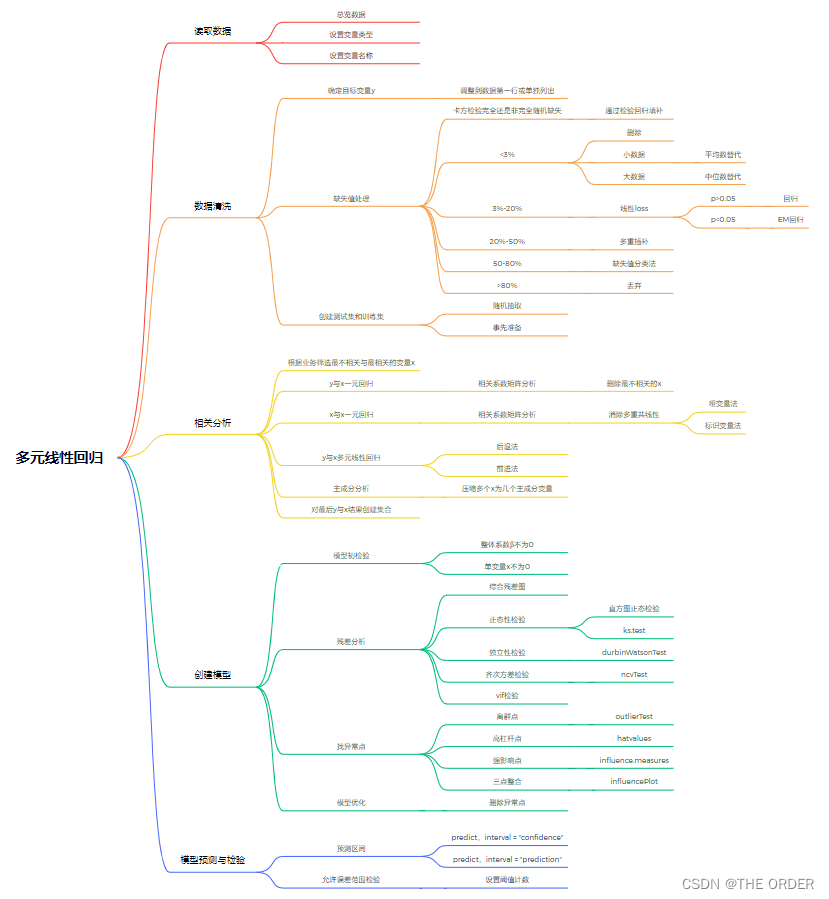
python数据分析多元 线性回归
本节是python实现多元回归的代码部分,理论参考链接: link.
代码下载地址link.
代码可直接赋值运行,如有问题请留言
本节使用的数据是收入与年龄,性别关系的多元线性回归
@[TOC](python数据分析多元 线性回归)
1 基本环境设置
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']='SimHei' #画图正常显示中文
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='sans-serif'
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
2 读取数据加载
def loadDataset(filename):
X=[]
Y=[]
with open(filename,'rb') as f:
for idx,line in enumerate(f):
line=line.decode('utf-8').strip()
if not line:
continue
eles=line.split(',')
if idx==0:
numFea=len(eles)
eles=list(map(float,eles))#map返回一个迭代对象
X.append(eles[:-1])
Y.append([eles[-1]])
return np.array(X),np.array(Y)
预览下数据,数据是如下图所示
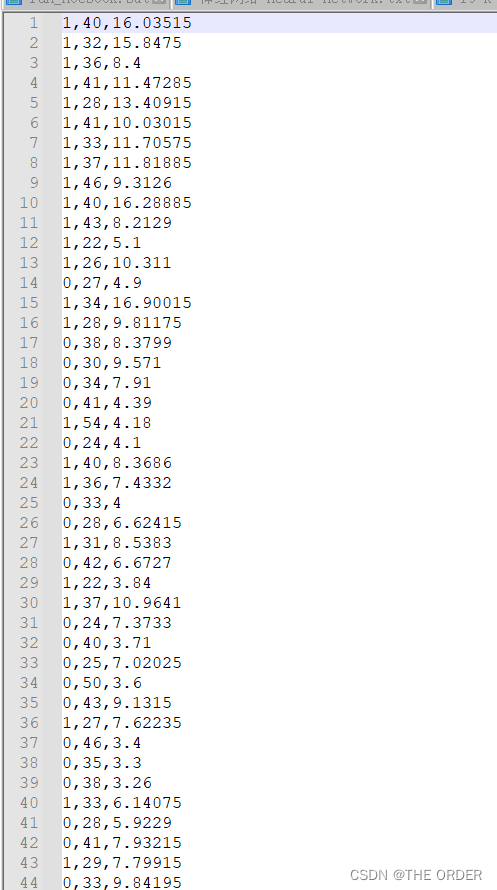
第一列性别,第二列年龄,第三列收入
3 y预估方法与误差方法设计
y 估计方法
def h(theta,X):
return np.dot(X,theta)
误差和估计
def J(theta,X,Y):
return np.sum(np.dot((h(theta,X)-Y).T,(h(theta,X)-Y))/(2*m))
4 梯度下降设计
def bgd(alpha,maxloop,epsilon,X,Y):
m,n=X.shape
theta=np.zeros((n,1))
count=0
converged=False
error=np.inf
errors=[J(theta,X,Y),]
thetas={}
for i in range(n):
thetas[i]=[theta[i,0],]
while count<=maxloop:
if(converged):
break
count=count+1
for j in range(n):
deriv=np.dot(X[:,j].T,(h(theta,X)-Y)).sum()/m
thetas[j].append(theta[j,0]-alpha*deriv)
for j in range(n):
theta[j,0]=thetas[j][-1]
error=J(theta,X,Y)
errors.append(error)
if(abs(errors[-1]-errors[-2])<epsilon):
converged=True
return theta,errors,thetas
5 数据处理
这里的数据没有异常值,缺失值。在R部分也讲过缺失值核异常值的处理,盖帽法填补,删除,或spss回归,knn填补
def standarize(X):
"""特征标准化处理
Args:
X 样本集
Returns:
标准化后的样本集
"""
m,n=X.shape
#归一化每一个特征
