Python调用VBA事件编程监控Excel
📢博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
📢欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 欢迎讨论!
📢本文由 小小明-代码实体 原创,首发于 CSDN🙉
今天我要演示的是如何使用Python监控Excel,并通过Excel事件编程实现一些有意思的效果。
首先,我们看看如何用Python打开Excel程序:
Python连接Excel应用程序详解
首先导入pywin32:
import win32com.client as win32
- 1
打开一个新的Excel程序有以下两种方法:
xlApp = win32.Dispatch("Excel.Application")
# 或
xlApp2 = win32.gencache.EnsureDispatch('Excel.Application')
- 1
- 2
- 3
这两者是否存储区别呢?
如果我们第一次运行:
xlApp = win32.Dispatch("Excel.Application")
xlApp
- 1
- 2
<COMObject Excel.Application>
- 1
可以看到是一个原生的COM对象。
如果运行:
xlApp = win32.gencache.EnsureDispatch('Excel.Application')
xlApp
- 1
- 2
<win32com.gen_py.Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library._Application instance at 0x2503324458952>
- 1
可以看到是gen_py的包装对象。
在此之后再重新以win32.Dispatch形式运行,发现获取的也是win32com.gen_py.Microsoft对象。
win32.gencache.EnsureDispatch相对win32.Dispatch区别在于是否执行Lib\site-packages\win32com\client\makepy.py,该脚本会在C:\Users\ASUS\AppData\Local\Temp\gen_py\3.7(ASUS为当前windows文件名,3.7为当前python版本)生成相应的缓存文件:
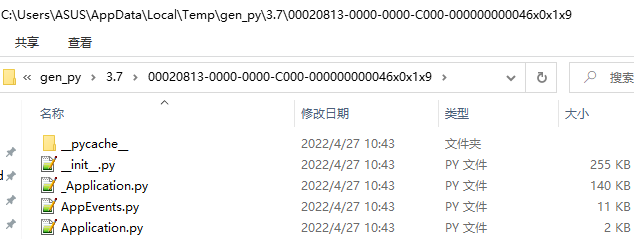
只要该缓存已经存在以后,win32.Dispatch也会为COM对象返回MakePy支持的包装器。
参考:《 Python Programming on Win32》的第12章:Advanced Python and COM
有一次我执行以上连接代码发生了报错,是因为我WPS的某个版本更改了本地EXCEL com组件的注册,导致原先生成的gen_py与目前注册的版本不一样。这个时候我们只需要删除上面的缓存目录并重新生成即可,除了手工删除外,还可以通过代码删除:
import os
import shutil
shutil.rmtree(os.path.join(os.environ.get('LOCALAPPDATA'), 'Temp', 'gen_py'))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
不过MakePy支持的包装器所预制的方法并不全面,所以我们在使用pywin32调用VBA时,不应该依赖Python的代码提示,而是依靠微软的VBA的官方文档:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/office/vba/api/overview/excel
以上两个方法在使用时并没有差别,但都有可能在已经打开Excel文件时,额外打开多余的Excel程序。还有一个方法可以获取已经打开的Excel对象:
xlApp = win32.GetActiveObject('Excel.Application')
- 1
在没有打开任何Excel程序时会报出:com_error: (-2147221021, '操作无法使用', None, None)类似的错误。而在Excel已经运行时,xlApp会打印出:<win32com.gen_py.None.Application>或<COMObject Excel.Application>(取决于gen_py目录下是否存在缓存)。
为Excel应用添加事件监控
上面我们通过pywin32获取到了Excel的Application对象,该对象表示一个Excel应用,它所支持的事件可以通过微软官网查看:
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/office/vba/api/overview/excel
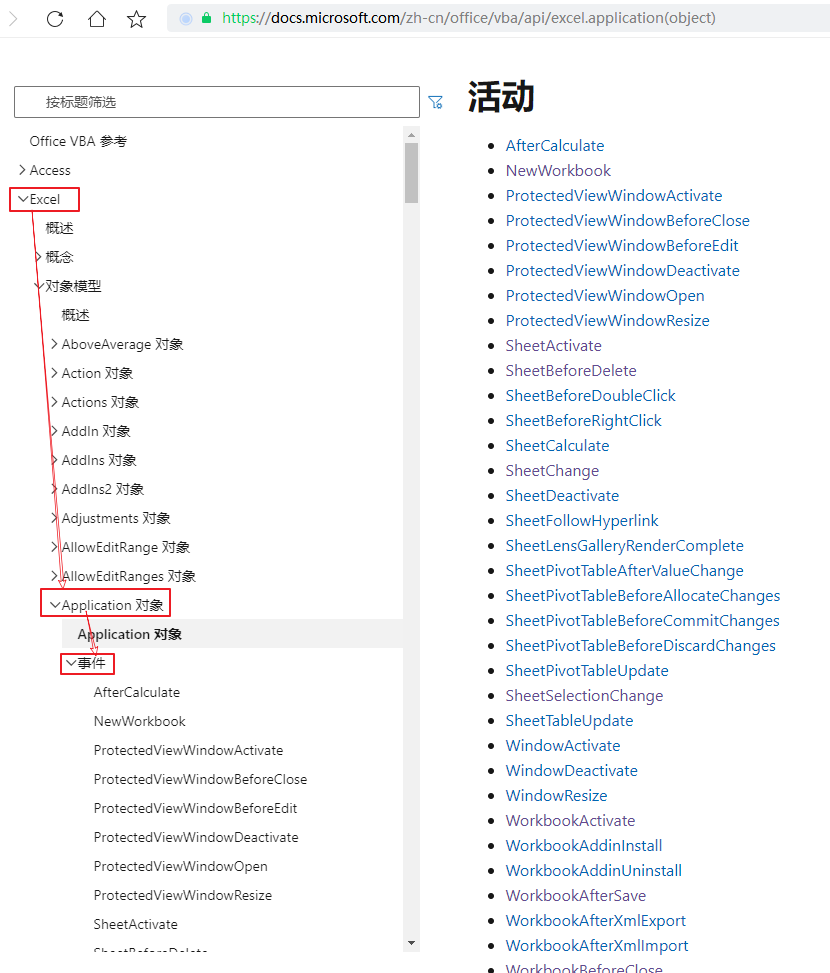
根据支持的事件,我编写了如下代码:
class ApplicationEvents:
def OnWorkbookActivate(self, wb):
print("激活工作簿:", wb.Name)
def OnNewWorkbook(self, wb):
print("新建工作簿:", wb.Name)
def OnSheetActivate(self, sheet):
print(f"激活工作表:", sheet.Name)
