深入JVM类加载器
01、类加载器原理
02、类加载器树状结构、双亲委托(代理)机制
03、自定义类加载器(文件、网络、加密)
04、线程上下文类加载器
05、服务器类加载原理
1、类加载器的作用
将class文件字节码内容加载到内存中,并将这些静态数据转换成方法区中的运行时数据结构,在堆中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区类数据的访问入口。
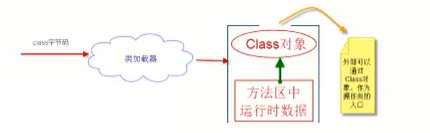
类缓存
标准的Java SE类加载器可以按要求查找类,但一旦某个类加载到类加载器中,它将维持加载(缓存)一段时间,不过JVM垃圾收集器可以回收这些Class对象。
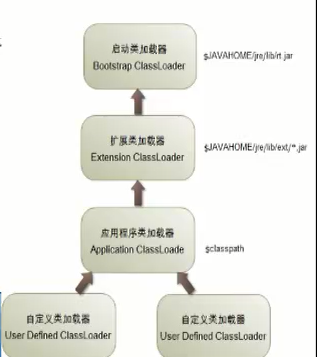
2、类加载器的层次结构(树状结构)
引导类加载器(bootstarap class loader)(C)
- 它用来加载java的核心库(JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/rt.jar或sun.boot.class.path路径下的内容),是用原生代码来实现的,并不继承自java.lang.ClassLoader。
- 加载扩展类和应用程序类加载器,并指定他们的父类加载器。
扩展类加载器(extensions class loader)(java)
- 用来加载java的扩展库(JAVA_HOME/jre/ext/*.jar,或java.ext.dirs路径下的内容)。Java虚拟机的实现会提供一个扩展库目录,该类加载器在此目录里面查找并加载java类。
- 由sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader实现
应用程序类加载器(application class loader)(java)
- 它根据java应用的类路径(classpath ,java.class.path路径类)
- 一般来说java应用的类都是由它来完成加载的
- 由sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader实现
自定义类加载器(java写的)
- 开发人员可以通过继承java.lang.ClassLoader类的方法实现自己的类加载器,以满足一些特殊的需求
Java.class.ClassLoader类介绍
作用:
-Java.lang.ClassLoader类的基本职责就是根据一个指定的类的名称,找到或者生成期对应的字节代码,然后从这些字节代码中定义一个java类,既java.lang.Class类的一个实例。
-除此之外,ClassLoader还负责加载java应用的所需资源,如图像文件和配置文件等。
相关方法
- getparent() 返回该类加载器的父类加载器
- loadClass(String name) 加载名称为name的类,返回结果是java.lang.Class类的实例
- findClass(String name)查找名称为name的类,返回结果是java.lang.Class类的实例
- findLoadedClass(String name) 查找名称为name的已经被加载过的类,返回结果是java.lang.Class类的实例
- defineClass(String name,byte[] b,int off,int len)把字节数组b中的内容转换成java类,返回的结果是java.lang.Class类的实例,这个方法被声明final的。
- resolveClass(Class
package com.lyy.test;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
System.out.println(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getParent());
System.out.println(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getParent().getParent()); //JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/rt.jar
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
System.out.println("=====================================");
String a = "gaogao";
System.out.println(a.getClass().getClassLoader());
System.out.println(a);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
类加载器的代理模式
代理模式
— 交给其他加载器来加载指定的类
双亲委托机制
— 就是某个特定的类加载器在接到加载类的请求时,首先将加载任务委托给父类加载器,一次追溯,知道最高的爷爷辈的,如果父类加载器可以完成类加载任务,就成功返回;只有父类加载器无法完成此加载任务时,才自己去加载。
— 双亲委托机制是为了保证java核心库的类型安全。
这种机制就保证不会出现用户自己能定义java.lang.Object类的情况。
类加载器除了用户加载类,也是安全的最基本的屏障。
双亲委托机制是代理模式的一种
— 并不是所有的类加载器都采用双亲委托机制。
— Tomcat服务器类加载器也使用代理模式,所不同的是它是首先尝试去加载某个类,如果找不到再代理给父类加载器,这与一般类加载器的顺序是相反的。

自定义类加载器
自定义类加载器的流程
— 首先检查请求的类型是否已经被这个类加载器装载到命名空间中了,
如果已经装载,直接返回;
— 委派类加载请求给父类加载器能够完成,则返回父类加载器加载的Class实例;
— 调用本类加载器的findClass(…)方法,视图获取对应的字节码,如果获取到,则调用defineClass(…)导入类型到方法区;如果获取不到对应的字节码或者其他原因失败,返回异常loadClass(…)loadClass(…)转抛异常,终止加载过程。
— 注意:被两个类加载器加载的同一个类,JVM不认为是相同的类
package com.lyy.temp;
public class HelloWrold {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("aaa");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
package com.lyy.test;
/**
* 测试自定义类加载器(FileSystemClassLoader)
* @author 01
*
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
FileSystemClassLoader load = new FileSystemClassLoader("E:/VIP");
FileSystemClassLoader load2 = new FileSystemClassLoader("E:/VIP");
Class<?> c = load.loadClass("com.lyy.temp.HelloWrold");
Class<?> c2 = load.loadClass("com.lyy.temp.HelloWrold");
Class<?> c3 = load2.loadClass("com.lyy.temp.HelloWrold");
Class<?> c4 = load2.loadClass("java.lang.String");
Class<?> c5 = load2.loadClass("com.lyy.test.Demo1");
System.out.println(c.hashCode());
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());//同一个类,被不同的加载器加载,JVM认为也是不相同的类
System.out.println(c4.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.getClassLoader());//自定义的类加载器
System.out.println(c4.getClassLoader());//引导类加载器
