Spark基础学习笔记29:Spark SQL内置函数
【摘要】
文章目录
零、本讲学习目标一、Spark SQL内置函数(一)内置函数概述1、10类内置函数2、两种使用方式
(二)内置函数演示1、通过编程方式使用内置函数upper()2、通过SQL语句的...
零、本讲学习目标
- 了解Spark SQL内置函数
- 学会使用自定义函数
- 学会自定义聚合函数
- 学会使用开窗函数
一、Spark SQL内置函数
(一)内置函数概述
1、10类内置函数
- Spark SQL内置了大量的函数,位于API org.apache.spark.sql.functions中。这些函数主要分为10类:UDF函数、聚合函数、日期函数、排序函数、非聚合函数、数学函数、混杂函数、窗口函数、字符串函数、集合函数,大部分函数与Hive中相同。
2、两种使用方式
- 使用内置函数有两种方式:一种是通过编程的方式使用;另一种是在SQL语句中使用。
(二)内置函数演示
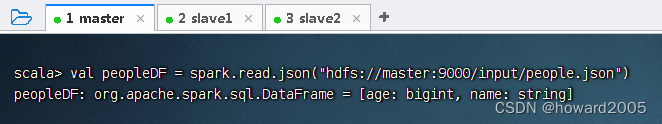
- 读取HDFS上的
people.json,得到数据帧,执行命令:val peopleDF = spark.read.json("hdfs://master:9000/input/people.json")

- 显示数据帧内容

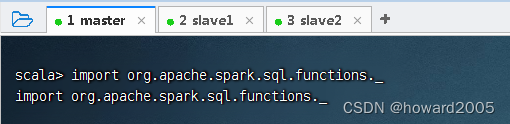
- 导入Spark SQL内置函数,执行命令:
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._

1、通过编程方式使用内置函数upper()
- 利用
upper()函数将姓名转成大写,执行命令:peopleDF.select(upper(col("name")).as("name")).show()

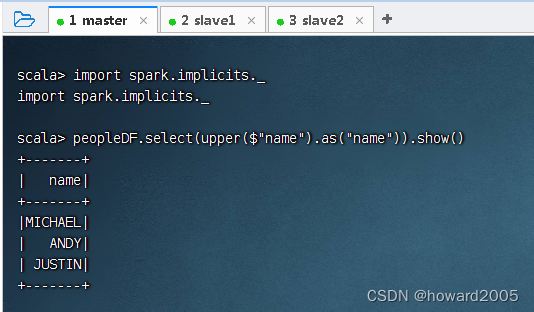
- 上述代码中,使用select()方法传入需要查询的列,使用as()方法指定列的别名。代码
col("name")指定要查询的列,也可以使用$"name"代替,但是需要导入import spark.implicits._,执行命令:peopleDF.select(upper($"name").as("name")).show()

