【git】(task2)Git分支管理及工具使用
学习总结
- 当我们在两个分支中对同一个文件的同一个部分进行了不同的修改,Git就没有办法顺利的合并他们,会在合并的时候产生合并冲突。比如我们在
issue102分支和master分支下对issue102.md文件进行了修改,当我们将issue102分支融合到主分支上时就会发生冲突。 - 可以通过
git status查看命令来查看那些因包含合并冲突而处于未合并(unmerged)状态的文件。当出现矛盾后,合并的文件内容将会出现"<<<<<<“,”=======“,”>>>>>>"等分割线来进行标记。 - 在实际开发中,应该按照以下几个基本原则进行分支开发工作流程
- master分支应该是最稳定的,也就是仅用来发布新版本,平时不能直接在上面进行操作,应该保存在远程。
- 短期分支是我们干活的分支,短期分支可以不用上传到远程,当我们完成了bug的修复,新功能的开发时才需要合并到主分支上。
- 多使用分支来进行开发工作。
- 本次学习的是git分支管理和工具使用,如签名、凭证存储、重置、Rerere 等高级功能后面再涉及。
文章目录
三、Git分支管理
3.1 分支的简介
- Git最重要的运用场景是多人协同开发,但是如何能保证每个人之间的开发不影响其他人的开发进程,Git 分支的出现就是解决了这个问题,使得每个人之间的开发是独立的,互不影响的。
- 与许多其它版本控制系统不同,Git 鼓励在工作流程中频繁地使用分支与合并,哪怕一天之内进行许多次。
3.2 分支的相关操作
(1)分支的创建和切换
【分支的创建】
Git分支的创建十分简单,我们可以使用git branch来查看现有的分支或创建新的分支。当不带任何命令参数时,输入git branch可以帮助我们查看当前项目所拥有的全部分支。并且Git会使用*来标明我们当前所处的分支上。
git branch
- 1
结果为:
* master
- 1
当我们想要新增加新的分支时,只需要在git branch命令后面加上我们想要新建的分支的名称即可。
# 创建issue102的分支
git branch issue102
# 查看现有的所有分支
git branch
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
# 现有的分支
issue102
*master
- 1
- 2
- 3
我们可以发现虽然创建了issue102的分支,但是当前分支还是在master上。我们可以通过git checkout命令来进行切换分支。
【分支的切换】
在上面的例子中我们发现虽然创建了新的分支,但是当前分支还是在master分支上,我们需要通过git checkout命令切换到新建的issue102分支上,来进行后续的开发操作。
git checkout issue102
- 1
Switched to branch 'issue102'
- 1
这是我们可以在查看下当前分支的状态,我们可以发现当前分支已经转换到了issue102分支上。

git branch
* issue102
master
- 1
- 2
- 3
切换分支后,我们就可以进行自己的开发。分支上的文件状态是不同的。我们可以通过下面的例子有着更深入的了解。
# 切换分支
git checkout issue102
# 在分支上创建下新的文件
touch issue102.md
git add issue102.md
git commit -m "update issue102.md"
touch issue102.html
git add issue102.html
git commit -m "update issue102.html"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
实际操作如下:

在完成上述命令后,我们可以通过git log --oneline检查下当前Git的记录。
cd836b0 (HEAD -> issue102) update issue102.html
7575f02 update issue102.md
242c407 (master) update hello.md
- 1
- 2
- 3
我们可以发现issue102分支上的记录与master的记录间隔开了。除此之外,当我们切换回主分支后,我们还会发现master分支下没有新建的issue102.md和issue102.html两个文件。正如下图所示:
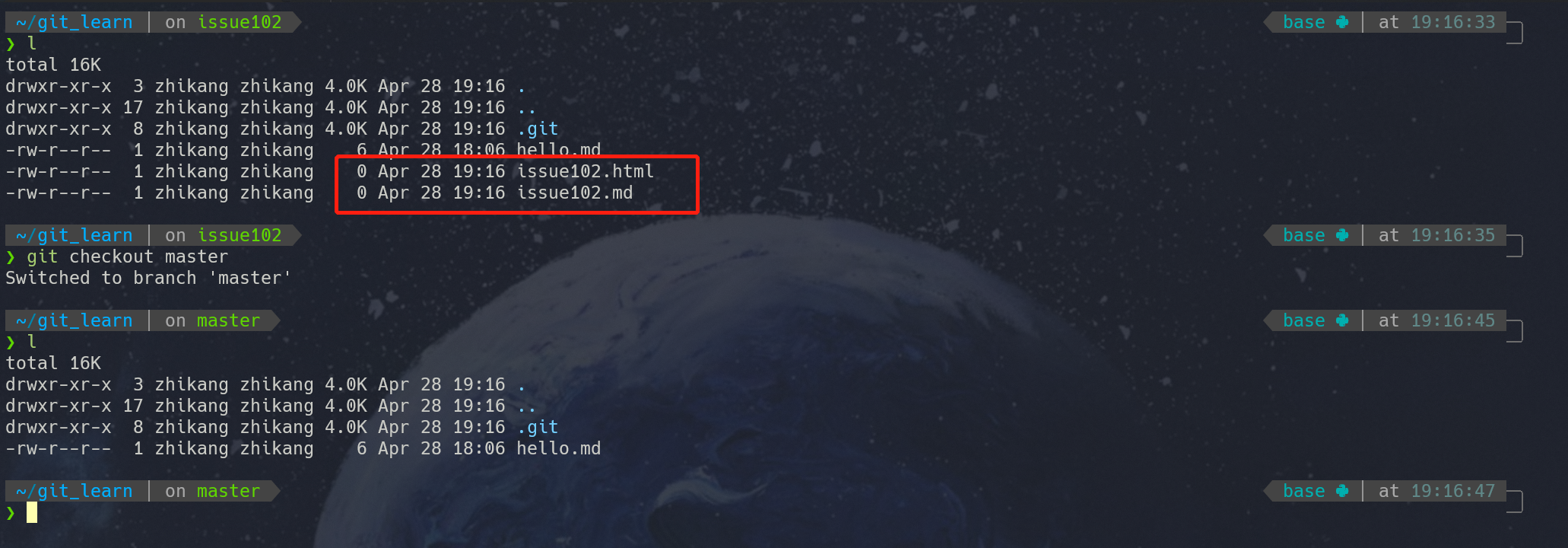
(2)分支的合并
当我们在分支上完成来开发工作后,我们需要将我们在当前分支进行的工作合并到主分支上。首先我们需要切回需要合并到的分支上,此处以issue102合并到master上为例子进行演示。
# 切换回主分支
git checkout master
# 使用git merge 进行合并
git merge issue102
# git branch --no-merged
# 查看所有未合并工作的分支
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

我们可以发现原来在issue102分支上的文件已经合并到了主分支上了,并且issue102分支还存在。大家可以根据实际的需求进行分支的保留与删除。
