优达学城深度学习之五——卷积神经网络
【摘要】
梯度下降算法推导与实现
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimport pandas as pd #Some helper functions for plotting and drawing lines def plot_points(X, y): admit...
梯度下降算法推导与实现
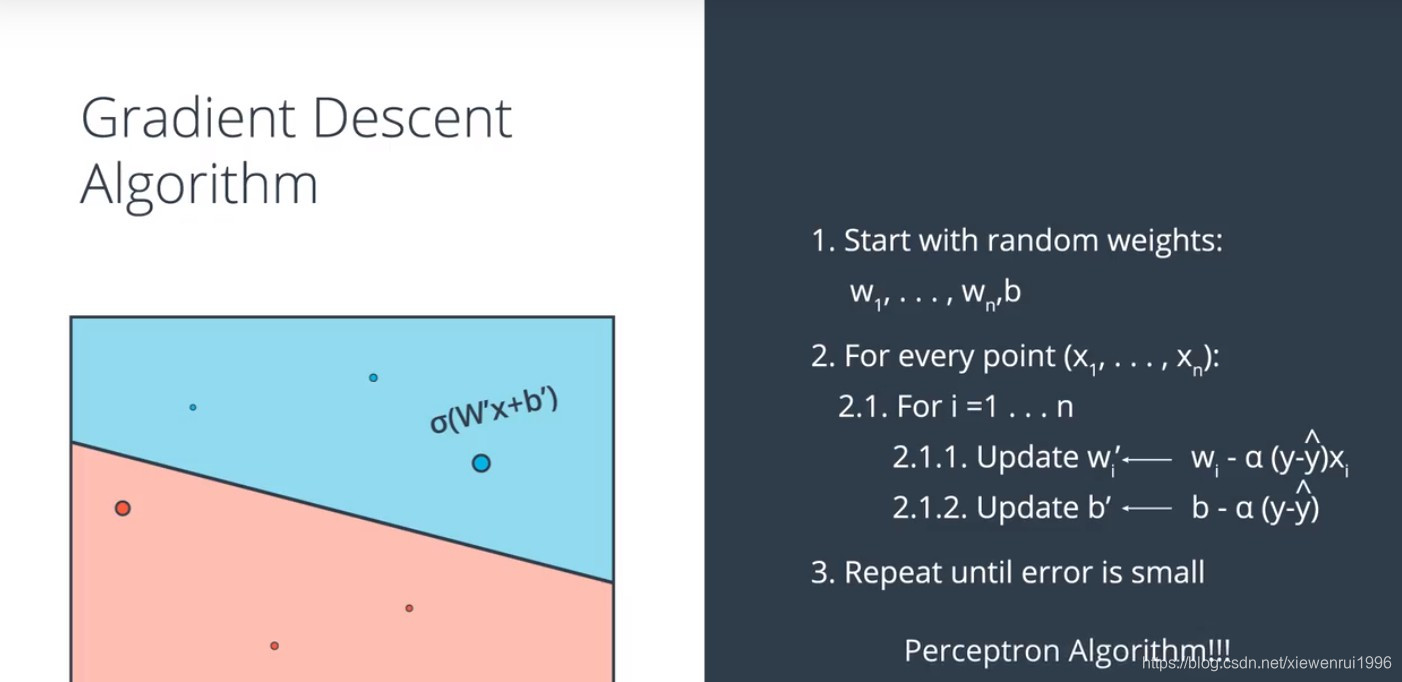
-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
import numpy as np
-
import pandas as pd
-
-
#Some helper functions for plotting and drawing lines
-
-
def plot_points(X, y):
-
admitted = X[np.argwhere(y==1)]
-
rejected = X[np.argwhere(y==0)]
-
plt.scatter([s[0][0] for s in rejected], [s[0][1] for s in rejected], s = 25, color = 'blue', edgecolor = 'k')
-
plt.scatter([s[0][0] for s in admitted], [s[0][1] for s in admitted], s = 25, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
-
-
def display(m, b, color='g--'):
-
plt.xlim(-0.05,1.05)
-
plt.ylim(-0.05,1.05)
-
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
-
plt.plot(x, m*x+b, color)
-
#读取与绘制数据
-
data = pd.read_csv('data.csv', header=None)
-
X = np.array(data[[0,1]])
-
y = np.array(data[2])
-
plot_points(X,y)
-
plt.show()
-
-
# Implement the following functions
-
-
# Activation (sigmoid) function
-
def sigmoid(x):
-
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
-
-
# Output (prediction) formula
-
def output_formula(features, weights, bias):
-
sigmoid(np.dot(features, weights) + bias)
-
-
# Error (log-loss) formula
-
def error_formula(y, output):
-
return - y*np.log(output) - (1 - y) * np.log(1-output)
-
-
# Gradient descent step
-
def update_weights(x, y, weights, bias, learnrate):
-
output = output_formula(x, weights, bias)
-
d_error = -(y - output)
-
weights -= learnrate * d_error * x
-
bias -= learnrate * d_error
-
return weights, bias
-
np.random.seed(44)
-
-
epochs = 100
-
learnrate = 0.01
-
-
def train(features, targets, epochs, learnrate, graph_lines=False):
-
-
errors = []
-
n_records, n_features = features.shape
-
last_loss = None
-
weights = np.random.normal(scale=1 / n_features**.5, size=n_features)
-
bias = 0
-
for e in range(epochs):
-
del_w = np.zeros(weights.shape)
-
for x, y in zip(features, targets):
-
output = output_formula(x, weights, bias)
-
error = error_formula(y, output)
-
