必学框架新版SpringBoot教程(上集)
个人简介
作者是一个来自河源的大三在校生,以下笔记都是作者自学之路的一些浅薄经验,如有错误请指正,将来会不断的完善笔记,帮助更多的Java爱好者入门。
@[toc]
SpringBoot
创建SpringBoot项目报错的问题

遇到这个问题我们可以在Custom输入:https://start.springboot.io,这个是阿里云的SpringBoot镜像

生成SpringBoot项目


再点击Next,勾选自己需要的模块,这样SpringBoot项目就构建好了。
SpringBoot的Hello World
1.在resources目录下的templates放页面

2.必须把Java代码放在springBoot主程序同级的目录下(也就是当前的boot目录),不然springboot检测不到

3.controller层方法。

然后去访问这个路径就OK啦。

运行时的异常。-datasource

很显然可以看出这是关于数据源的异常,因为我们在构建SpringBoot项目时勾选了Datasource模块,SpringBoot的AutoConfiguration自动去配置数据源,而我们没有对数据源进行配置,所以就会报错。
解决办法:application.properties配置如下
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssmrl?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=18420163207
SpringBoot运行原理
POM.XML
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
SpringBoot有父依赖。
我们点进去spring-boot-starter-parent看看。

springBoot里面自带了很多依赖,这些依赖都在spring-boot-dependencies里面。
我们截取了一段代码。

说明SpringBoot自带了很多依赖,和控制了这些依赖的version(版本)==》spring-boot-dependencies是版本控制中心
springBoot的启动器

我们点进去一个看看。


结论:可以看出来,很多我们在WEB开发需要用的,SpringBoot都给我们封装好了,变成了一个个starter(启动器),简化了开发。也就是说启动器里面就是我们要用的依赖。
SpringBoot的主程序

上面短短的几句代码就可以把SpringBoot项目运行起来。说明里面的原理是很复杂的。
SpringBoot主程序注解
点开@SpringBootApplication:

SpringBoot底层运用了大量的Spring底层注解。
@SpringBootConfiguration:说明这个类是SpringBoot的配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能。SpringBoot最核心的功能就是自动配置。大大的简化了开发,所以这个注解是非常重要的
**@ComponentScan:**Spring的注解,也就是去扫描这些类,并添加到SpringIOC容器中。
进去**@SpringBootConfiguration注解里面:**


因为@SpringBootConfiguration里面有@Configuration注解,@Configuration里面又有@Component注解。
说明@SpringBootConfiguration是以一个Spring组件添加进来的。
点进去**@EnableAutoConfiguration**注解:

我们可以看到两个注解:@AutoConfigurationPackage和@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
在@AutoConfigurationPackage里面有如下代码:
@Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}
Registrar.class:作用是将springBoot主程序类所在的包和所在包的子包,也就是目前的“boot”目录下所有类进行扫描,并加载到SpringIOC容器中,所以也就是为什么在boot外面的Java代码会没有作用,正因为springBoot在自动配置包注解中,默认只会扫描主程序类所在的包和所在包的子包的类
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}):导入自动配置导入选择器类
在AutoConfigurationImportSelector类中,有如下代码:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
作用是得到候选配置
点进去 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()方法:
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
我们在点进(List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse)的loadSpringFactories方法中
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}
我们可以看到它频繁的出现META-INF/spring.factories。我们去搜索它


在这里我们可以看到非常多的配置信息。这就是SpringBoot自动配置的根源所在,在SpringBoot运行的时候,自动配置类会在类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories里面去找到对应的值,只有导入了这些对应的值,自动配置才能生效
SpringBoot主程序的Run方法:
我们点进去run(),找到SpringApplication的构造器。
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
.............
............. #上面省略
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
SpringApplication
结论:SpringApplication这个类会做如下的事:
- 先去推断这个项目是不是WEB项目
- 从SpringFactories实例中查找出所有初始化器,并设置到initializers属性中
- 从SpringFactories实例中查找出所有应用监听器,并设置到listeners属性中
- 推断SpringBoot主程序类,并设置到mainApplicationClass中
yml配置注入
SpringBoot自带了application.properties,但是呢,SpringBoot更加推荐用yml或者yaml,不过本质上其实是差不多的,只是语法有些许不同罢了,yml和yaml会更加简洁
#yml语法:key:空格 值
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssmrl?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 18420163207
#properties语法:key=值
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
问:我们如何用SpringBoot自带的配置文件对一个对象进行封装,以便我们用@Autowired对这个类进行注入

