【目标跟踪】基于matlab卡尔曼滤波多目标跟踪【含Matlab源码 1832期】
一、Kalman简介
运动物体跟踪实际上就是对运动物体位置的测量和估计,和称小兔兔体重一样,我们也有两个渠道可以知道运动物体的位置,一个是我们观察到的,目标A在的某一帧图像的某个坐标点,另一个是我们根据前面几帧里目标的运动情况估计出来的,这个估计是假定目标运动是光滑的(当然也可以有其他模型),在这个根据以前运动做出的估计和我们测出来的目标点位置之间做个加权平均,就是现在的估计值,对下一帧做同样处理,加权平均的权值就是Kalman增益,根据Kalman提供的算法可由以往的误差大小和分布推出,这就是全部的用Kalman滤波做目标跟踪的概念。
Kalman滤波理论主要应用在现实世界中个,并不是理想环境。主要是来跟踪的某一个变量的值,跟踪的依据是首先根据系统的运动方程来对该值做预测,比如说我们知道一个物体的运动速度,那么下面时刻它的位置按照道理是可以预测出来的,不过该预测肯定有误差,只能作为跟踪的依据。另一个依据是可以用测量手段来测量那个变量的值,当然该测量也是有误差的,也只能作为依据,不过这2个依据的权重比例不同。最后kalman滤波就是利用这两个依据进行一些列迭代进行目标跟踪的。
在这个理论框架中,有2个公式一定要懂,即:



二、部分源代码
function varargout = MainTrack(varargin)
% MAINTRACK MATLAB code for MainTrack.fig
% MAINTRACK, by itself, creates a new MAINTRACK or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = MAINTRACK returns the handle to a new MAINTRACK or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% MAINTRACK('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in MAINTRACK.M with the given input arguments.
%
% MAINTRACK('Property','Value',...) creates a new MAINTRACK or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before MainTrack_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to MainTrack_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help MainTrack
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 29-Mar-2022 23:32:54
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @MainTrack_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @MainTrack_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before MainTrack is made visible.
function MainTrack_OpeningFcn(hObject, ~, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to MainTrack (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for MainTrack
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes MainTrack wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = MainTrack_OutputFcn(~, ~, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% 最核心的函数,检测按钮
function mainB_Callback(~, ~, handles)
%数据的前期准备
set(handles.numText,'string',0);%计数框清零
set(handles.endTime,'string',0);%结束时间清零
set(handles.startTime,'string',datestr(datetime('now')));
set(handles.infoP,'Visible','on');
%视频获取途径的选择
camSwitch=get(handles.radioCam,'value');%获取值
position=handles.position;
areaSwitch=handles.areaSwitch;
if areaSwitch>0;
BW = handles.BW;%传递二进制图
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
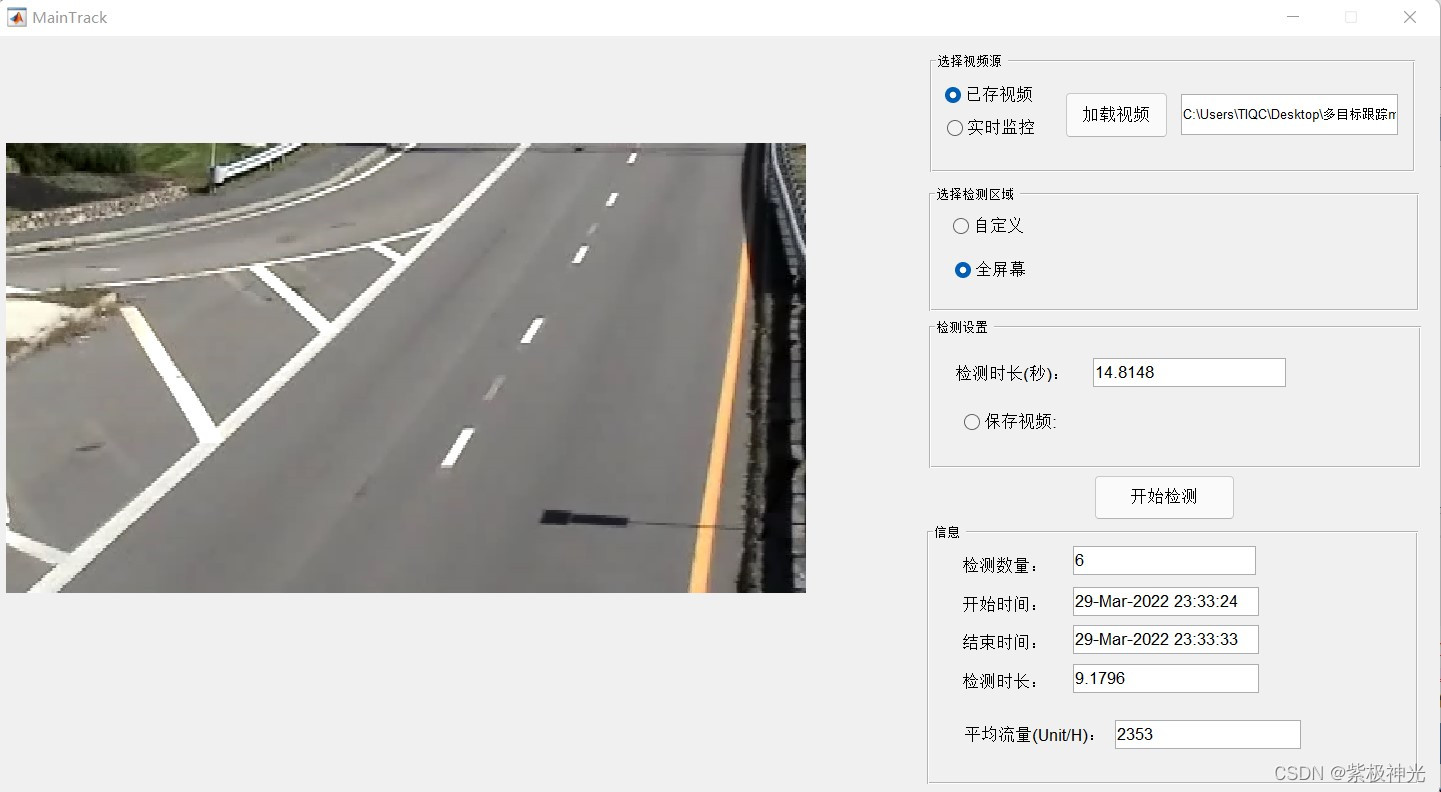
三、运行结果
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/123867398
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)