System.out.println(c5.getClassLoader());//系统默认的类加载器
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
文件类加载器
package com.lyy.test;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 自定义文件系统加载器
* @author 01
*
*/
public class FileSystemClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
//com.lyy.test.User --> d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
private String rootDir;
public FileSystemClassLoader(String rootDir){
this.rootDir=rootDir;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
//首先查询是否加载过该类,如果已经加载过,直接返回已经加载好的类,否则加载新的类
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
ClassLoader parent = this.getParent();
c = parent.loadClass(name); //委派给父类加载
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
byte[] classData = getClassData(name);
if(classData==null){
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}else{
c = defineClass(name, classData,0, classData.length);
}
}
}
return c;
}
private byte[] getClassData(String name) { //com.lyy.test.User d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
String path = rootDir+"/"+name.replace('.', '/')+"class";
//IOUtils,可以使用它将流中的数据转成字节数据
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
is = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int temp = 0;
while((temp=is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,temp);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally{
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
if(baos != null){
baos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
网络类加载器
package com.lyy.test;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* 网络类加载器
* @author 01
*
*/
public class NetClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
//com.lyy.test.User --> www.baidu.com
private String rootUrl;
public NetClassLoader(String rootUrl){
this.rootUrl=rootUrl;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
//首先查询是否加载过该类,如果已经加载过,直接返回已经加载好的类,否则加载新的类
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
ClassLoader parent = this.getParent();
c = parent.loadClass(name); //委派给父类加载
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
byte[] classData = getClassData(name);
if(classData==null){
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}else{
c = defineClass(name, classData,0, classData.length);
}
}
}
return c;
}
private byte[] getClassData(String name) { //com.lyy.test.User d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
String path = rootUrl+"/"+name.replace('.', '/')+"class";
//IOUtils,可以使用它将流中的数据转成字节数据
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
URL url = new URL(path);
is = url.openStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int temp = 0;
while((temp=is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,temp);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally{
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
if(baos != null){
baos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
加密解密加载器(取反操作,DES对称加密解密)
package com.lyy.test;
/**
* 测试简单加密解密(取反)操作
* @author 01
*
*/
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//测试取反操作
// int a = 3;//0000011
// System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a^0xff));
//加密后的class文件,正常的类加载器无法加载,报clasformatError
// FileSystemClassLoader load = new FileSystemClassLoader("E:/VIP/temp");
// Class<?> c = load.loadClass("HelloWrold");
// System.out.println(c);
DecrptClassLoader loader = new DecrptClassLoader("E:/VIP/temp");
Class<?> c = loader.loadClass("com.lyy.temp.HelloWrold");
System.out.println(c);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
package com.lyy.test;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 自定义文件系统加载器
* @author 01
*
*/
public class FileSystemClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
//com.lyy.test.User --> d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