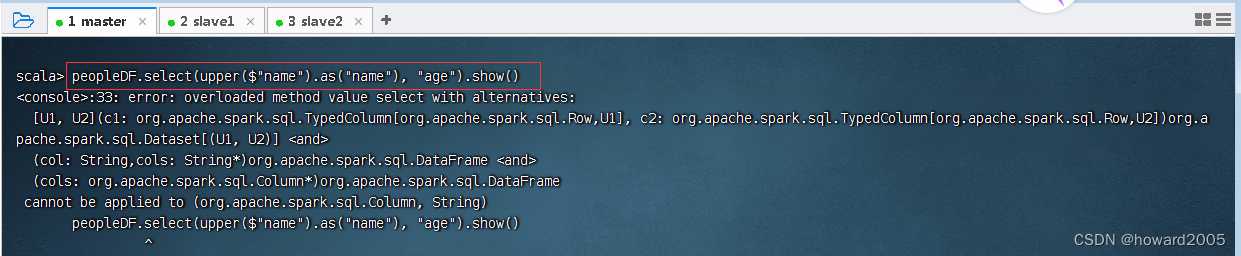
- 对某列使用了内置函数,如果还要显示其它列,就会报错

2、通过SQL语句的方式使用内置函数upper()
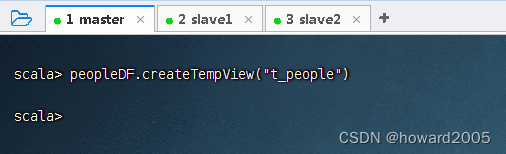
- 定义临时视图,执行命令:
peopleDF.createTempView("t_people")

- 执行命令:
spark.sql("select upper(name) as name from t_people").show()

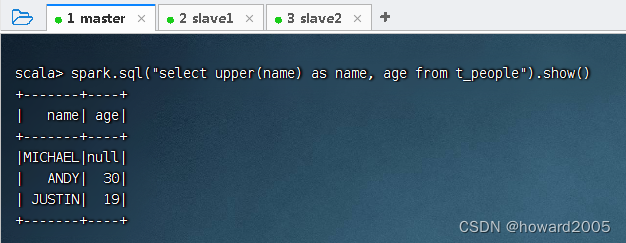
- 执行命令:
spark.sql("select upper(name) as name, age from t_people").show()

3、演示其它内置函数的使用
- 打印Schema信息,执行命令:
peopleDF.printSchema()

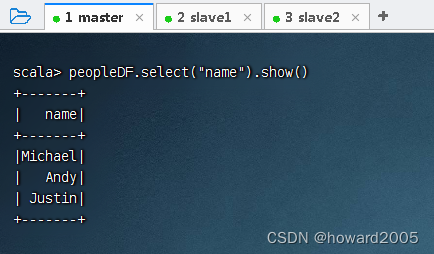
- 查询
name列,执行命令:peopleDF.select("name").show()

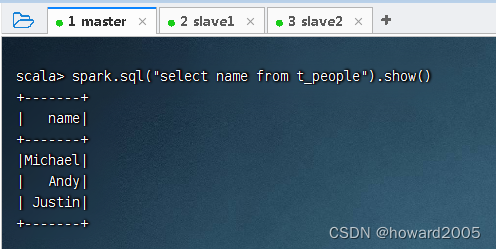
- 可用SQL语句方式来完成同样的任务

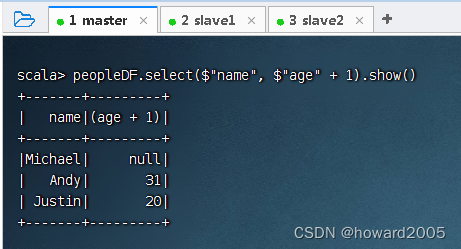
- 查询
name列和age列,其中将age列的值增加1,执行命令:peopleDF.select($"name", $"age" + 1).show()

- 可用SQL语句方式来完成同样的任务

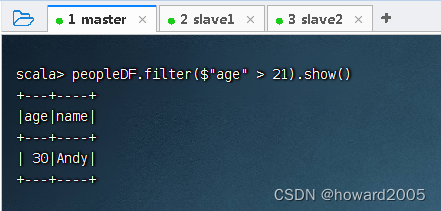
- 查询年龄大于21的记录,执行命令:
peopleDF.filter($"age" > 21).show()

- 可用SQL语句方式来完成同样的任务

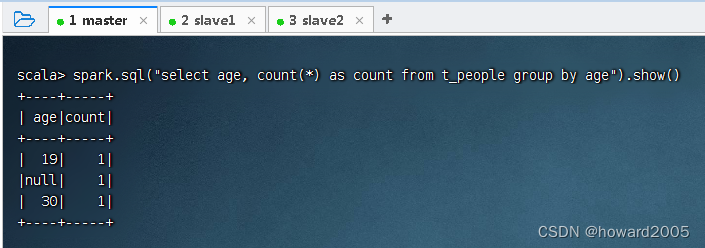
- 根据
age进行分组,并求每一组的数量,执行命令:peopleDF.groupBy("age").count().show()

