优达学城深度学习之六——TensorFlow卷积神经网络
TensorFlow卷积层
TensorFlow 提供了 tf.nn.conv2d() 和 tf.nn.bias_add() 函数来创建你自己的卷积层。
-
# Output depth
-
k_output = 64
-
-
# Image Properties
-
image_width = 10
-
image_height = 10
-
color_channels = 3
-
-
# Convolution filter
-
filter_size_width = 5
-
filter_size_height = 5
-
-
# Input/Image
-
input = tf.placeholder(
-
tf.float32,
-
shape=[None, image_height, image_width, color_channels])
-
-
# Weight and bias
-
weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(
-
[filter_size_height, filter_size_width, color_channels, k_output]))
-
bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(k_output))
-
-
# Apply Convolution
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.conv2d(input, weight, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
-
# Add bias
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.bias_add(conv_layer, bias)
-
# Apply activation function
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.relu(conv_layer)
TensorFlow最大池化提供函数:tf.nn.max_pool()
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.conv2d(input, weight, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.bias_add(conv_layer, bias)
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.relu(conv_layer)
-
# Apply Max Pooling
-
conv_layer = tf.nn.max_pool(
-
conv_layer,
-
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
-
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
-
padding='SAME')
tf.nn.max_pool() 函数实现最大池化时, ksize参数是滤波器大小,strides参数是步长。2x2 的滤波器配合 2x2 的步长是常用设定。
ksize 和 strides 参数也被构建为四个元素的列表,每个元素对应 input tensor 的一个维度 ([batch, height, width, channels]),对 ksize 和 strides 来说,batch 和 channel 通常都设置成 1
注意:池化层的输出深度与输入的深度相同。另外池化操作是分别应用到每一个深度切片层。
池化对应的代码:
-
input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, 4, 4, 5))
-
filter_shape = [1, 2, 2, 1]
-
strides = [1, 2, 2, 1]
-
padding = 'VALID'
-
pool = tf.nn.max_pool(input, filter_shape, strides, padding)
pool 的输出维度是 [1, 2, 2, 5],即使把 padding 改成 'SAME' 也是一样。
TensorFlow中的卷积神经网络
你从之前的课程中见过这节课的代码。这里我们导入 MNIST 数据集,用一个方便的函数完成对数据集的 batch,scale 和 One-Hot编码。
-
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
-
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(".", one_hot=True, reshape=False)
-
-
import tensorflow as tf
-
-
# Parameters
-
# 参数
-
learning_rate = 0.00001
-
epochs = 10
-
batch_size = 128
-
-
# Number of samples to calculate validation and accuracy
-
# Decrease this if you're running out of memory to calculate accuracy
-
# 用来验证和计算准确率的样本数
-
# 如果内存不够,可以调小这个数字
-
test_valid_size = 256
-
-
# Network Parameters
-
# 神经网络参数
-
n_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
-
dropout = 0.75 # Dropout, probability to keep units
-
Weights and Biases
-
# Store layers weight & bias
-
weights = {
-
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 1, 32])),
-
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 32, 64])),
-
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64, 1024])),
-
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, n_classes]))}
-
-
biases = {
-
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([32])),
-
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64])),
-
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
-
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))}
-
def conv2d(x,w,b,strides=1):
-
x=tf.nn.conv2d(tf.Variable(x,w,strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='SAME')
-
x=tf.nn.add_add(x,b)
-
return tf.nn.relu(x)
在 TensorFlow 中,strides 是一个4个元素的序列;第一个位置表示 stride 的 batch 参数,最后一个位置表示 stride 的特征(feature)参数。最好的移除 batch 和特征(feature)的方法是你直接在数据集中把他们忽略,而不是使用 stride。要使用所有的 batch 和特征(feature),你可以把第一个和最后一个元素设成1。
中间两个元素指纵向(height)和横向(width)的 stride,之前也提到过 stride 通常是正方形,height = width。当别人说 stride 是 3 的时候,他们意思是 tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 3, 3, 1])。
为了更简洁,这里的代码用了tf.nn.bias_add() 来添加偏置。 tf.add() 这里不能使用,因为 tensors 的维度不同。
模型建立
-
def conv_net(x, weights, biases, dropout):
-
# Layer 1 - 28*28*1 to 14*14*32
-
conv1 = conv2d(x, weights['wc1'], biases['bc1'])
-
conv1 = maxpool2d(conv1, k=2)
-
-
# Layer 2 - 14*14*32 to 7*7*64
-
conv2 = conv2d(conv1, weights['wc2'], biases['bc2'])