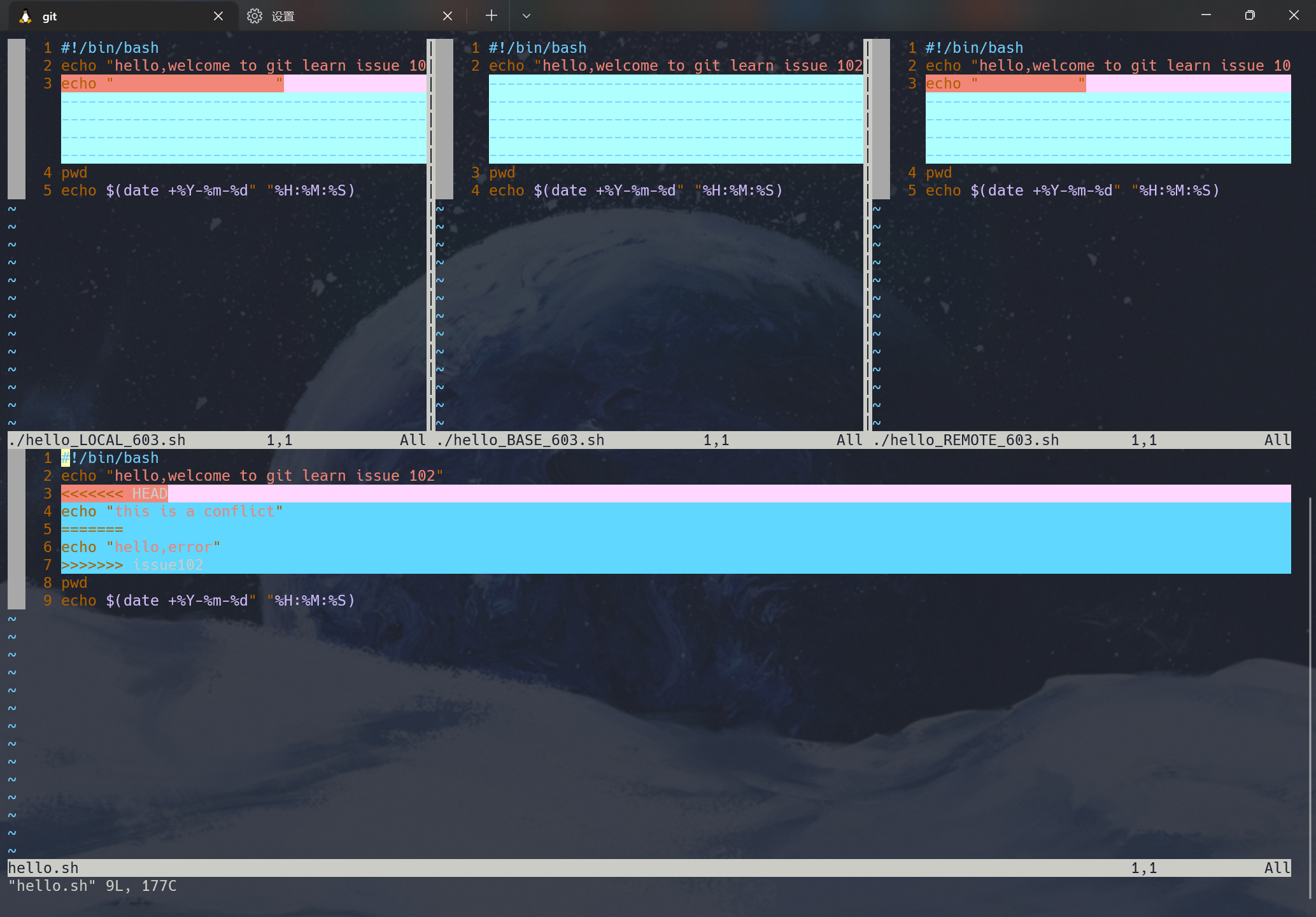
有时候分支的合并不会一番顺利,当我们在两个分支中对同一个文件的同一个部分进行了不同的修改,Git就没有办法顺利的合并他们,会在合并的时候产生合并冲突。比如我们在issue102分支和master分支下对issue102.md文件进行了修改,当我们将issue102分支融合到主分支上时就会发生冲突。如下图所示:

我们也可以通过git status查看命令来查看那些因包含合并冲突而处于未合并(unmerged)状态的文件。当出现矛盾后,合并的文件内容将会出现"<<<<<<“,”=======“,”>>>>>>"等分割线来进行标记。如下图所示:

当出现了矛盾时,我们需要进行手动解决或者放弃合并。
-
手动合并
手动合并的方法很简单,就是我们选择我们要保留的代码,然后再把>>>>>, ======, <<<<<<这些提示行给去掉。最后重新进行add commit的操作即可。
-
放弃合并
当我们发现冲突所导致的改动量很大时,我们可以选择放弃该次的合并。我们可以使用
git merge --abort放弃此次的融合。如果我们在运行了git merge之后又进行了一些人为的改动,那么在abort之后,所进行的改动也会被回滚掉。 -
mergetool
除了手动合并以及放弃合并之外,我们还有一些其他的合并工具。git官方开发了一个专门用来合并的工具,叫做git mergetool(下图所示),它会将找到一份两个分支的祖先代码作为base(基准),然后再将两个分支的改动都列举出来作为对比,让我们在git编辑器当中决定要留下什么。在此处,我们不做过多的阐述,感兴趣的同学可以点击下方链接进行查看。
(3)分支推送到远程
在很多情况下,我们都需要将分支推送到远程,在这一部分,我们将讲一些远程的相关操作。
首先,我们可以使用git remote -v查看远程库的详细信息。会显示我们可以抓取或推送的origin地址。
$ git remote -v
origin git@github.com:ProjectOwner/ProjectName.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:ProjectOwner/ProjectName.git (push)
- 1
- 2
- 3
当我们需要推送本地分支到远程时,需要指定具体的本地分支。
# 推送本地的master分支到远程
git push origin master
# 推送本地的issue102分支到远程
git push origin issue102
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
但是当我们多人协作进行开发的时候,可能会出现远程分支比我们本地更新的情况,这时,我们就需要使用git pull的命令来试图合并。如果合并出现冲突时,我们需要解决冲突再提交。
更多参考:廖雪峰老师的Git教程中的多人协作。
(4)分支的删除
在Git中没有什么分支是不可以删除的(除了当前所在的分支不能删除),包括master分支也是可以进行删除。
Git的分支删除可以分为删除本地分支和远程分支。
- 删除本地分支
# branchName 是需要删除的本地分支名字
git branch -d branchName
- 1
- 2
当我们想强行删除分支时,只需要将参数d改为D即可。
- 删除远程分支
# origin 是远程的主机名
# branch 需要删除的远程分支
git push origin --delete branch
- 1
- 2
- 3
(5)分支的重命名
当我们需要重命名分支的名称时,我们可以使用git branch命令来进行,具体方式如下:
# oldBranchName: 旧分支名
# newBranchName :新分支名
git branch -m oldBranchName newBranchName
- 1
- 2
- 3
当我们想要将改名后的分支推送到远程时,我们需要进行如下操作:
git branch -m oldBranchName newBranchName # 将本地的分支进行重命名
git push origin newBranchName # 将新的分支推送到远程
git push --delete origin oldBranchName # 删除远程的旧的分支
- 1
- 2
- 3
3.3 分支开发工作流
常见的分支开发工作流程:
由于分支管理的便捷,才衍生出这些典型的工作模式,可以根据项目实际情况进行使用。
(1)长期分支
- 在整个项目开发周期的不同阶段,我们可以同时拥有多个分支;然后我们可以定期地把某些主题分支合并入其他分支中。比如只在 master 分支上保留完全稳定的代码——有可能仅仅是已经发布或即将发布的代码。
- 他们还有一些名为 develop 或者 next 的平行分支,被用来做后续开发或者测试稳定性——这些分支不必保持绝对稳定,但是一旦达到稳定状态,它们就可以被合并入 master 分支了。
- 在确保这些已完成的主题分支(短期分支,比如之前的 issue102 分支)能够通过所有测试,并且不会引入更多 bug 之后,就可以合并入主干分支中,等待下一次的发布。

(2)短期分支
- 短期分支也可以叫做主题分支,它的作用是用来实现某一种特性或者相关工作(修复bug,开发产品新特性)。
