeft=maxLineXRigh;
maxLineXRigh=temp;
end;
if (minLineXLeft>minLineXRigh)
temp=minLineXLeft;
minLineXLeft=minLineXRigh;
minLineXRigh=temp;
end;
if (maxLineXLeft<minLineXLeft)
%% 长线段起点在短线段起点左侧
if (maxLineXRigh<minLineXLeft)
%% 长线段终点也在短线段起点左侧(有间隔)
if ((minLineXLeft-maxLineXRigh)<latThre)
coaFlag=1;
end;
elseif (maxLineXRigh<minLineXRigh)
%% 长线段终点在短线段起点右侧,但在短线段终点左侧(有重叠)
coaFlag=1;
else
%% 长线段终点在短线段右侧(覆盖)
coaFlag=1;
end;
else
%% 短线段起点在长线段起点左侧
if (minLineXRigh<maxLineXLeft)
%% 短线段终点也在长线段起点左侧(有间隔)
if ((maxLineXLeft-minLineXRigh)<latThre)
coaFlag=1;
end;
elseif (minLineXRigh<maxLineXRigh)
%% 短线段终点在长线段起点右侧,但在长线段终点左侧(有重叠)
coaFlag=1;
else
coaFlag=1;
%% 短线段终点在长线段右侧(出错)
disp('error');
end;
end;
%% 如果满足融合条件
if (coaFlag==1)
%% 融合后的线段的Y坐标按照两线段长短的比重进行分配,长线段的比重大,融合后线段靠近长线段
P1=maxLine.len/lenSum;
P2=minLine.len/lenSum;
newX=[maxLine.x1,maxLine.x2,minLine.x1,minLine.x2];
newY=(P1*maxLineY+P2*minLineY).*ones(1,4);
minX=Inf;
maxX=-Inf;
%% 确认新线段的起始点坐标
for m=1:4
if (newX(m)>maxX)
maxX=newX(m);
maxY=newY(m);
end;
if (newX(m)<minX)
minX=newX(m);
minY=newY(m);
end;
end;
tempLinesInfo(iter1).x1=minX;
tempLinesInfo(iter1).y1=minY;
tempLinesInfo(iter1).x2=maxX;
tempLinesInfo(iter1).y2=maxY;
tempLinesInfo(iter1).len=maxX-minX;
tempLinesInfo(iter2)=[];
else
iter2=iter2+1;
end;
end;
afLen=length(tempLinesInfo);
if (exLen==afLen)
iter1=iter1+1;
end;
end;
%% 将融合后的线段按照倾斜角重新旋转回原角度
for i=1:length(tempLinesInfo)
curLine=tempLinesInfo(i);
ang=atand(curLine.k);
if (ang<0)
ang=ang+180;
end;
X1=curLine.x1*cosd(ang)-curLine.y1*sind(ang);
Y1=curLine.x1*sind(ang)+curLine.y1*cosd(ang);
X2=curLine.x2*cosd(ang)-curLine.y2*sind(ang);
Y2=curLine.x2*sind(ang)+curLine.y2*cosd(ang);
tempLinesInfo(i).x1=X1;
tempLinesInfo(i).y1=Y1;
tempLinesInfo(i).x2=X2;
tempLinesInfo(i).y2=Y2;
tempLinesInfo(i).b=(Y1+Y2)/2-curLine.k*(X1+X2)/2;
end;
linesInfoOut=tempLinesInfo;
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
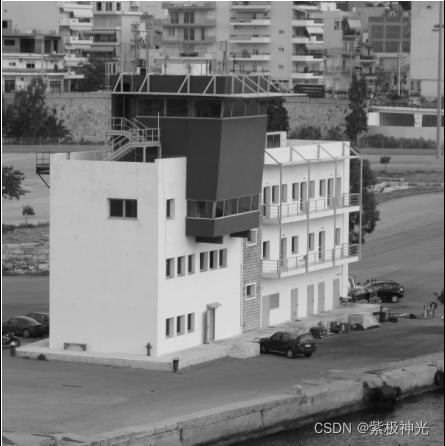
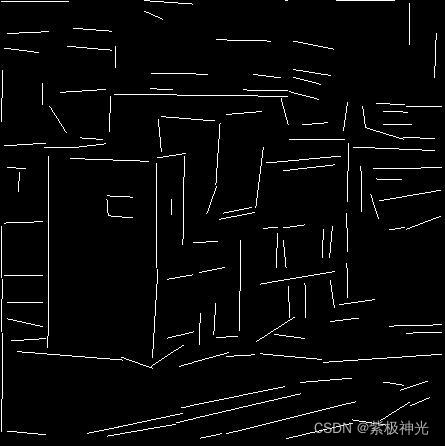
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[5]曹义亲,何恬,刘龙标.基于改进LSD直线检测算法的钢轨表面边界提取[J].华东交通大学学报. 2021,38(03)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/122802014
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)