-
conv2 = maxpool2d(conv2, k=2)
-
-
# Fully connected layer - 7*7*64 to 1024
-
fc1 = tf.reshape(conv2, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
-
fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['wd1']), biases['bd1'])
-
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
-
fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1, dropout)
-
-
# Output Layer - class prediction - 1024 to 10
-
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['out']), biases['out'])
-
return out
session运行
-
# tf Graph input
-
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 28, 28, 1])
-
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
-
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
-
-
# Model
-
logits = conv_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)
-
-
# Define loss and optimizer
-
cost = tf.reduce_mean(\
-
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y))
-
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)\
-
.minimize(cost)
-
-
# Accuracy
-
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
-
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
-
-
# Initializing the variables
-
init = tf. global_variables_initializer()
-
-
# Launch the graph
-
with tf.Session() as sess:
-
sess.run(init)
-
-
for epoch in range(epochs):
-
for batch in range(mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size):
-
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
-
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={
-
x: batch_x,
-
y: batch_y,
-
keep_prob: dropout})
-
-
# Calculate batch loss and accuracy
-
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={
-
x: batch_x,
-
y: batch_y,
-
keep_prob: 1.})
-
valid_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
-
x: mnist.validation.images[:test_valid_size],
-
y: mnist.validation.labels[:test_valid_size],
-
keep_prob: 1.})
-
-
print('Epoch {:>2}, Batch {:>3} -'
-
'Loss: {:>10.4f} Validation Accuracy: {:.6f}'.format(
-
epoch + 1,
-
batch + 1,
-
loss,
-
valid_acc))
-
-
# Calculate Test Accuracy
-
test_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
-
x: mnist.test.images[:test_valid_size],
-
y: mnist.test.labels[:test_valid_size],
-
keep_prob: 1.})
-
print('Testing Accuracy: {}'.format(test_acc))
使用tensor做卷积
让我们用所学知识在 TensorFlow 里构建真的 CNNs。在下面的练习中,你需要设定卷积核滤波器(filters)的维度,weight,bias。这在很大程度上来说是 TensorFlow CNNs 最难的部分。一旦你知道如何设置这些属性的大小,应用 CNNs 会很方便。
这些也是需要你回顾的:
- TensorFlow 变量。
- Truncated 正态分布 - 在 TensorFlow 中你需要在一个正态分布的区间中初始化你的权值。
-
根据输入大小、滤波器大小,来决定输出维度(如下所示)。你用这个来决定滤波器应该是什么样:
-
new_height = (input_height - filter_height + 2 * P)/S + 1
-
new_width = (input_width - filter_width + 2 * P)/S + 1
-
"""
-
Setup the strides, padding and filter weight/bias such that
-
the output shape is (1, 2, 2, 3).
-
"""
-
import tensorflow as tf
-
import numpy as np
-
-
# `tf.nn.conv2d` requires the input be 4D (batch_size, height, width, depth)
-
# (1, 4, 4, 1)
-
x = np.array([
-
[0, 1, 0.5, 10],
-
[2, 2.5, 1, -8],
-
[4, 0, 5, 6],
-
[15, 1, 2, 3]], dtype=np.float32).reshape((1, 4, 4, 1))
-
X = tf.constant(x)
-
-
-
def conv2d(input):
-
# Filter (weights and bias)
-
# The shape of the filter weight is (height, width, input_depth, output_depth)
-
# The shape of the filter bias is (output_depth,)
-
# TODO: Define the filter weights `F_W` and filter bias `F_b`.
-
# NOTE: Remember to wrap them in `tf.Variable`, they are trainable parameters after all.
-
F_W = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal((2,2,1,3)))
-
F_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(3))
-
# TODO: Set the stride for each dimension (batch_size, height, width, depth)
-
strides = [1, 2, 2, 1]
-
# TODO: set the padding, either 'VALID' or 'SAME'.
-
padding = 'VALID'
-
# https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r0.11/api_docs/python/nn.html#conv2d
-
# `tf.nn.conv2d` does not include the bias computation so we have to add it ourselves after.
-
return tf.nn.conv2d(input, F_W, strides, padding) + F_b
-
-
out = conv2d(X)
-
在TensorFlow使用池化层
-
"""
-
Set the values to `strides` and `ksize` such that
-
the output shape after pooling is (1, 2, 2, 1).