- 比如当我们的产品出现了bug时,我们应该新建一个分支并起名为bug分支,并在该分支上进行bug的修复,等我们的代码确定不会引起其他bug时,我们就可以合并到主分支上进行修复。
- 当我们看见issue时,我们也可以使用同样的方式来解决issue的问题。常见的短期分支还有上面提到的develop,topic分支。
在实际开发中,我们应该按照以下几个基本原则进行分支开发工作流程
- master分支应该是最稳定的,也就是仅用来发布新版本,平时不能直接在上面进行操作,应该保存在远程。
- 短期分支是我们干活的分支,短期分支可以不用上传到远程,当我们完成了bug的修复,新功能的开发时才需要合并到主分支上。
- 多使用分支来进行开发工作。
四、Git 工具(选)
本章主要介绍 Git 常用的工具,可能不会经常用到
4.0 开始你的工作
需要一些简单的文件和目录来演示该章节,如果可以的话,请 fork 这个演示项目至你的个人账号下。
https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/app
后续演示均以这个 repo 操作。
4.1 引用修订版本
Git 支持多种方式来引用单个提交、一组提交或一定范围内的提交。
(1)引用 Commit 的记录
你可以通过任意一个提交的 40 位字符的 SHA-1散列值来指定它。
$ 是终端交互的提示符,不需要输入。如果系统或者终端不一样,只需输入$后的内容即可,本文后续不再累述
切换至本项目工作目录,执行 git log 能看到类似提交日志的输出。(shell 通过 pipe | 将输出信息传递给 more 做多页显示)。
$ git log | more
commit 44328544187650f2f6ecc253ef3a2b099c51baa5
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 13:41:55 2022 +0800
add model module
commit a55ea122894272b13c3a43129ca0b74cfd2b6a4a
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 13:33:17 2022 +0800
Initial commit
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
从日志能明显的看到多次提交的记录,每次包括 commit + 一串字符、作者、提交时间 和详细信息等。
这里的主角就是 commit 后跟的 40 位的字符,这个值是一个 SHA-1 哈希值。它是对内容和头信息 Header 的一个校验和 checksum,Git 使用 SHA-1 并不是为了数据的安全性,而是数据的完整性;它保证,在很多年后,你重新 checkout 某个 commit 时,一定是当时的状态,完全一摸一样。 有兴趣进一步了解这个 SHA-1 的值,可以 参考这里。
想查看某次提交信息,可以通过 git show 来查看,如:
$ git show 44328544187650f2f6ecc253ef3a2b099c51baa5
commit 44328544187650f2f6ecc253ef3a2b099c51baa5 (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD)
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 13:41:55 2022 +0800
add model module
diff --git a/.gitmodules b/.gitmodules
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f9d131a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.gitmodules
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+[submodule "model"]
+ path = model
+ url = https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
diff --git a/model b/model
new file mode 160000
index 0000000..a8328fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/model
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+Subproject commit a8328fd6ee683ef8f6a2d7c4edfefed2923b0795
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
查看所有所有提交 SHA-1 字符串
$ git log|grep '^commit'|awk '{print $2}'
44328544187650f2f6ecc253ef3a2b099c51baa5