- 可用SQL语句方式来完成同样的任务

二、自定义函数
(一)自定义函数概述
- 当Spark SQL提供的内置函数不能满足查询需求时,用户可以根据自己的业务编写自定义函数(User Defined Functions,UDF),然后在Spark SQL中调用。
(二)演示自定义函数
1、提出任务:手机号保密
- 有这样一个需求:为了保护用户的隐私,当查询数据的时候,需要将用户手机号的中间4位用星号()代替,比如手机号158***1170。这时就可以写一个自定义函数来实现这个需求。
2、编写程序,完成任务
- 创建
SparkSQLUDF单例对象

package net.hw.sparksql
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{StringType, StructField, StructType}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}
/**
* 功能:演示自定义函数
* 作者:华卫
* 日期:2022年05月13日
*/
object SparkSQLUDF {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 创建或得到SparkSession
val spark = SparkSession.builder()
.appName("SparkSQLUDF")
.master("local[*]")
.getOrCreate()
// 第一步:创建测试数据(亦可读取文件)
// 创建电话模拟数据
val arr = Array("15892925678", "13567892345", "18034561290", "13967678901")
// 将数组转换成RDD
val rdd: RDD[String] = spark.sparkContext.makeRDD(arr)
// 将RDD[String]转为RDD[Row]
val rowRDD: RDD[Row] = rdd.map(line => Row(line))
// 定义数据的schema
val schema = StructType(
List {
StructField("phone", StringType, true)
}
)
// 将RDD[Row]转为DataFrame
val df = spark.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)
// 第二步:创建自定义函数(phoneHide)
val phoneUDF = (phone: String) => {
var result = "手机号码错误!"
if (phone != null && phone.length == 11) {
val buffer = new StringBuffer()
buffer.append(phone.substring(0, 3))
buffer.append("****")
buffer.append(phone.substring(7))
result = buffer.toString
}
result
}
// 注册函数(第一个参数为函数名称,第二个参数为自定义的函数)
spark.udf.register("phoneHide", phoneUDF)
// 第三步:调用自定义函数
// 创建临时视图
df.createTempView("t_phone")
// 查询表,调用自定义函数处理phone字段
spark.sql("select phoneHide(phone) as phone from t_phone").show()
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 上述代码通过
spark.udf.register()方法注册一个自定义函数phoneHide,然后使用spark.sql()方法传入SQL语句,在SQL语句中调用自定义函数phoneHide并传入指定的列,该列的每一个值将依次被自定义函数phoneHide处理。 - 运行程序,查看结果

三、自定义聚合函数
(一)自定义聚合函数概述
- Spark SQL提供了一些常用的聚合函数,如count()、countDistinct()、avg()、max()、min()等。此外,用户也可以根据自己的业务编写自定义聚合函数(User Defined AggregateFunctions,UDAF)。
- UDF主要是针对单个输入返回单个输出,而UDAF则可以针对多个输入进行聚合计算返回单个输出,功能更加强大。
(二)演示自定义聚合函数
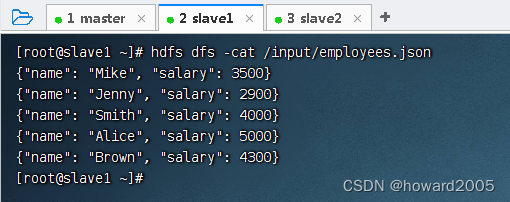
1、提出任务:实现求员工平均工资功能的UDAF
- 员工工资数据存储于HDFS上
/input目录里的employees.json文件中

