【语音去噪】基于matlab GUI软阈值+硬阈值+软硬折中阈值语音去噪【含Matlab源码 1810期】
一、小波阈值语音降噪简介
0 引言
语音信号在传输过程中, 会不可避免地受到外界环境噪声的干扰, 从而影响人们之间的相互交流与沟通。如何从含噪语音信号中将原始信号提取出来, 提高信号信噪比, 是现代语音信号处理领域的研究热点之一。小波阈值去噪法因其实现简单, 运算量小等优点被广泛应用于信号处理领域。
小波阈值去噪法的关键是阈值函数的选取。常规的阈值函数选取过于简单, 考虑不全面, 去噪效果受到限制。针对这些不足做了大量研究, 提出了一些改进方法。本文在软阈值函数的基础上, 提出了一种优化的参数阈值函数, 使得去噪效果得到较大提升。基于对实验结果的分析, 又提出了一种最优参数选择法, 进一步提升了去噪效果。
1 小波阈值语音去噪原理
小波阈值语音去噪可分为以下三个步骤:
(1) 含噪语音信号的小波分解。选择一个合适的小波基并确定分解层数l, 进行分解计算, 得到小波分解的各层高频系数ωd (1) , ωd (2) , …, ωd (l) 和低频系数ωa (l) 。

2 阈值函数的选取
在阈值量化过程中, 常规的阈值函数有软、硬阈值函数[10]两种:
硬阈值函数:
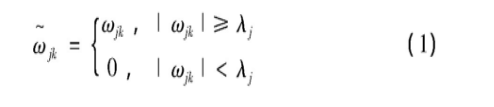
软阈值函数:

硬阈值函数可以很好地保留信号的局部特征, 但由于硬阈值函数不连续, 信号在重构的时候可能会产生一些震荡;软阈值函数是连续的, 但当小波系数较大时, 处理后的小波系数会出现较大的恒定偏差, 影响重构信号与真实信号的逼近程度。
本文提出了一种参数阈值函数:
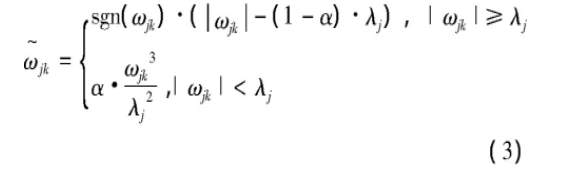
其中, α∈[0, 1]为参数, 当α=0时, 即为软阈值函数。
图1为上述三种阈值函数图像的对比, 由图1可看出, 参数阈值函数介于软、硬阈值函数之间, 且在±λ点是连续的, 避免了硬阈值函数处理信号时发生震荡的问题;当|ωjk|<λ时, 将小波系数平滑过渡到0而非直接将其置零, 既抑制了噪声, 又避免信息丢失严重。