a55ea122894272b13c3a43129ca0b74cfd2b6a4a
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Git 非常聪明的知道在没有歧义的情况下,通过前几个字符来替代上述 40 位字符,如上可简化成:
$ git show 4432854
- 1
甚至简化成
$ git show 4432
- 1
当然你的确保没有歧义。Git 可以为 SHA-1 值生成出简短且唯一的缩写,可以在 git log 后加 --abbrev-commit 参数,输出结果就会显示简短且唯一的值了。默认情况使用 7 个字符,有时为来避免歧义,会增加字符数。
$ git log --abbrev-commit
commit 4432854 (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD)
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 13:41:55 2022 +0800
add model module
commit a55ea12
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 13:33:17 2022 +0800
Initial commit
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
通过在 git log后增加 --pretty=oneline简化输出内容
$ git log --abbrev-commit --pretty=oneline
4432854 (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD) add model module
a55ea12 Initial commit
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(2)引用分支
如果你要查看一个分支的最后一次对象,可以通过分支名查看。查看本地分支列表通过git branch查看
$ git branch
develop
main
* stable
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
* 表示当前工作的分支
查看远程分支通过后加参数-r
$ git branch -r
origin/HEAD -> origin/main
origin/main
origin/stable
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
我们尝试通过git show stable查看指定分支最后一次提交信息
$ git show stable
commit 11671bae8489621c02a4c99dbcf24b0dede1b1b1 (HEAD -> stable)
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 14:16:00 2022 +0800
stable model for app
diff --git a/.gitmodules b/.gitmodules
index f9d131a..47d8924 100644
--- a/.gitmodules
+++ b/.gitmodules
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
[submodule "model"]
path = model
url = https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
+ branch = stable
diff --git a/model b/model
index a8328fd..ca79fae 160000
--- a/model
+++ b/model
@@ -1 +1 @@
-Subproject commit a8328fd6ee683ef8f6a2d7c4edfefed2923b0795
+Subproject commit ca79fae869c9b4ddd7999f06ffd48ac25971b9dd
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
如果你的 branch 的名称和当前目录名称很不巧的重名了,那么应该会出现意外的输出 😭 并没有我们期盼中的结果。
创建同名测试目录
$ mkdir stable
- 1
再次执行git show stable
$ git show stable
fatal: ambiguous argument 'stable': both revision and filename
Use '--' to separate paths from revisions, like this:
'git <command> [<revision>...] -- [<file>...]'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Git 不知道如何处理,我们需要通过 -- 明确告知.