private String rootDir;
public FileSystemClassLoader(String rootDir){
this.rootDir=rootDir;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
//首先查询是否加载过该类,如果已经加载过,直接返回已经加载好的类,否则加载新的类
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
ClassLoader parent = this.getParent();
c = parent.loadClass(name); //委派给父类加载
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
byte[] classData = getClassData(name);
if(classData==null){
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}else{
c = defineClass(name, classData,0, classData.length);
}
}
}
return c;
}
private byte[] getClassData(String name) { //com.lyy.test.User d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
String path = rootDir+"/"+name.replace('.', '/')+"class";
//IOUtils,可以使用它将流中的数据转成字节数据
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
is = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int temp = 0;
while((temp=is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,temp);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally{
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
if(baos != null){
baos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
package com.lyy.test;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 加载文件系统加密后的class字节码的类加载器
* @author 01
*
*/
public class DecrptClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
//com.lyy.test.User --> d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
private String rootDir;
public DecrptClassLoader(String rootDir){
this.rootDir=rootDir;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
//首先查询是否加载过该类,如果已经加载过,直接返回已经加载好的类,否则加载新的类
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
ClassLoader parent = this.getParent();
c = parent.loadClass(name); //委派给父类加载
if(null != c){
return c;
}else{
byte[] classData = getClassData(name);
if(classData==null){
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}else{
c = defineClass(name, classData,0, classData.length);
}
}
}
return c;
}
private byte[] getClassData(String name) { //com.lyy.test.User d:/myjava/com/lyy/test/User.class
String path = rootDir+"/"+name.replace('.', '/')+"class";
//IOUtils,可以使用它将流中的数据转成字节数据
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
is = new FileInputStream(path);
int temp = -1;
while((temp=is.read()) != -1){
baos.write(temp^0xff); //取反操作,相当于解密操作
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally{
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
if(baos != null){
baos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
线程上下文类加载器
双亲委托机制以及类加载器的问题
一般情况下,保证同一个类中所关联的其他类都是由当前类的类加载器所加载的。
比如,Class本身在Ext下找到,那么他里面new出来的一些类也就只能用ext去查找了(不会低一个级别),所以有些明明app可以找到的,却找不到了。
JDBC API 他有实习那的driven部门(mysql/sql server),我们的JDBC API都是由Boot或者Ext来载入的,但是Service Prover却是由EXT或者App来载入,那么就有可能找不到driver了,在java领域中,其实只要分成这种Api-SPI(Service Provide Interface,特定厂商提供)的,都会遇到此问题。
常见的SPi 有JDBC、JCE、JNXP和JBI等。
package com.lyy.test;
/**
* 线程上下文类加载器
* @author 01
*
*/
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader loader = Demo5.class.getClassLoader();
System.out.println(loader);
ClassLoader laoder2 = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
System.out.println(laoder2);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(new FileSystemClassLoader("E:/VIP/"));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
Class<Demo1> c = (Class<Demo1>)Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass("com.lyy.test.Demo1");
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(c.getClassLoader());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
TOMCAT服务器的类加载机制

文章来源: muxiaonong.blog.csdn.net,作者:牧小农,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:muxiaonong.blog.csdn.net/article/details/52668116
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)