for j in range(n):
features=X[:,j]
meanVal=features.mean(axis=0)
std=features.std(axis=0)
if std!=0:
X[:,j]=(features-meanVal)/std
else:
X[:,j]=0
return X
读取属于与预览维度
ori_X,Y=loadDataset(’./data/income.csv’)
print(ori_X.shape)
print(Y.shape)
结果如下:
(100, 2)
(100, 1)
6 模型运行
m,n=ori_X.shape
X=standarize(ori_X.copy())
X=np.concatenate((np.ones((m,1)),X),axis=1)
alpha=0.3
maxloop=5000
epsilon=0.0000000000000001
result=bgd(alpha,maxloop,epsilon,X,Y)
theta,errors,thetas=result
print(errors)
print(theta)
结果如下:
[24.33730066195, 13.505993103864864, 8.227069671967811, 5.646107653055884, 4.380348621596483, 3.7577018007906924, 3.450468610785003, 3.2983894621721754, 3.2228610964245137, 3.1852188396658816, 3.166387845485983, 3.1569292252947605, 3.152157461763612, 3.149738790112871, 3.1485065999017103, 3.1478754430280538, 3.1475502771380808, 3.147381731762091, 3.147293811506613, 3.1472476466986463, 3.14722324380204, 3.1472102569749523, 3.147203299011644, 3.1471995464497224, 3.1471975096191853, 3.1471963972545858, 3.1471957862237945, 3.147195448748745, 3.1471952614181884, 3.147195156950363, 3.147195098447062, 3.147195065560232, 3.1471950470106522, 3.1471950365163703, 3.1471950305635144, 3.147195027178879, 3.1471950252505327, 3.1471950241499296, 3.147195023520792, 3.147195023160675, 3.1471950229543095, 3.147195022835933, 3.147195022767972, 3.1471950227289267, 3.147195022706478, 3.1471950226935674, 3.1471950226861374, 3.147195022681859, 3.1471950226793957, 3.1471950226779772, 3.1471950226771592, 3.147195022676689, 3.147195022676417, 3.14719502267626, 3.1471950226761694, 3.1471950226761174, 3.147195022676087, 3.1471950226760703, 3.147195022676061, 3.1471950226760543, 3.147195022676051, 3.1471950226760494, 3.147195022676048, 3.147195022676048]