- – 前面的为 revision 可以是分支,tag 等
- – 后面的为 file 即要操作的文件
$ git show stable --
- 1
我们通过 git rev-parse可以查看某个分支指向那个特定的 SHA-1, 并通过 git show 去查看这个 SHA-1 值对应的提交信息。
$ git rev-parse stable
11671bae8489621c02a4c99dbcf24b0dede1b1b1
$ git show 11671bae8489621c02a4c99dbcf24b0dede1b1b1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
我们能看到是一致的信息。
(3)引用日志
当你在工作时, Git 会在后台保存一个引用日志(reflog), 引用日志记录了最近几个月你的 HEAD 和分支引用所指向的历史。
你可以使用 git reflog 来查看引用日志
$ git reflog
11671ba (HEAD -> stable, origin/stable) HEAD@{0}: commit: stable model for app
4432854 (origin/main, origin/HEAD, main, develop) HEAD@{1}: checkout: moving from main to stable
4432854 (origin/main, origin/HEAD, main, develop) HEAD@{2}: commit: add model module
a55ea12 HEAD@{3}: clone: from https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/app
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
每当你的 HEAD 所指向的位置发生了变化,Git 就会将这个信息存储到引用日志这个历史记录里。 你也可以通过 reflog 数据来获取之前的提交历史。 如果你想查看仓库中 HEAD 在 2 次前的所指向的提交,你可以使用 @{n} 来引用 reflog 中输出的提交记录。
$ git show HEAD@{2}
commit 44328544187650f2f6ecc253ef3a2b099c51baa5 (origin/main, origin/HEAD, main, develop)
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 13:41:55 2022 +0800
add model module
diff --git a/.gitmodules b/.gitmodules
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f9d131a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.gitmodules
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+[submodule "model"]
+ path = model
+ url = https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
diff --git a/model b/model
new file mode 160000
index 0000000..a8328fd
--- /dev/nullq
+++ b/model
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+Subproject commit a8328fd6ee683ef8f6a2d7c4edfefed2923b0795
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
4.2 交互式暂存
当你修改大量文件后,希望将改动拆分成多个提交而不是一起提交的时候,可以通过如下命令操作。
如果运行 git add 后加 -i 或者 --interactive 选项的时候,Git 会进入一个交互式命令模式,如:
$ git add -i
staged unstaged path
1: +532/-0 nothing src/trace/events.go
2: +365/-0 nothing src/trace/histogram.go
3: +325/-0 nothing src/trace/histogram_test.go
4: +1130/-0 nothing src/trace/trace.go
5: +178/-0 nothing src/trace/trace_test.go
*** Commands ***
1: status 2: update 3: revert 4: add untracked
5: patch 6: diff 7: quit 8: help
What now>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
可以看到这个命令以和平时不同的视图:显示了暂存区。基本上与 git status 是相同的信息,但是更简明扼要一些。 它将暂存的修改列在左侧,未暂存的修改列在右侧。
在这块区域后是 Commands 命令区域。 在这里你可以做一些工作,包括暂存文件、取消暂存文件、暂存文件的一部分、添加未被追踪的文件、显示暂存内容的区别。
(1)暂存、取消文件
在 Waht now>> 提示符后输入u或者2,它会提示你要暂存哪个文件
$ git add -i
staged unstaged path
1: +532/-0 nothing src/trace/events.go
2: +365/-0 nothing src/trace/histogram.go
3: +325/-0 nothing src/trace/histogram_test.go
4: +1130/-0 nothing src/trace/trace.go
5: +178/-0 +1/-1 src/trace/trace_test.go
*** Commands ***
1: status 2: update 3: revert 4: add untracked
5: patch 6: diff 7: quit 8: help
What now> u
staged unstaged path
1: +178/-0 +1/-1 src/trace/trace_test.go
Update>> 1
staged unstaged path
* 1: +178/-0 +1/-1 src/trace/trace_test.go
Update>>
updated 1 path
*** Commands ***
1: status 2: update 3: revert 4: add untracked
5: patch 6: diff 7: quit 8: help
What now> s
staged unstaged path
1: +532/-0 nothing src/trace/events.go
2: +365/-0 nothing src/trace/histogram.go
3: +325/-0 nothing src/trace/histogram_test.go
4: +1130/-0 nothing src/trace/trace.go
5: +178/-0 nothing src/trace/trace_test.go
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
再输入u 后根据提示的文件列表,输入序号,这里我们要暂存src/trace/trace_test.go,输入 5, 会看到文件名称有个*,意味着选中的文件将被暂存。如果不需要其他操作了,直接按回车,不输入任何东西返回命令行界面。通过命令s查看状态,发现src/trace/trace_test.go 已经被暂存了。
如果想取消暂存,在 Waht now>> 提示符后输入r或者3,进行撤销,同上的操作。
如果想要查看已暂存内容的区别,可以使用 d 或 6(区别)命令。 它会显示暂存文件的一个列表,可以从中选择想要查看的暂存区别。 这跟你在命令行指定 git diff --cached 非常相似:
$ git add -i
staged unstaged path
1: +1/-1 nothing src/trace/trace_test.go
What now> d
staged unstaged path
1: +1/-1 nothing src/trace/trace_test.go
Review diff>> 1
diff --git a/src/trace/trace_test.go b/src/trace/trace_test.go
index 8cc7998..33732e6 100644
--- a/src/trace/trace_test.go
+++ b/src/trace/trace_test.go
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
// Copyright 2015 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
-
+//
package trace
import (
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
通过这些基本命令,可以使用交互式添加模式来轻松地处理暂存区。
(2)暂存补丁
Git 也可以暂存文件的特定部分。 例如,如果在 TODO 文件中做了两处修改,但只想要暂存其中的一个而不是另一个,Git 会帮你轻松地完成。 在和上一节一样的交互式提示符中,输入 p 或 5。
$ git add -i
staged unstaged path
1: unchanged +2/-1 src/trace/trace_test.go
*** Commands ***
1: status 2: update 3: revert 4: add untracked
5: patch 6: diff 7: quit 8: help
What now> p
staged unstaged path
1: unchanged +2/-1 src/trace/trace_test.go
Patch update>> 1
staged unstaged path
* 1: unchanged +2/-1 src/trace/trace_test.go
Patch update>>
diff --git a/src/trace/trace_test.go b/src/trace/trace_test.go
index 8cc7998..a95f46e 100644
--- a/src/trace/trace_test.go
+++ b/src/trace/trace_test.go
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
// Copyright 2015 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
-
+//
+// copy from go framework
package trace
import (