2、编写程序,完成任务
- 创建
MyAverage类,继承UserDefinedAggregateFunction类

package net.hw.sparksql
import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.{MutableAggregationBuffer, UserDefinedAggregateFunction}
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{DataType, DoubleType, LongType, StructField, StructType}
/**
* 功能:自定义聚合函数类,求平均值
* 作者:华卫
* 日期:2022年05月13日
*/
class MyAverage extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction {
// 聚合函数输入参数的类型,运行时会将需要聚合的每一个值输入聚合函数中
// inputColumn为输入的列名,不做特殊要求,相当于一个列占位符
override def inputSchema: StructType = StructType (
List(StructField("inputColumn", LongType))
)
// 定义存储聚合运算产生的中间数据的Schema
// sum和count不作特殊要求,为自定义名称
override def bufferSchema: StructType = StructType(
List(
StructField("sum", LongType), // 参与聚合的数据总和
StructField("count", LongType) // 参与聚合的数据数量
)
)
// 定义数据类型
override def dataType: DataType = DoubleType
// 针对给定的同一组输入,聚合函数是否返回相同的结果,通常为true
override def deterministic: Boolean = true
// 初始化聚合运算的中间结果,中间结果存储于buffer中,buffer是一个Row类型
override def initialize(buffer: MutableAggregationBuffer): Unit = {
buffer(0) = 0L // 与bufferSchema中的第一个字段(sum)对应,即sum的初始值
buffer(1) = 0L // 与bufferSchema中的第二个字段(count)对应,即count的初始值
}
// 由于参与聚合的数据会依次输入聚合函数,因此每当向聚合函数输入新的数据时,都会调用该函数更新聚合中间结果
override def update(buffer: MutableAggregationBuffer, input: Row): Unit = {
if (!input.isNullAt(0)) {
buffer(0) = buffer.getLong(0) + input.getLong(0) // 更新参与聚合的数据总和
buffer(1) = buffer.getLong(1) + 1 // 更新参与聚合的数据数量
}
}
// 合并多个分区的buffer中间结果(分布式计算,参与聚合的数据存储于多个分区,每个分区都会产生buffer中间结果
override def merge(buffer1: MutableAggregationBuffer, buffer2: Row): Unit = {
buffer1(0) = buffer1.getLong(0) + buffer2.getLong(0) // 合并参与聚合的数据总和
buffer1(1) = buffer1.getLong(1) + buffer2.getLong(1) // 合并参与聚合的数据数量
}
// 计算最终结果,数据总和 / 数据数量 = 平均值
override def evaluate(buffer: Row): Double = buffer.getLong(0).toDouble / buffer.getLong(1)
}
/**
* 测试自定义聚合函数
*/
object MyAverage {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 创建或得到SparkSession
val spark = SparkSession.builder()
.appName("SparkSQLUDF")
.master("local[*]")
.getOrCreate()
// 注册自定义聚合函数
spark.udf.register("myAverage", new MyAverage)
// 读取员工JSON数据
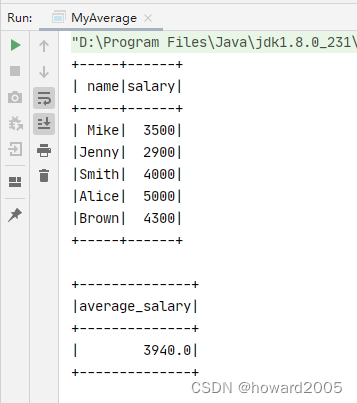
val df = spark.read.json("hdfs://master:9000/input/employees.json")
// 显示数据帧内容
df.show()
// 创建临时视图
df.createOrReplaceTempView("employees")
// 调用聚合函数进行查询
val result = spark.sql("select myAverage(salary) as average_salary from employees")
// 显示查询结果
result.show()
// 停止会话
spark.toString
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 运行程序,查看结果