[[ 6.142094 ]
[ 2.16407412]
[-0.03431546]]
7 模型可视化
使用的是三维绘图
%matplotlib
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
from matplotlib import cm
import matplotlib.ticker as mtick
fittingFig=pl.figure(figsize=(16,12))
title='bgd:rate=%.3f,maxloop=%d,epsilon=%.3f \n'%(alpha,maxloop,epsilon)
ax=fittingFig.gca(projection='3d')
xx=np.linspace(0,1,100)
yy=np.linspace(0,100,100)
zz=np.zeros((100,100))
for i in range(100):
for j in range(100):
normalizegender=(xx[i]-ori_X[:,0].mean(0))/ori_X[:,0].std(0)
normalizeAge=(yy[j]-ori_X[:,1].mean(0))/ori_X[:,1].std(0)
x=np.matrix([[1,normalizegender,normalizeAge]])
zz[i,j]=h(theta,x)
xx,yy=np.meshgrid(xx,yy)
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(mtick.FormatStrFormatter('%.2e'))
ax.plot_surface(xx,yy,zz,rstride=1,cstride=1,cmap=cm.rainbow,alpha=0.1,antialiased=True)
xs=ori_X[:,0].flatten()
ys=ori_X[:,1].flatten()
zs=Y[:,0].flatten()
ax.scatter(xs,ys,zs,c='b',marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(u'性别')
ax.set_ylabel(u'年龄')
ax.set_zlabel(u'收入')
可以发现模型的平面将数据按照维度较好拟合
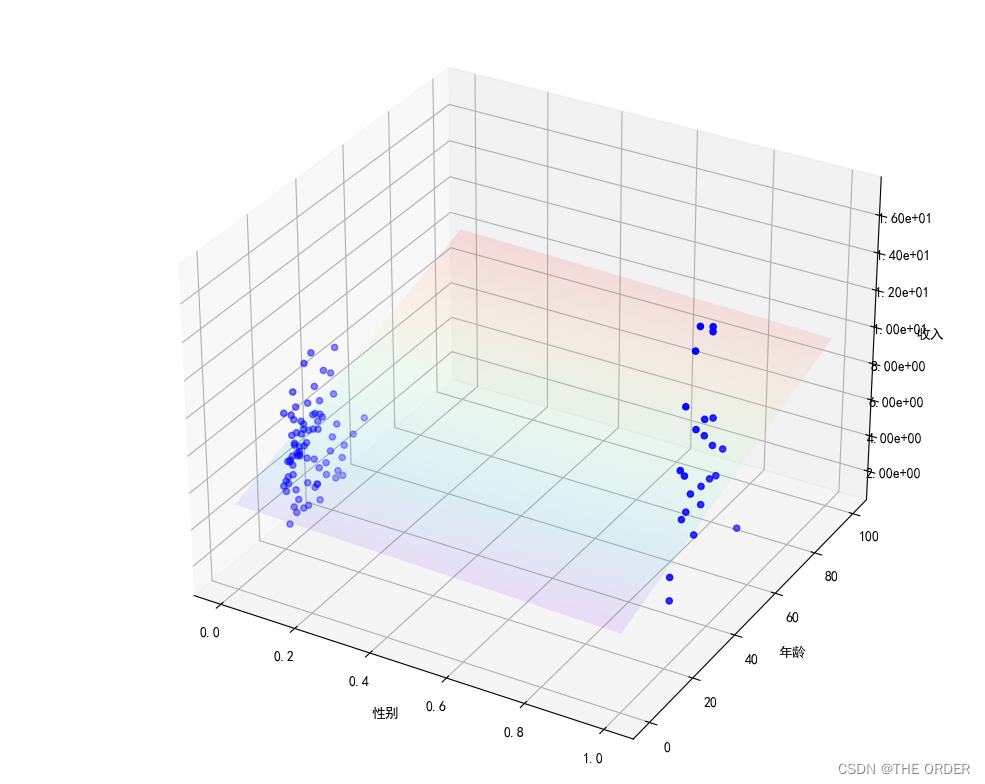
8 误差绘图
%matplotlib inline
errorsFig=pl.figure()
ax=errorsFig.add_subplot(111)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(mtick.FormatStrFormatter('%.2e'))
pl.plot(range(len(errors)),errors)
pl.xlabel(u'迭代次数')
pl.ylabel(u'代价函数')
pl.show()
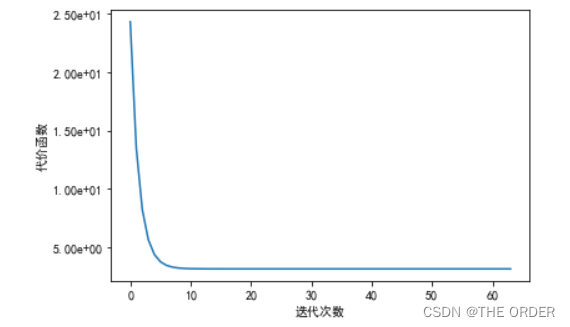
链接: link.
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)