(1/1) Stage this hunk [y,n,q,a,d,e,?]?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
输入p 后,选择你需要操作的文件后,直接敲回车,会逐一询问你是否需要暂存他们,(1/1) 表示当前是第 1 个初变更,共 1 处变更。选项很多,输入?可以查看具体的解释
y - stage this hunk
n - do not stage this hunk
q - quit; do not stage this hunk or any of the remaining ones
a - stage this hunk and all later hunks in the file
d - do not stage this hunk or any of the later hunks in the file
g - select a hunk to go to
/ - search for a hunk matching the given regex
j - leave this hunk undecided, see next undecided hunk
J - leave this hunk undecided, see next hunk
e - manually edit the current hunk
? - print help
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
通过y或者n来选择是否要暂存每一区块,当然也可以通过a暂存从这到后面所有当前文件的修改。暂存成功后,退出交互命令,我们就可以通过git commit来提交这部分暂存的文件了。
4.3 贮藏与清理
很多时候,你在当前分支上工作了一段时间后,东西变得很混乱。你想切换至新的分支而又不想放弃放弃的修改,或者纯粹想先做其他分支的事情的时候,就该git stash上场了。
stash 会处理工作目录的的状态,跟踪文件的修改和暂存的改动,然后将未完成的修改保存至一个栈上,这样就可以在后续任何时间切换回来。
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: src/trace/trace_test.go
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
文件被修改了一大坨,但是还没修改完,暂时还不想提交,而我又想切换至新的分支,这时候就需要stash,先把变更推送至栈上,运行git stash 或者 git stash push
$ git stash
Saved working directory and index state WIP on main: a123887 sample codes for demonstration
- 1
- 2
- 3
然后再查看git status
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
nothing to commit, working tree clean
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
我们能看到当前目录已经非常干净了,这时候你可以按常规操作一样,做你想做的其他的事情。如切换新的分支,或者我想不到的事情.
那么要返回刚才那坨文件该怎么办呢?通过 git stash list 查看所有 stash 的列表
$ git stash list
stash@{0}: WIP on main: 36c4cad sample codes for demonstration
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
切换至最后 stash 变更,直接执行 git stash apply 即可,当然如果有多个,可以通过 git stash apply stash@{n} 中的 n 来获取指定的的变更。
$ git stash apply
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: src/trace/trace_test.go
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
git stash apply stash@{0} 会输出同样的内容。
可以通过 git stash drop 或者 git stash pop 来删除 stash 的内容。
$ git stash drop stash@{0}
Dropped stash@{0} (36c4cad0bafa4dbbd78ae469b0afa38ae2808102)
- 1
- 2
- 3
(1)清理工作目录
对于一些不需要的文件或目录,你需要的是清理它而不是保存修改记录,git clean就是用来做这个事情的
需要注意的是,这个命令会移除未被跟踪的文件,可以考虑执行 git stash --all 来移除所有文件并保存到栈上。
使用 git clean -f -d 命令来移除工作目录中所有未追踪的文件以及空的子目录。 -f 意味着强制移除,使用它需要 Git 配置变量 clean.requireForce 没有显式设置为 false。
如果你只是想看下或者删除前小心翼翼的确认: 它到底会删除那些东西. 可以通过--dry-run或者-n选项来执行命令,这只是告诉你会删除什么,而不会真的删除.
创建一些临时文件用于测试
$ touch temp; mkdir log; mkdir target; touch target/main
- 1
通过git clean -n查看
$ git clean -n
Would remove temp
- 1
- 2
- 3
默认情况下,git clean 命令只会移除没有忽略的未跟踪文件。 任何与 .gitignore 或其他忽略文件中的模式匹配的文件都不会被移除。如果你也想移除,可以通过增加选项-x
$ git clean -n -x
Would remove .DS_Store
Would remove temp
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
同样增加选项-d可以删除目录
$ git clean -n -x -d
Would remove .DS_Store
Would remove log/
Would remove target/
Would remove temp
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
如果你想交互删除,可以通过选项 -i来操作
Would remove the following items:
.DS_Store log/ target/ temp
*** Commands ***
1: clean 2: filter by pattern 3: select by numbers 4: ask each 5: quit
6: help
What now>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
通过What now后输入命令或序号交互操作,不知道可以输入 help 查看具体的描述
What now> help
clean - start cleaning
filter by pattern - exclude items from deletion
select by numbers - select items to be deleted by numbers
ask each - confirm each deletion (like "rm -i")
quit - stop cleaning
help - this screen
? - help for prompt selection
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4.4 搜索
无论仓库里的代码量有多少,你经常需要查找一个函数是在哪里调用或者定义的,或者显示一个方法的变更历史。 Git 提供了两个有用的工具来快速地从它的数据库中浏览代码和提交。 我们来简单的看一下。
(1)Git Grep
Git 提供了一个grep命令,可以很方便的从提交历史,工作目录,甚至索引中查找一个字符串或者正则表达式。
默认情况下git grep会查找你的工作目录文件。
$ git grep a.percentileBoundary
src/trace/histogram.go:func (h *histogram) percentileBoundary(percentile float64) int64 {
src/trace/histogram.go: return h.percentileBoundary(0.5)
src/trace/histogram_test.go: percentile := a.percentileBoundary(test.fraction)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
通过-n或者--line-number显示匹配的行号
$ git grep -n percentileBoundary
src/trace/histogram.go:120:func (h *histogram) percentileBoundary(percentile float64) int64 {
src/trace/histogram.go:166: return h.percentileBoundary(0.5)
src/trace/histogram_test.go:181: percentile := a.percentileBoundary(test.fraction)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
通过-c或者--count输出统计信息
git grep -c percentileBoundary
src/trace/histogram.go:2
src/trace/histogram_test.go:1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
通过-p 或者 --show-function 显示每个匹配字符串所在的方法或函数
git grep -p percentileBoundary
src/trace/histogram.go=func (h *histogram) standardDeviation() float64 {
src/trace/histogram.go:func (h *histogram) percentileBoundary(percentile float64) int64 {
src/trace/histogram.go=func (h *histogram) median() int64 {
src/trace/histogram.go: return h.percentileBoundary(0.5)
src/trace/histogram_test.go=func TestPercentileBoundary(t *testing.T) {
src/trace/histogram_test.go: percentile := a.percentileBoundary(test.fraction)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
(2)Git 日志搜索