def OnSheetSelectionChange(self, sheet, target):
print(f"选中了{target.Address}")
def OnSheetChange(self, sheet, target):
if target.Count == 1:
print(f"修改{target.Address}为内容为{target.Value}")
else:
print(f"{target.Address}区域被批量修改")
def OnSheetBeforeDelete(self, sh):
print("删除sheet:", sh.Name)
def OnWorkbookBeforeClose(self, wb, cancel):
print("关闭工作簿:", wb.Name)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
ApplicationEvents这个类名任意,只要把这个类与Application对象绑定,就表示是Application对象的事件处理器。
然后定义需要处理的事件的方法,在Python上每个方法名需要以 On+事件名 的形式命名,例如对于NewWorkbook事件的处理,对应的方法名为OnNewWorkbook。
绑定事件处理器只需:
win32.WithEvents(xlApp, ApplicationEvents)
- 1
如果我们还需要监控新建工作表的事件,则需要针对工作簿对象绑定事件处理器,因为Application对象没有针对新建工作表的事件:
class WookbookEvents:
def OnNewSheet(self, sh):
print("新建sheet:", sh.Name)
workbook = xlApp.ActiveWorkbook
win32.WithEvents(workbook, WookbookEvents)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
完整监控示例:
"""
小小明的代码
CSDN主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
"""
__author__ = '小小明'
__time__ = '2022/4/26'
import pythoncom
import win32com.client as win32
class ApplicationEvents:
def OnWorkbookActivate(self, wb):
print("激活工作簿:", wb.Name)
def OnNewWorkbook(self, wb):
print("新建工作簿:", wb.Name)
def OnSheetActivate(self, sheet):
print(f"激活工作表:", sheet.Name)
def OnSheetSelectionChange(self, sheet, target):
print(f"选中了{target.Address}")
def OnSheetChange(self, sheet, target):
if target.Count == 1:
print(f"修改{target.Address}为内容为{target.Value}")
else:
print(f"{target.Address}区域被批量修改")
def OnSheetBeforeDelete(self, sh):
print("删除sheet:", sh.Name)
def OnWorkbookBeforeClose(self, wb, cancel):
print("关闭工作簿:", wb.Name)
class WookbookEvents:
def OnNewSheet(self, sh):
print("新建sheet:", sh.Name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取已经启动的Excel应用程序
xlApp = win32.GetActiveObject('Excel.Application')
win32.WithEvents(xlApp, ApplicationEvents)
workbook = xlApp.ActiveWorkbook
win32.WithEvents(workbook, WookbookEvents)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
大家可以在已经打开Excel的情况启动上述代码,于是可以看到监控Excel使用情况的效果。
事件编程实现点击颜色设置
下面我们看看有关事件编程的实用例子。
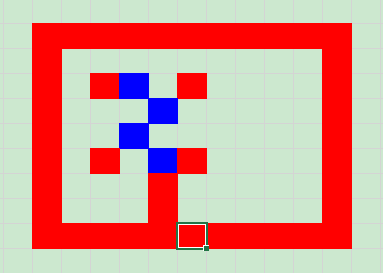
示例1:点击Excel任意单元格左键单击标红,双击取消颜色,右击标蓝。
"""
小小明的代码
CSDN主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
"""
__author__ = '小小明'
__time__ = '2022/4/26'
import pythoncom
import win32com.client as win32
class ApplicationEvents:
def OnSheetSelectionChange(self, sheet, target):