**@ConfigurationProperties(prefix=“前缀”):把这个类的对象交给SpringBoot配置文件,我们可以在配置文件中用 前缀.属性名去赋值,这样SpringBoot就会把这些属性值封装成一个‘’对象‘’,放在IOC容器里,这样我们通过自动装配就可以获得这个对象 **
**如图上所示,报了一个错误====Not registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties, marked as Spring component, or scanned via @ConfigurationPropertiesScan **
意思是:我们少了一个@EnableConfigurationProperties注解,我们必须开启这个注解,@ConfigurationProperties才会生效
解决方法:
1.
<!-- 1.在Pom.xml上导入这个依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
2.
@EnableConfigurationProperties(emp.class) //必须要加上这个注解,并指定类
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
进入application.yml:
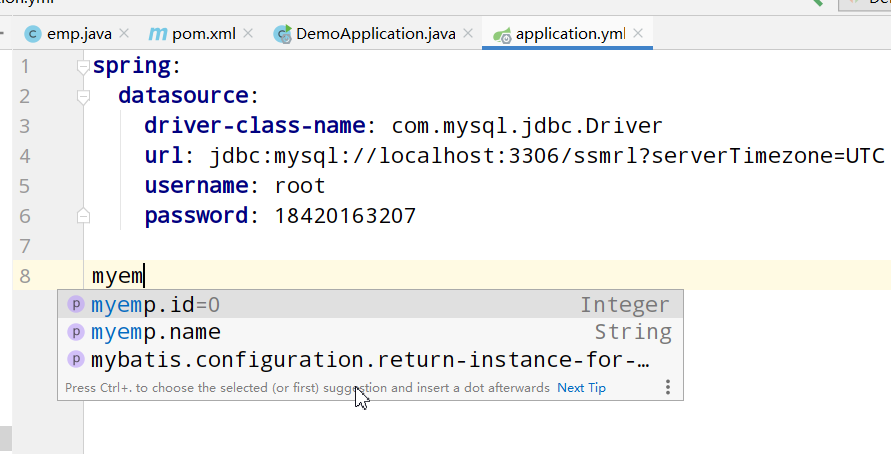
======说明我们已经通过@ConfigurationProperties绑定到这个类了
去绑定一下:
myemp:
id: 999
name: springBoot
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private emp emp;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}

====然后我们就绑定成功了!!!
多环境切换
在实际的开发中,我们可能会需要有多种环境,比如开发环境、测试环境、真实环境,我们如何做到这一点呢?
在resources目录下创建application-dev.properties
此时这个环境名就叫做:dev
springBoot默认会读取application.properties而不是application-dev.properties,所以我们要切换环境只能如下操作:
application.properties
server.port=8080 #设置该环境服务器的端口号
spring.profiles.active=dev #环境切换成dev
application-dev.properties
server.port=8081
当我们去启动SpringBoot项目,下面有一段日志写着:

在application.properties我们配置的端口号是8080,在application-dev.properties我们配置的端口号是8081,但是启动时我们发现初始化端口号是8081,说明我们已经顺利的切换了环境。
SpringBoot自动装配原理
@EnableAutoConfiguration //开启自动配置功能
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
....
}
我们进去@EnableAutoConfiguration:
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) //将指定的类导入到容器中
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
我们再点进去AutoConfigurationImportSelector
找到如下:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
进入loadFactoryNames()
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
再进入(List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse)
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
//1.获取所有META-INF/spring.factories
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
//2.把所有META-INF/spring.factories封装成properties
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}
结论:
- 当springBoot启动时,会去搜索所有/META-INF/spring.factories

并把所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值导入到容器中,然后自动配置才会生效
xxxAutoConfiguration会和xxxProperties绑定在一起,xxxAutoConfiguration需要的值会在xxxProperties里面取,xxxProperties的默认值可以通过application.properties来设置
静态资源处理
SpringBoot项目自带的静态资源目录

注意:templates目录只用来存放html页面。
欢迎页
我们先打开WebMvcAutoConfiguration,会看到如下代码
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext, FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(this.getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
在 WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());代码中有一句:this.getWelcomePage(),我们进入这个方法看看,看它是如何得到欢迎页的
进入后代码如下:
private Optional<Resource> getWelcomePage() {
String[] locations = WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
return Arrays.stream(locations).map(this::getIndexHtml).filter(this::isReadable).findFirst();
}
.......
.....
private Resource getIndexHtml(String location) {
return this.resourceLoader.getResource(location + "index.html");
} //欢迎页就是location下面的index.html而已
再进入this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()方法
public String[] getStaticLocations() {
return this.staticLocations;
}
点进this.staticLocations之后我们会发现有如下代码:
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
private boolean addMappings;
private boolean customized;
private final WebProperties.Resources.Chain chain;
private final WebProperties.Resources.Cache cache;
public Resources() {
this.staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
this.addMappings = true;
this.customized = false;
this.chain = new WebProperties.Resources.Chain();
this.cache = new WebProperties.Resources.Cache();
}
这就是SpringBoot对静态资源的处理
这段代码 private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{“classpath:/META-INF/resources/”, “classpath:/resources/”, “classpath:/static/”, “classpath:/public/”};说明了SpringBoot只去认这些路径下面的静态资源,其他路径的静态资源是无效的
回到上一步,我们进入WelcomePageHandlerMapping这个类,会有如下代码:
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders, ApplicationContext applicationContext, Optional<Resource> welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage.isPresent() && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage.get());
this.setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
} else if (this.welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
this.setRootViewName("index");
}
}
上面我们说了,所有在"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", “classpath:/resources/”, “classpath:/static/”, "classpath:/public/"路径下的静态资源都会被SpringBoot扫描,上面的代码可以看出SpringBoot会扫描这些路径下的index.html,作为欢迎页

静态资源处理的两种方式
在WebMvcAutoConfiguration里面有一段代码,里面写着怎么处理静态资源
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl).setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified()));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl).setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified()));
}
}
}
-
方式一: this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl).setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified())); //用webjars方式 -
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl).setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified())); }在(2)里面有一个this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations(),进入我们可以看到
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
private boolean addMappings;
private boolean customized;
private final WebProperties.Resources.Chain chain;
private final WebProperties.Resources.Cache cache;
public Resources() {
this.staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
this.addMappings = true;
this.customized = false;
this.chain = new WebProperties.Resources.Chain();
this.cache = new WebProperties.Resources.Cache();
}
方式二: private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"}; //只要资源文件在这里面的目录,就可以被扫描到
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)