通过git log可以很强大的知道一些特定的提交信息。
如通过-S选项知道内容的新增和删除提交记录,我们这里以 CTP 的 Python 的 wrapper 为例:
$ git log -S percentileBoundary
a123887 (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD) sample codes for demonstration
- 1
- 2
- 3
通过-L选项进行行日志搜索,它可以展示代码中一行或者一个函数的历史。
$ git log -L :percentileBoundary:src/trace/histogram.go
commit a123887e43424c979b3e47b3cf9c672c579a6faa (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD)
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 14:34:18 2022 +0800
sample codes for demonstration
diff --git a/src/trace/histogram.go b/src/trace/histogram.go
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/trace/histogram.go
@@ -0,0 +120,45 @@
+func (h *histogram) percentileBoundary(percentile float64) int64 {
+ total := h.total()
+
+ // Corner cases (make sure result is strictly less than Total())
+ if total == 0 {
+ return 0
+ } else if total == 1 {
+ return int64(h.average())
+ }
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
如果 Git 无法匹配到你的函数或者方法,可以通过正则表达式,如这个命令和上面是等效的
$ git log -L '/percentileBoundary/',/^}/:src/trace/histogram.go
commit a123887e43424c979b3e47b3cf9c672c579a6faa (HEAD -> main, origin/main, origin/HEAD)
Author: Martin Xu <martin.xus@gmail.com>
Date: Wed May 4 14:34:18 2022 +0800
sample codes for demonstration
diff --git a/src/trace/histogram.go b/src/trace/histogram.go
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/trace/histogram.go
@@ -0,0 +120,43 @@
+func (h *histogram) percentileBoundary(percentile float64) int64 {
+ total := h.total()
+
+ // Corner cases (make sure result is strictly less than Total())
+ if total == 0 {
+ return 0
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
4.5 子模块
项目中经常会遇到包含另外一个项目,如:第三方库,或者你将自己的项目切分成多个子项目,然后在其他项目中引用,如,将项目中的 model 独立处理,独立维护;其他项目组引用这个项目,并不维护 model。这里我们可以将 model 做子项目添加到当前项目中。
(1)添加子模块
通过 git submodule add 添加子模块, 大家可以使用 https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model 进行测试,如
$ git submodule add https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
Cloning into '/Users/martin/project/datawhalechina/app/model'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 5, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
remote: Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (5/5), done.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
参数同 clone,默认是 repo 的名称,如果你想改名,可以在后续增加新的名称或路径。
通过 git status 能看到新的 model 库。
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
new file: .gitmodules
new file: model
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
能看到有个新增的 model 和 .gitmodules文件,该配置文件保存了项目 URL 和本地目录的 mapping 关系。
$ cat .gitmodules
[submodule "model"]
path = model
url = https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
如果有多个子模块,这里会列出多条。
通过git diff能看到更详细的信息
$ git diff --cached model
diff --git a/model b/model
new file mode 160000
index 0000000..a8328fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/model
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+Subproject commit a8328fd6ee683ef8f6a2d7c4edfefed2923b0795
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
虽然 model 是工作目录中的一个子目录,但 Git 还是会将它视作一个子模块。当你不在那个目录中时,Git 并不会跟踪它的内容, 而是将它看作子模块仓库中的某个具体的提交。
如果你想看到更漂亮的差异输出,可以给 git diff 传递 --submodule 选项。
$ git diff --cached --submodule
diff --git a/.gitmodules b/.gitmodules
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f9d131a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.gitmodules
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
+[submodule "model"]
+ path = model
+ url = https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
Submodule model 0000000...a8328fd (new submodule)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
当你提交时,会看到类似下面的信息:
$ git commit -am 'add model module'
[main 4432854] add model module
2 files changed, 4 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 .gitmodules
create mode 160000 model
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
注意 app 记录的 160000 模式。这是 Git 中的一种特殊模式,它本质上意味着你是将一次提交记作一项目录记录的,而非将它记录成一个子目录或者一个文件。
然后推送至服务端
git push origin main
Enumerating objects: 4, done.
Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done.
Delta compression using up to 12 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 457 bytes | 457.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
To https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/app
a55ea12..4432854 main -> main
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(2)克隆含有子模块的项目
我们在 clone 一个含子模块的项目时,默认是不会包含子模块内容的,只有目录,如重新 clone 上述的 app 项目
$ git clone https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/app.git new_app
Cloning into 'new_app'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 8, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (8/8), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (7/7), done.
remote: Total 8 (delta 1), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (8/8), done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), done.
$ cd new_app/model
$ ls -alh
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 martin staff 64B May 4 13:46 .
drwxr-xr-x 8 martin staff 256B May 4 13:46 ..