weights, bias = update_weights(x, y, weights, bias, learnrate)
-
-
# Printing out the log-loss error on the training set
-
out = output_formula(features, weights, bias)
-
loss = np.mean(error_formula(targets, out))
-
errors.append(loss)
-
if e % (epochs / 10) == 0:
-
print("\n========== Epoch", e,"==========")
-
if last_loss and last_loss < loss:
-
print("Train loss: ", loss, " WARNING - Loss Increasing")
-
else:
-
print("Train loss: ", loss)
-
last_loss = loss
-
predictions = out > 0.5
-
accuracy = np.mean(predictions == targets)
-
print("Accuracy: ", accuracy)
-
if graph_lines and e % (epochs / 100) == 0:
-
display(-weights[0]/weights[1], -bias/weights[1])
-
# Plotting the solution boundary
-
plt.title("Solution boundary")
-
display(-weights[0]/weights[1], -bias/weights[1], 'black')
-
-
# Plotting the data
-
plot_points(features, targets)
-
plt.show()
-
-
# Plotting the error
-
plt.title("Error Plot")
-
plt.xlabel('Number of epochs')
-
plt.ylabel('Error')
-
plt.plot(errors)
-
plt.show()
-
#训练算法
-
train(X, y, epochs, learnrate, True)
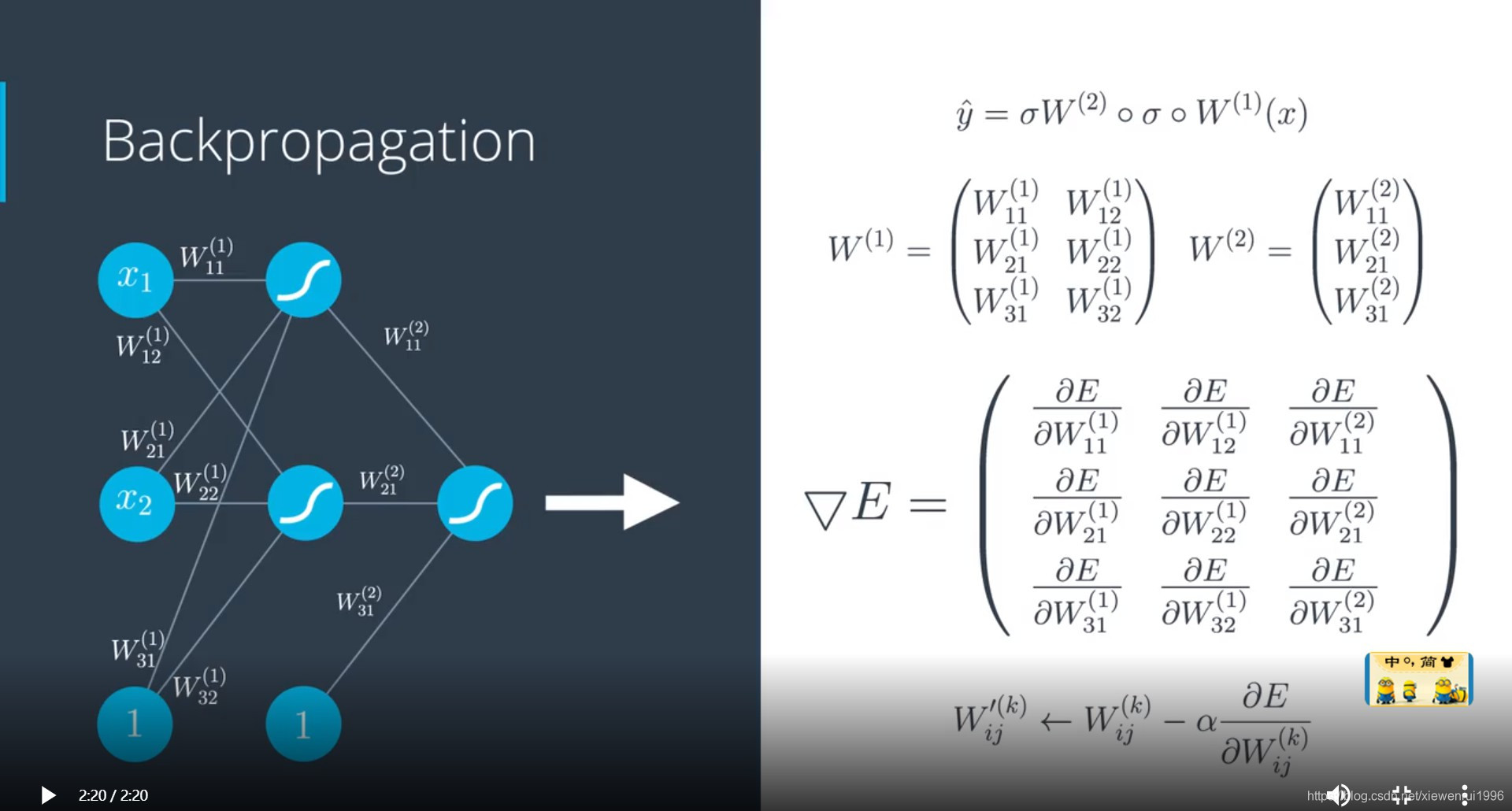
反向传播
反向传播流程如下:
- 进行前向反馈运算。
- 将模型的输出与期望的输出进行比较。
- 计算误差。
- 向后运行前向反馈运算(反向传播),将误差分散到每个权重上。
- 更新权重,并获得更好的模型。
- 继续此流程,直到获得很好的模型。
实战演练:利用神经网络来预测学生录取情况
数据集来源: http://www.ats.ucla.edu/
-
# Importing pandas and numpy
-
import pandas as pd
-
import numpy as np
-
-
# Reading the csv file into a pandas DataFrame
-
data = pd.read_csv('student_data.csv')
-
-
# Printing out the first 10 rows of our data
-
data[:10]
-
#绘制数据
-
# Importing matplotlib
-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
%matplotlib inline
-
# Function to help us plot
-
def plot_points(data):
-
X = np.array(data[["gre","gpa"]])
-
y = np.array(data["admit"])
-
admitted = X[np.argwhere(y==1)]
-
rejected = X[np.argwhere(y==0)]
-
plt.scatter([s[0][0] for s in rejected], [s[0][1] for s in rejected], s = 25, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
-
plt.scatter([s[0][0] for s in admitted], [s[0][1] for s in admitted], s = 25, color = 'cyan', edgecolor = 'k')
-
plt.xlabel('Test (GRE)')
-
plt.ylabel('Grades (GPA)')
-
-
# Plotting the points
-
plot_points(data)
-
plt.show()
-
# Separating the ranks
-