-
"""
-
import tensorflow as tf
-
import numpy as np
-
-
# `tf.nn.max_pool` requires the input be 4D (batch_size, height, width, depth)
-
# (1, 4, 4, 1)
-
x = np.array([
-
[0, 1, 0.5, 10],
-
[2, 2.5, 1, -8],
-
[4, 0, 5, 6],
-
[15, 1, 2, 3]], dtype=np.float32).reshape((1, 4, 4, 1))
-
X = tf.constant(x)
-
-
def maxpool(input):
-
# TODO: Set the ksize (filter size) for each dimension (batch_size, height, width, depth)
-
ksize = [1, 2, 2, 1]
-
# TODO: Set the stride for each dimension (batch_size, height, width, depth)
-
strides = [1, 2, 2, 1]
-
# TODO: set the padding, either 'VALID' or 'SAME'.
-
padding = 'SAME'
-
# https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r0.11/api_docs/python/nn.html#max_pool
-
return tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize, strides, padding)
-
-
out = maxpool(X)
自编码器
自编码器是一种执行数据压缩的网络架构。其中压缩和解压功能是从数据本身学习来,而非人工设计的。一般思路如下:
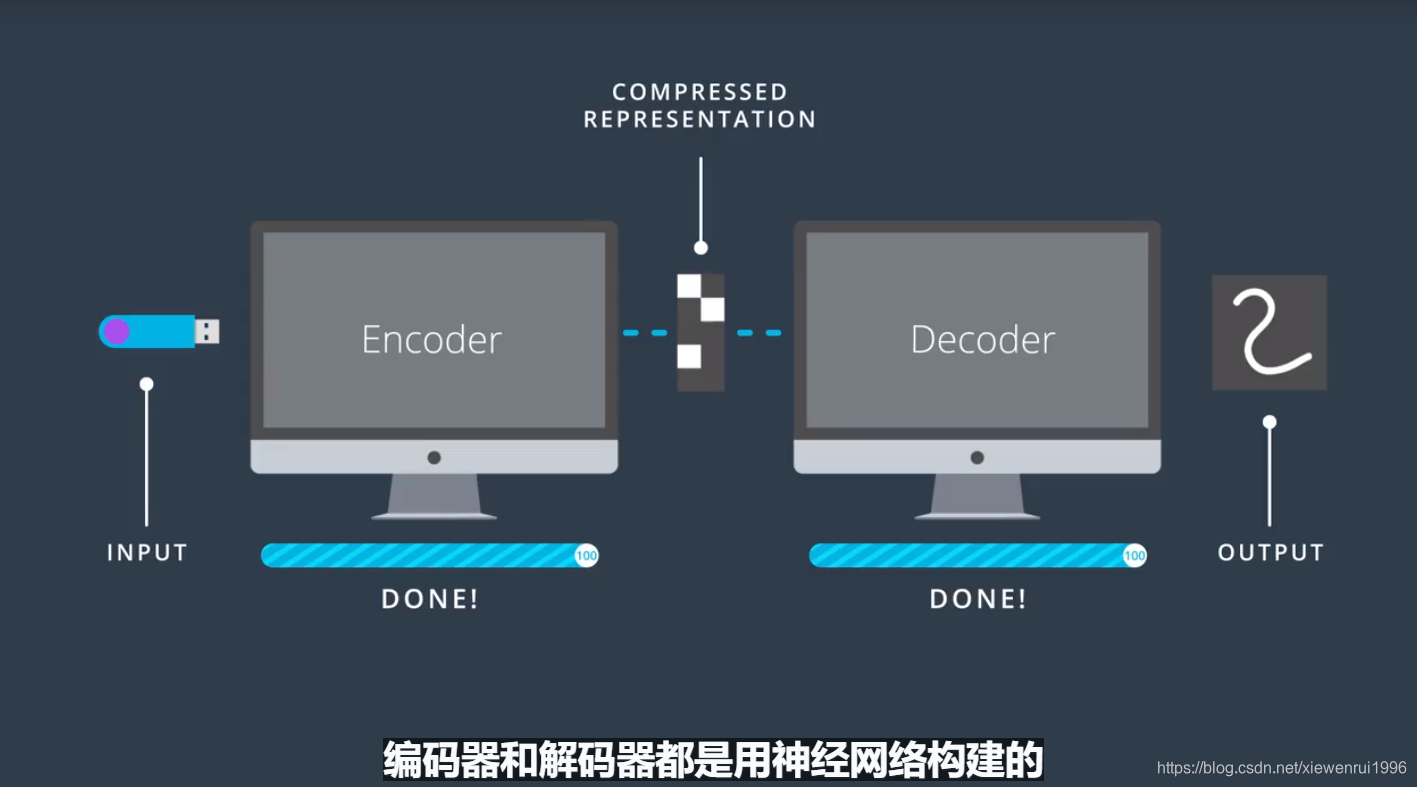
编码器一般用在图像降噪、JPG等文件中。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:小小谢先生,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/xiewenrui1996/article/details/89929940
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)