target.Interior.Color = 255
def OnSheetBeforeRightClick(self, sht, target, cancel):
target.Interior.Color = -4142
def OnSheetBeforeDoubleClick(self, sht, target, cancel):
target.Interior.Color = int("FF0000", 16)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取已经启动的Excel应用程序
xlApp = win32.GetActiveObject('Excel.Application')
win32.WithEvents(xlApp, ApplicationEvents)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
在运行以上代码后,Excel被单击或选中的位置会变红,双击则会变蓝:
示例2:实现WPS的阅读模式的效果,即:
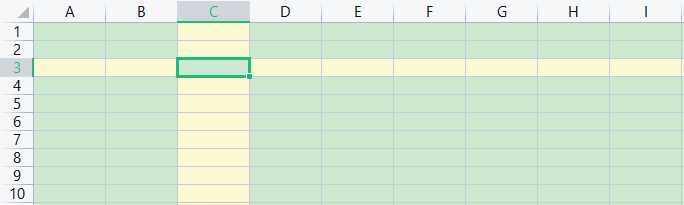
选中的单元格的对应行和列进行高亮显示。
"""
小小明的代码
CSDN主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
"""
__author__ = '小小明'
__time__ = '2022/4/26'
import pythoncom
import win32com.client as win32
class ApplicationEvents:
def OnSheetSelectionChange(self, sheet, target):
sheet.Cells.Interior.Color = -4142
target.EntireRow.Interior.Color = 13826554
target.EntireColumn.Interior.Color = 13826554
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取已经启动的Excel应用程序
xlApp = win32.GetActiveObject('Excel.Application')
win32.WithEvents(xlApp, ApplicationEvents)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
office中的效果:
事件编程实现表内级联跳转
素材取自:全民一起VBA-杨老师课堂\提高篇-38课时\第二十二回.巧用事件实现自动跳转
VBA事件编程结合Python更适合制作一些对Excel进行监控的程序,如果要开发工作簿或工作表级别的事件编程则直接在Excel里面使用VBA方便。
下面我们看看一个级联跳转的示例,数据如下:
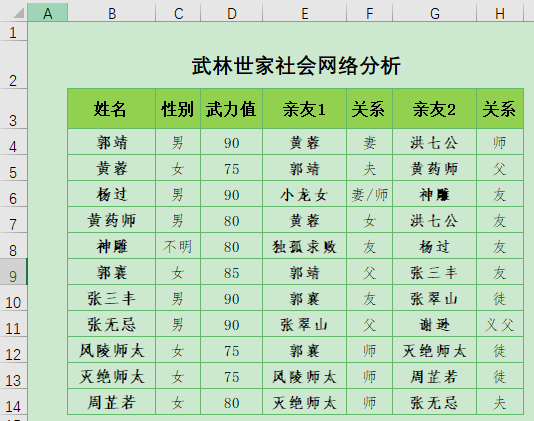
现在要求在点击亲友1或亲友2这两列的姓名时,选中位置自动跳转到姓名列对应的位置。
将该素材保存为xlam格式后打开VBE编写VBA代码:
最终编写的纯VBA代码为:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim r As Range, cell As Range
' 选中区域的左上角的单元格
Set r = Target.Cells(1, 1)
If r.Row > 3 Or (r.Column = 5 Or r.Column = 7) Then
For Each cell In [B4:B14]
If Trim(cell.Value) = Trim(r.Value) Then
Application.EnableEvents = False
cell.Select
Application.EnableEvents = True
Exit For
End If
Next
End If
End Sub
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
以上纯VBA代码对于使用者来说使用方便,但是对于Python开发者来说编写起来了麻烦了许多,如果以上功能是提供给熟悉python的童鞋使用,我们直接使用Python开发也会更简单。
Python实现:
"""
小小明的代码
CSDN主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
"""
__author__ = '小小明'
__time__ = '2022/4/26'
import pythoncom
import win32com.client as win32
class ApplicationEvents:
def OnSheetSelectionChange(self, sheet, target):
r = target.Cells(1, 1)
if r.Row < 4 or r.Row > 14 or r.Column not in (5, 7):
return
for cell in sheet.Range("B4:B14"):
if cell.Value.strip() == r.Value.strip():
xlApp.EnableEvents = False
cell.Select()
xlApp.EnableEvents = True