data_rank1 = data[data["rank"]==1]
-
data_rank2 = data[data["rank"]==2]
-
data_rank3 = data[data["rank"]==3]
-
data_rank4 = data[data["rank"]==4]
-
-
# Plotting the graphs
-
plot_points(data_rank1)
-
plt.title("Rank 1")
-
plt.show()
-
plot_points(data_rank2)
-
plt.title("Rank 2")
-
plt.show()
-
plot_points(data_rank3)
-
plt.title("Rank 3")
-
plt.show()
-
plot_points(data_rank4)
-
plt.title("Rank 4")
-
plt.show()
-
#将评级进行one-shot编码
-
# TODO: Make dummy variables for rank
-
one_hot_data = pd.concat([data, pd.get_dummies(data['rank'], prefix='rank')], axis=1)
-
-
# TODO: Drop the previous rank column
-
one_hot_data = one_hot_data.drop('rank', axis=1)
-
-
# Print the first 10 rows of our data
-
one_hot_data[:10]
-
#缩放数据
-
# Making a copy of our data
-
processed_data = one_hot_data[:]
-
-
# TODO: Scale the columns
-
processed_data['gre']=processed_data['gre']/800
-
processed_data['gpa']=processed_data['gpa']/4.0
-
-
# Printing the first 10 rows of our procesed data
-
processed_data[:10]
-
#将数据分成训练集和测试集
-
sample = np.random.choice(processed_data.index, size=int(len(processed_data)*0.9), replace=False)
-
train_data, test_data = processed_data.iloc[sample], processed_data.drop(sample)
-
-
print("Number of training samples is", len(train_data))
-
print("Number of testing samples is", len(test_data))
-
print(train_data[:10])
-
print(test_data[:10])
-
#将数据分成特征和目标
-
features = train_data.drop('admit', axis=1)
-
targets = train_data['admit']
-
features_test = test_data.drop('admit', axis=1)
-
targets_test = test_data['admit']
-
-
print(features[:10])
-
print(targets[:10])
-
#训练二层神经网络
-
Activation (sigmoid) function
-
def sigmoid(x):
-
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
-
def sigmoid_prime(x):
-
return sigmoid(x) * (1-sigmoid(x))
-
def error_formula(y, output):
-
return - y*np.log(output) - (1 - y) * np.log(1-output)
-
#误差反向传播
-
# TODO: Write the error term formula
-
def error_term_formula(y, output):
-
return (y-output)*sigmoid_prime(x)
-
def error_term_formula(x, y, output):
-
return (y-output) * output * (1 - output)
-
# Neural Network hyperparameters
-
epochs = 1000
-
learnrate = 0.5
-
-
# Training function
-