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
会发现什么也没有,需要通过如下两个命令来获取内容
git submodule init初始化本地配置文件git submodule update则从该项目中抓取所有数据并检出父项目中列出的合适的提交。
$ git submodule init
Submodule 'model' (https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model) registered for path './'
$ git submodule update
Cloning into '/Users/martin/project/datawhalechina/new_app/model'...Cloning into '/Users/martin/project/datawhalechina/new_app/model'...
Submodule path './': checked out 'a8328fd6ee683ef8f6a2d7c4edfefed2923b0795'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
不过还有更简单一点的方式。 如果给 git clone 命令传递 --recurse-submodules 选项,它就会自动初始化并更新仓库中的每一个子模块, 包括可能存在的嵌套子模块。
$ git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/app.git new_app2
Cloning into 'new_app2'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 8, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (8/8), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (7/7), done.
remote: Total 8 (delta 1), reused 3 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (8/8), done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), done.
Submodule 'model' (https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model) registered for path 'model'
Cloning into '/Users/martin/project/datawhalechina/new_app/model/new_app2/model'...
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
如果你已经克隆了项目但忘记了 --recurse-submodules,那么可以运行 git submodule update --init 将 git submodule init 和 git submodule update 合并成一步。如果还要初始化、抓取并检出任何嵌套的子模块, 请使用简明的 git submodule update --init --recursive。
(3)更新子模块
当子模块有更新的时候,执行 git submodule update --remote
$ git submodule update --remote
- 1
该命令默认会更新 main 分支,如果你想设置为其他分支,可以在 .gitmodules 文件中设置 (这样其他人也可以跟踪它),也可以只在本地的 .git/config 文件中设置,我们在.gitmodules中配置它
$ git config -f .gitmodules submodule.model.branch stable
$ cat .gitmodules
[submodule "model"]
path = model
url = https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
branch = stable
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
很明显很看到 branch 已经变化。当运行 git submodule update --remote 时,Git 默认会尝试更新 所有 子模块, 所以如果有很多子模块的话,你可以传递想要更新的子模块的名字。如 git submodule update --remote model
$ git submodule update --remote model
remote: Enumerating objects: 5, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (1/1), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 1), reused 3 (delta 1), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), 266 bytes | 133.00 KiB/s, done.
From https://github.com/datawhalechina-git-samples/model
a8328fd..ca79fae main -> origin/main
* [new branch] stable -> origin/stable
Submodule path 'model': checked out 'ca79fae869c9b4ddd7999f06ffd48ac25971b9dd'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
4.6 打包
Git 提供了多种网络传输的方法,如 SSH、HTTP 等,但是还有种不太常用的功能又什么有效。
Git 可以就将它的数据"打包"到一个文件中,通过 git bundle来实现。bundle 命令会将git push命令所传输的所有内容打包成一个二进制文件,你可以将这个文件转发给别人,然后解包到仓库中。
$ git bundle create repo.bundle HEAD main
Enumerating objects: 90, done.
Counting objects: 100% (90/90), done.
Compressing objects: 100% (83/83), done.
Total 90 (delta 12), reused 24 (delta 3), pack-reused 0
$ ls -alh repo.bundle
-rw-r--r-- 1 martin staff 6.2M May 4 12:05 repo.bundle
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
这个 repo.bundle 就是我打包之后的文件,改文件包含了所有重建仓库 main 分支所需要的数据。在使用 bundle 命令时,你需要列出所有你希望打包的引用或者提交的区间。 如果你希望这个仓库可以在别处被克隆,你应该像例子中那样增加一个 HEAD 引用。
别人就可以从这个二级制文件 clone 一个目录,就像从git clone https/ssh 一样的功能
$ git clone repo.bundle repo
Cloning into 'repo'...
Receiving objects: 100% (90/90), 6.20 MiB | 88.21 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (12/12), done.
$ git log --oneline
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
如果你在打包时没有包含 HEAD 引用,你还需要在命令后指定一个 -b main 或者其他被引入的分支, 否则 Git 不知道应该检出哪一个分支。
如果只是要提交最新提交的修改,这需要我们手工计算,可以通过如下的指令计算差别
$ git log --oneline origin/main..main
- 1
或者
$ git log --oneline main ^origin/main
- 1
这里将获得到我们希望被打包的提交列表,将这些提交打包,通过 git bundle create操作
$ git bundle create commits.bundle main ^5de18d5
- 1
可以将 commits.bundle 文件分享给合作者,他可以将这个文件导入到原始仓库中。在导入前可通过bundle verify 命令检查这个文件是否是一个合法的 Git 包,是否拥有共同的祖先。
git bundle verify commits.bundle
- 1
如果打包工具打包的并不是全部的变更,而是最后几个变更,原始仓库则无法导入这个包,因为这个包缺失必要的提交信息。
Reference
- datawhale notebook
- Git Book
- 廖雪峰Git教程
- Git权威指南
- freenode
- Github-cheat-sheet
- 动手学Git
- learn git branching
时间表
| Task | 任务信息 | 时间 |
|---|---|---|
| Task01: | Git基础:第一、二章(2天) | 16、17号,即周一周二 |
| Task02: | Git分支管理及工具使用:第三、四章(2天) | 18、19号,即周三周四 |
| Task03: | Git内部原理及工作流实战:第五、六章(3天) | 20、21、22号,即周五周六周日 |
| Task04: | Git提交规范及Github/Gitee的使用:第七、八章(3天) | 23、24、25号,即周一周二周三 |
| Task05: | Git可视化工具下载和团队协作:第九、十章(3天) | 26、27、28号,即周四周五周六 |
文章来源: andyguo.blog.csdn.net,作者:山顶夕景,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:andyguo.blog.csdn.net/article/details/124783508
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)