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取已经启动的Excel应用程序
xlApp = win32.GetActiveObject('Excel.Application')
win32.WithEvents(xlApp, ApplicationEvents)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
但是上述代码有个问题,假如我们需要修改亲友1 或 亲友2 列的数据会出现难以修改的情况,因为每次单击都自动跳转了。我的解决方案是先添加一个ActiveX的复选框控件:
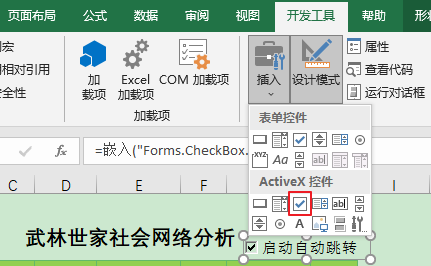
修改控件的名称和标题后关闭设计模式:
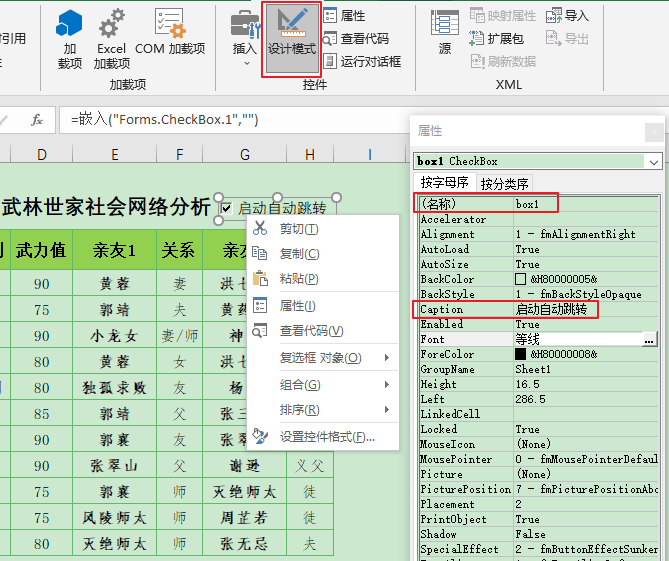
然后vba代码添加对控件值的判断:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim r As Range, cell As Range
' 选中区域的左上角的单元格
Set r = Target.Cells(1, 1)
If box1.Value And (r.Row > 3 Or (r.Column = 5 Or r.Column = 7)) Then
For Each cell In [B4:B14]
If Trim(cell.Value) = Trim(r.Value) Then
Application.EnableEvents = False
cell.Select
Application.EnableEvents = True
Exit For
End If
Next
End If
End Sub
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
可惜本人并没有研究出通过python访问Excel中的ActiveX控件属性的方法,于是我将上述ActiveX控件的复选框更换为普通的表单控件:
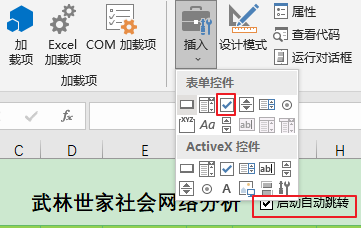
此时VBA代码应更新为:
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim r As Range, cell As Range
' 选中区域的左上角的单元格
Set r = Target.Cells(1, 1)
If ActiveSheet.CheckBoxes(1).Value = 1 And (r.Row > 3 Or (r.Column = 5 Or r.Column = 7)) Then
For Each cell In [B4:B14]
If Trim(cell.Value) = Trim(r.Value) Then
Application.EnableEvents = False
cell.Select
Application.EnableEvents = True
Exit For
End If
Next
End If
End Sub
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
对应的python实现:
"""
小小明的代码
CSDN主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
"""
__author__ = '小小明'
__time__ = '2022/4/26'
import pythoncom
import win32com.client as win32
class ApplicationEvents:
def OnSheetSelectionChange(self, sheet, target):
r = target.Cells(1, 1)
if sheet.CheckBoxes(1).Value != 1 or r.Row < 4 or r.Row > 14 or r.Column not in (5, 7):
return
for cell in sheet.Range("B4:B14"):
if cell.Value.strip() == r.Value.strip():
xlApp.EnableEvents = False
cell.Select()
xlApp.EnableEvents = True
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 获取已经启动的Excel应用程序
xlApp = win32.GetActiveObject('Excel.Application')
win32.WithEvents(xlApp, ApplicationEvents)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
数据:https://gitcode.net/as604049322/vba
文章来源: xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net,作者:小小明-代码实体,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net/article/details/124457082
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)