def train_nn(features, targets, epochs, learnrate):
-
-
# Use to same seed to make debugging easier
-
np.random.seed(42)
-
-
n_records, n_features = features.shape
-
last_loss = None
-
-
# Initialize weights
-
weights = np.random.normal(scale=1 / n_features**.5, size=n_features)
-
-
for e in range(epochs):
-
del_w = np.zeros(weights.shape)
-
for x, y in zip(features.values, targets):
-
# Loop through all records, x is the input, y is the target
-
-
# Activation of the output unit
-
# Notice we multiply the inputs and the weights here
-
# rather than storing h as a separate variable
-
output = sigmoid(np.dot(x, weights))
-
-
# The error, the target minus the network output
-
error = error_formula(y, output)
-
-
# The error term
-
# Notice we calulate f'(h) here instead of defining a separate
-
# sigmoid_prime function. This just makes it faster because we
-
# can re-use the result of the sigmoid function stored in
-
# the output variable
-
error_term = error_term_formula(x,y, output)
-
-
# The gradient descent step, the error times the gradient times the inputs
-
del_w += error_term * x
-
-
# Update the weights here. The learning rate times the
-
# change in weights, divided by the number of records to average
-
weights += learnrate * del_w / n_records
-
-
# Printing out the error on the training set
-
if e % (epochs / 10) == 0:
-
out = sigmoid(np.dot(features, weights))
-
loss = np.mean((out - targets) ** 2)
-
print("Epoch:", e)
-
if last_loss and last_loss < loss:
-
print("Train loss: ", loss, " WARNING - Loss Increasing")
-
else:
-
print("Train loss: ", loss)
-
last_loss = loss
-
print("=========")
-
print("Finished training!")
-
return weights
-
-
weights = train_nn(features, targets, epochs, learnrate)
-
#计算测试数据的准确度
-
# Calculate accuracy on test data
-
tes_out = sigmoid(np.dot(features_test, weights))
-
predictions = tes_out > 0.5
-
accuracy = np.mean(predictions == targets_test)
-
print("Prediction accuracy: {:.3f}".format(accuracy))
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:小小谢先生,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/xiewenrui1996/article/details/89856069
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)