花了两天肝出来的Spring注解编程的发展历程,相信对每个小伙伴都会有帮助的,建议收藏哦。
Spring对于每个Java程序员的重要性都是不言而喻的。但是对于Spring的注解编程的发展,我相信有很多小伙伴还是不清楚的,本文就彻底给大家梳理下。
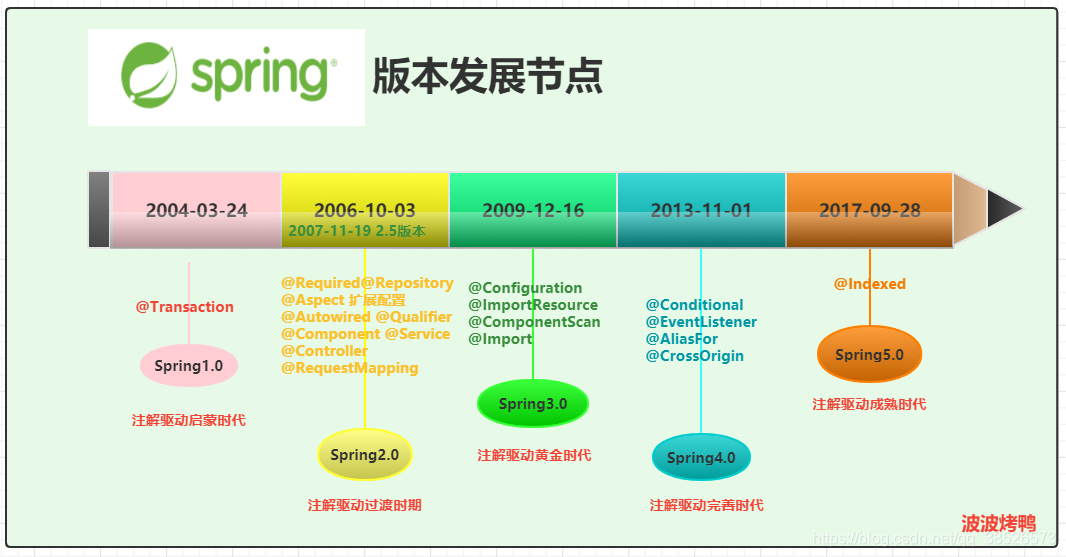
Spring注解编程的发展过程
1 Spring 1.x
2004年3月24日,Spring1.0 正式发布,提供了IoC,AOP及XML配置的方式。
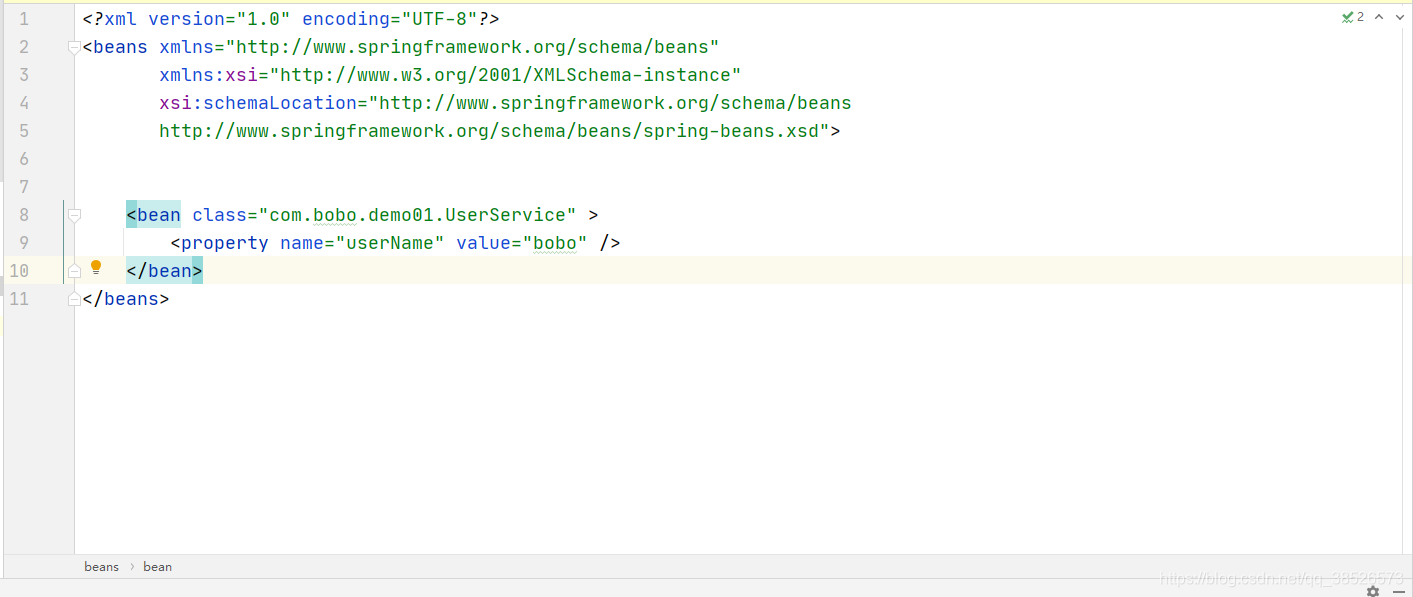
在Spring1.x版本中提供的是纯XML配置的方式,也就是在该版本中我们必须要提供xml的配置文件,在该文件中我们通过 <bean> 标签来配置需要被IoC容器管理的Bean。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.bobo.demo01.UserService" />
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
