python 数据分析之logistic(逻辑)回归
【摘要】 python 数据分析之logistic(逻辑)回归
链接: link.
本节理论部分参考链接
@[TOC](python 数据分析之logistic(逻辑)回归)
1 环境准备
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']='SimHei' #画图正常显示中文
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='sans-serif'
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #决绝保存图像是负号‘-’显示方块的问题
2 读取数据集
def loadDataset(filename):
X=[]
Y=[]
with open(filename,'rb') as f:
for idx,line in enumerate(f):
line=line.decode('utf-8').strip()
if not line:
continue
eles=line.split(',')
if idx==0:
numFea=len(eles)
eles=list(map(float,eles))#map返回一个迭代对象
X.append(eles[:-1])
Y.append([eles[-1]])
return np.array(X),np.array(Y)
3 sigmoid函数和误差函数设计
这是logistic回归的sigmoid方法
def sigmoid(z): #需要用浮点数,否则整数和浮点数可能发生截断问题
return 1.0/(1.0+np.exp(-z))
def J(theta,X,Y,theLambda=0):
m,n=X.shape
h=sigmoid(np.dot(X,theta))
J=(-1.0/m)*(np.log(h).T.dot(y)+np.log(1-h).T.dot(1-y))+(theLambda/(2.0*m))*np.sum(np.square(theta[1:]))
if np.isnan(J[0]):
return np.inf
return J.flatten()[0]
4 梯度下降方法设计
def gradient(X,y,options):
"""
options.alpha 学习率
options.theLambda 正则化参数λ
options.maxloop 最大迭代次数
options.epsilon 判断收敛的条件
options.method
-'sgd' 随机梯度下降
-'bgd' 批量梯度下降
"""
m,n=X.shape
#初始化模型参数,n个特征对应n个参数
theta=np.zeros((n,1))
error=J(theta,X,y)#当前误差
errors=[error,] #迭代每一轮的误差
thetas=[theta,] #
alpha=options.get('alpha',0.01)
epsilon=options.get('epsilon',0.0000000001)
maxloop=options.get('maxloop',1000)
theLambda=float(options.get('theLambda',0))
method=options.get('method','bgd')
def _sgd(theta):
count=0
converged=False
while count<maxloop:
if converged:
break
#随机梯度下降,每一个样本都要更新
for i in range(m):
h=sigmoid(np.dot(X[i].reshape((1,n)),theta))
theta=theta-alpha*((1.0/m)*X[i].reshape(n,1)*(h-y[i])+(theLambda/m)*np.r_[[[0]],theta[1:]])
thetas.append(theta)
error=J(theta,X,y,theLambda)
errors.append(error)
if abs(errors[-1]-errors[-2])<epsilon:
converged=True
break
count+=1
return thetas,errors,count
def _bgd(theta):
count=0
converged=False
while count < maxloop:
if converged:
break
h=sigmoid(np.dot(X,theta))
theta=theta-alpha*((1.0/m)*np.dot(X.T,(h-y))+(theLambda/m)*np.r_[[[0]],theta[1:]])
thetas.append(theta)
error=J(theta,X,y,theLambda)
errors.append(error)
count +=1
if abs(errors[-1]-errors[-2])<epsilon:
converged=True
break
return thetas,errors,count
methods={'sgd':_sgd,'bgd':_bgd}
return methods[method](theta)
5 读取数据设置参数
ori_X,y=loadDataset('./data/gender_predict.csv')
m,n=ori_X.shape
X=np.concatenate((np.ones((m,1)),ori_X),axis=1)
options={
'alpha': 0.0003, #学习率过大会产生局部震荡
'epsilon':0.0000000001,
'maxloop':10000,
'method':'bgd'
}
thetas,errors,iterationCount=gradient(X,y,options)
errors[-1],errors[-2],iterationCount
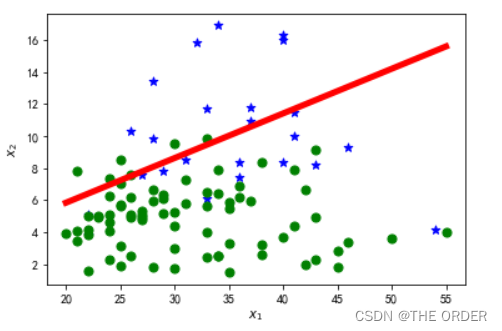
6 绘制决策边界
%matplotlib inline
#绘制决策边界
for i in range(m):
x=X[i]
if y[i]==1:
pl.scatter(x[1],x[2],marker='*',color='blue',s=50)
else:
pl.scatter(x[1],x[2],marker='o',color='green',s=50)
hSpots=np.linspace(X[:,1].min(),X[:,1].max(),100)
theta0,theta1,theta2=thetas[-1]
vSpots=-(theta0+theta1*hSpots)/theta2
pl.plot(hSpots,vSpots,color='red',linewidth=5)
pl.xlabel(r'$x_1$')
pl.ylabel(r'$x_2$')
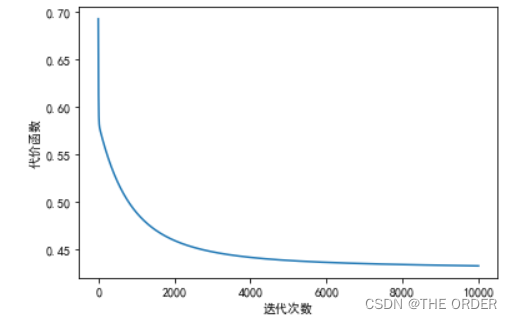
7 绘制误差曲线和参数theta变化
#绘制误差曲线
pl.plot(range(len(errors)),errors)
pl.xlabel(u’迭代次数’)
pl.ylabel(u’代价函数’)
pl.show()
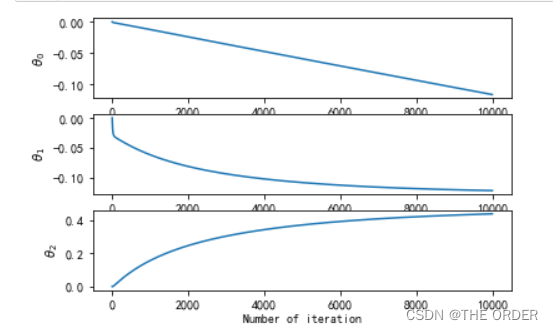
#绘制参数theta变化
thetasFig,ax=pl.subplots(len(thetas[0]))
thetas=np.asarray(thetas)
for idx,sp in enumerate(ax):
thetaList=thetas[:,idx]
sp.plot(range(len(thetaList)),thetaList)
sp.set_xlabel('Number of iteration')
sp.set_ylabel(r'$\theta_%d$'%idx)
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)