四、开窗函数
(一)开窗函数概述
row_number()开窗函数是Spark SQL中常用的一个窗口函数,使用该函数可以在查询结果中对每个分组的数据,按照其排序的顺序添加一列行号(从1开始),根据行号可以方便地对每一组数据取前N行(分组取TOPN)。
(二)开窗函数使用格式
row_number() over (partition by 列名 order by 列名 desc) 行号列别名
- 1
- partition by:按照某一列进行分组
- order by:分组后按照某一列进行组内排序
- desc:降序,默认升序
(三)开窗函数案例演示
1、提出任务:统计前3名
- 统计每一个产品类别的销售额前3名(相当于分组求TOPN)
2、编写程序,实现功能,完成任务
- 创建
SparkSQLWindowFunctionDemo单例对象

package net.hw.sparksql
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{IntegerType, StringType, StructField, StructType}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}
/**
* 功能:
* 作者:华卫
* 日期:2022年05月14日
*/
object SparkSQLWindowFunctionDemo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 创建或得到SparkSession
val spark = SparkSession.builder()
.appName("SparkSQLUDF")
.master("local[*]")
.getOrCreate()
// 第一步:创建测试数据(字段:日期、产品类别、销售额)
val arr = Array(
"2022-05-10,A,710",
"2022-05-10,B,530",
"2022-05-10,C,670",
"2022-05-11,A,520",
"2022-05-11,B,730",
"2022-05-11,C,610",
"2022-05-12,A,500",
"2022-05-12,B,700",
"2022-05-12,C,650",
"2022-05-13,A,620",
"2022-05-13,B,690",
"2022-05-13,C,700",
"2022-05-14,A,720",
"2022-05-14,B,680",
"2022-05-14,C,590"
)
// 转为RDD[Row]
val rowRDD = spark.sparkContext
.makeRDD(arr)
.map(line => Row(
line.split(",")(0),
line.split(",")(1),
line.split(",")(2).toInt
))
// 构建数据帧元数据
val structType = StructType(
List(
StructField("date", StringType, true),
StructField("type", StringType, true),
StructField("money", IntegerType, true)
))
// 将RDD[Row]转成数据帧
val df = spark.createDataFrame(rowRDD, structType)
// 第二步:使用开窗函数取每个类别的金额前3名
// 创建临时视图
df.createTempView("t_sales")
// 执行SQL查询,显示每个类别排名
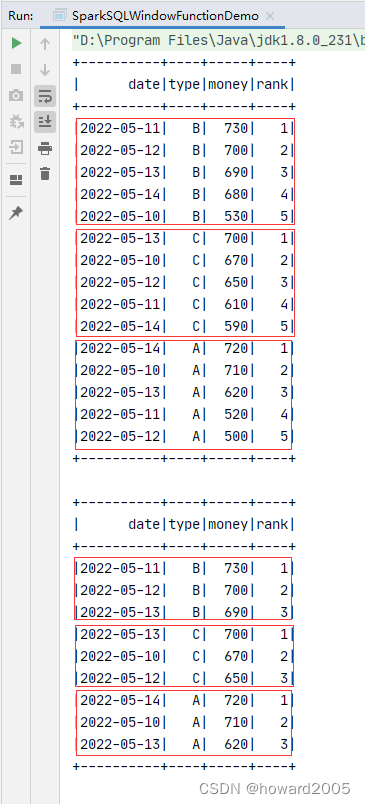
spark.sql(
"""
|select date, type, money,
| row_number() over (partition by type order by money desc) rank
| from t_sales
|""".stripMargin
).show()
// 执行SQL查询,取每个类别前3名
spark.sql(
"""
|select date, type, money, rank from
| (
| select date, type, money,
| row_number() over (partition by type order by money desc) rank
| from t_sales
| ) sale
|where sale.rank <= 3
|""".stripMargin
).show()
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 运行程序,查看结果

文章来源: howard2005.blog.csdn.net,作者:howard2005,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:howard2005.blog.csdn.net/article/details/124759297
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者












评论(0)