图1 三种阈值函数的对比 (α=0.5)
二、部分源代码
function varargout = untitled(varargin)
% UNTITLED MATLAB code for untitled.fig
% UNTITLED, by itself, creates a new UNTITLED or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = UNTITLED returns the handle to a new UNTITLED or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% UNTITLED('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in UNTITLED.M with the given input arguments.
%
% UNTITLED('Property','Value',...) creates a new UNTITLED or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before untitled_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to untitled_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help untitled
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 20-Mar-2022 22:34:59
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @untitled_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @untitled_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before untitled is made visible.
function untitled_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to untitled (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for untitled
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes untitled wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = untitled_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
fs=audioread('Ring01.wav');
y=fs(40000:120000);
N=length(y);
axes(handles.axes1);
plot(y);
ylabel('幅值 A');
title('原始信号');
s=awgn(y,15,'measured');%加入高斯白噪声
axes(handles.axes2);
plot(s);
ylabel('幅值 A');
title('加噪信号');
wname='db3';%选db3小波基
lev=5;%5层分解
[c,l]=wavedec(s,lev,wname);
a5=appcoef(c,l,wname,lev);
d5=detcoef(c,l,5);
d4=detcoef(c,l,4);
d3=detcoef(c,l,3);
d2=detcoef(c,l,2);
d1=detcoef(c,l,1);
cD=[d1,d2,d3,d4,d5];
a=8500;b=13;
sigma=median(abs(cD))/3.647
thr1=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(2));
cD1=wthresh(d1,'s',thr1);
thr2=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(3));
cD2=wthresh(d2,'s',thr2);
thr3=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(4));
cD3=wthresh(d3,'s',thr3);
thr4=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(5));
cD4=wthresh(d4,'s',thr4);
thr5=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(6));
cD5=wthresh(d5,'s',thr5);
cd=[a5,cD5,cD4,cD3,cD2,cD1];
c=cd;
ys=waverec(c,l,wname);
axes(handles.axes3);
plot(ys);
title('软阈值处理');
thr1=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(2));
cD1=wthresh(d1,'h',thr1);
thr2=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(3));
cD2=wthresh(d2,'h',thr2);
thr3=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(4));
cD3=wthresh(d3,'h',thr3);
thr4=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(5));
cD4=wthresh(d4,'h',thr4);
thr5=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(N))))/(log10(6));
cD5=wthresh(d5,'h',thr5);
cd=[a5,cD5,cD4,cD3,cD2,cD1];
c=cd;
yh=waverec(c,l,wname);
axes(handles.axes4);
plot(yh);
title('硬阈值处理');
thr1=(sigma*sqrt(2*(log10(length(d1)))))/(log10(1+1));
for i=1:length(d1)
if(abs(d1(i))>=thr1)
cD1(i)=sign(d1(i))*(abs(d1(i))-b*thr1/(a^(abs(abs(d1(i))-thr1))+b-1));%估计第一层小波系数
else
cD1(i)=0;
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
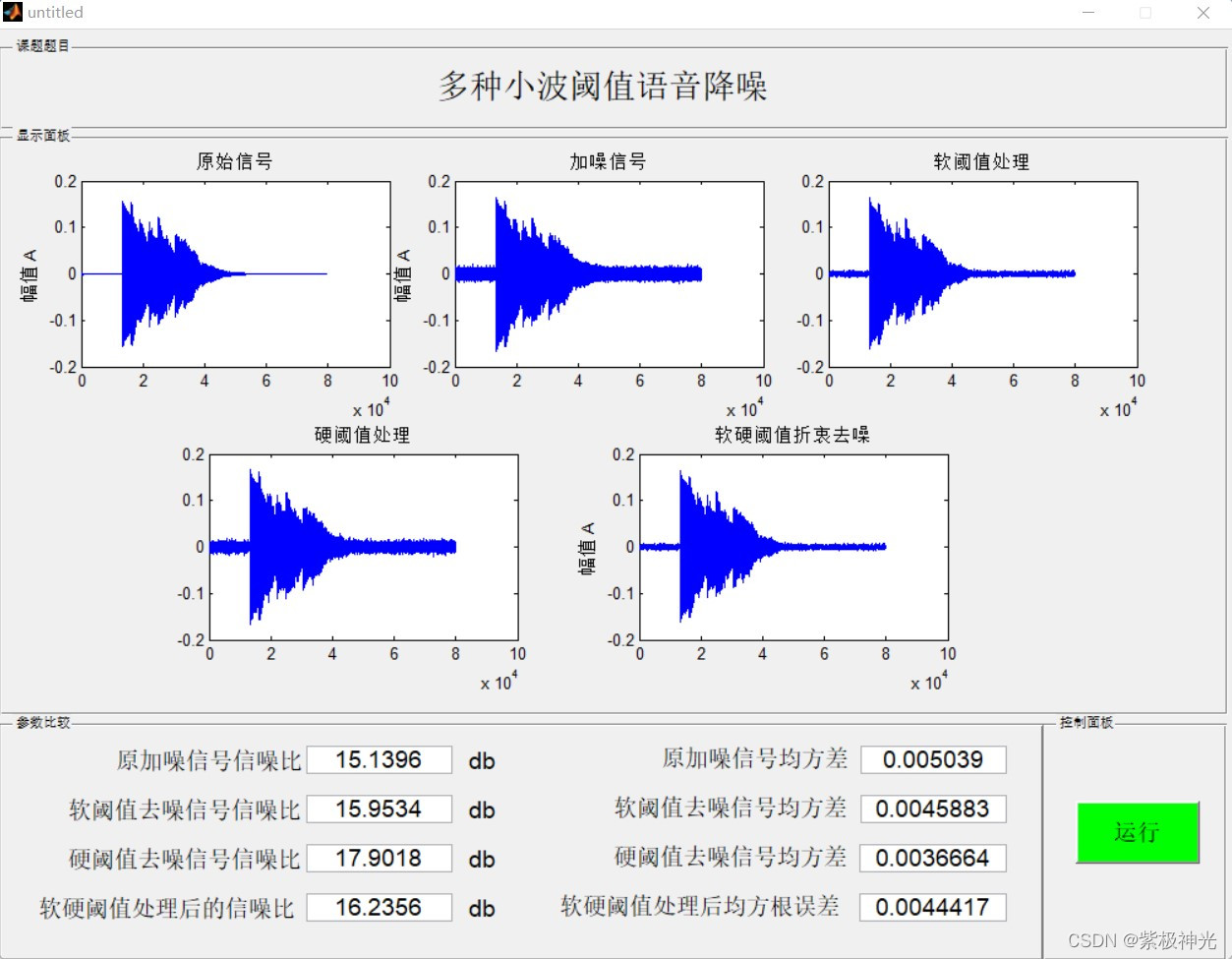
三、运行结果
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[3]张宝,魏连鑫.基于参数阈值函数的小波阈值语音去噪[J].信息技术. 2017,(08)
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/123690648
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)