调试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext01.xml");
System.out.println("ac.getBean(UserService.class) = " + ac.getBean(UserService.class));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
输出结果
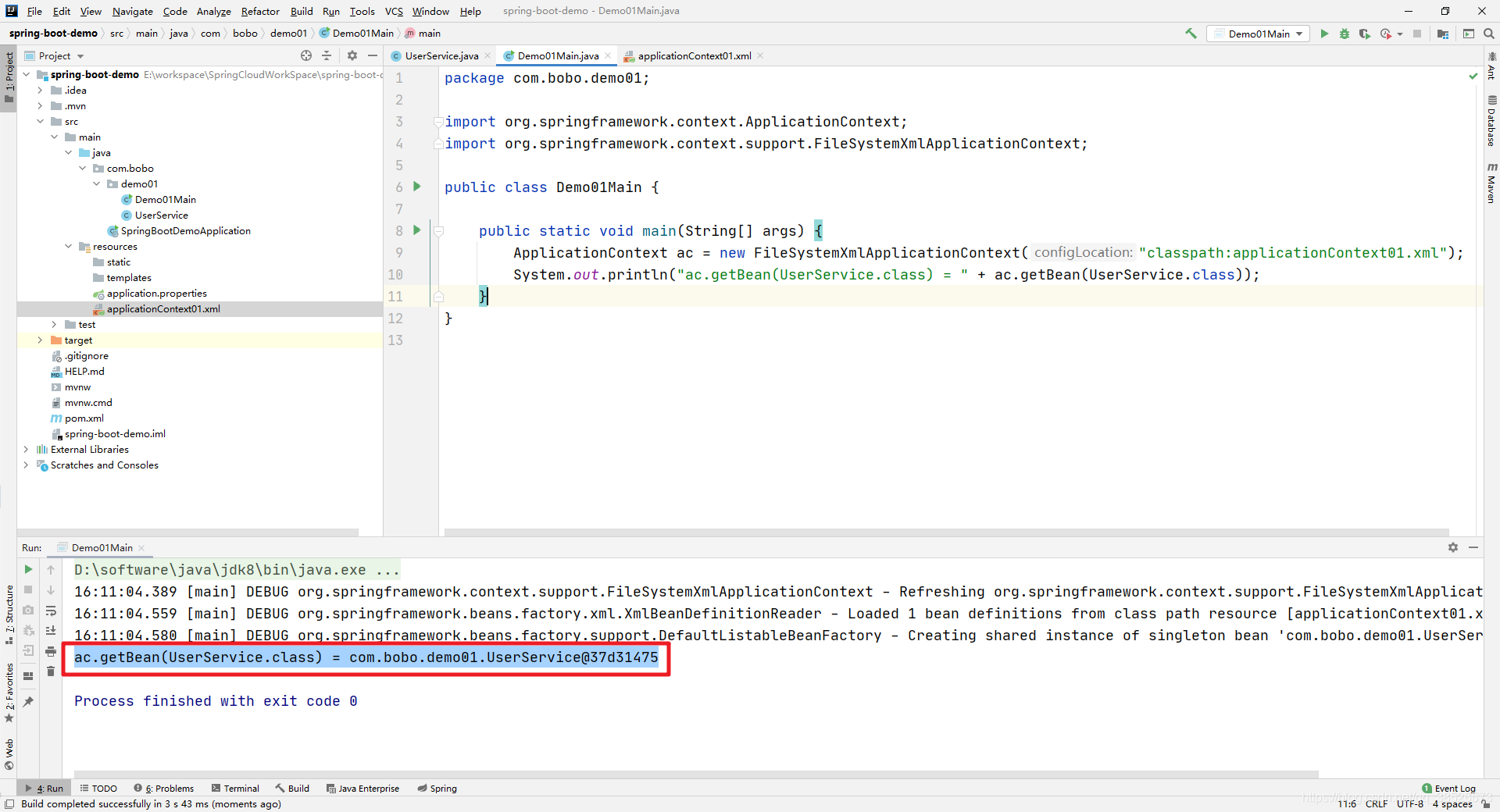
在Spring1.2版本的时候提供了@Transaction (org.springframework.transaction.annotation )注解。简化了事务的操作.
2 Spring 2.x
在2006年10月3日 Spring2.0问世了,在2.x版本中,比较重要的特点是增加了很多注解
Spring 2.5之前
在2.5版本之前新增的有 @Required @Repository @Aspect,同时也扩展了XML的配置能力,提供了第三方的扩展标签,比如<dubbo>
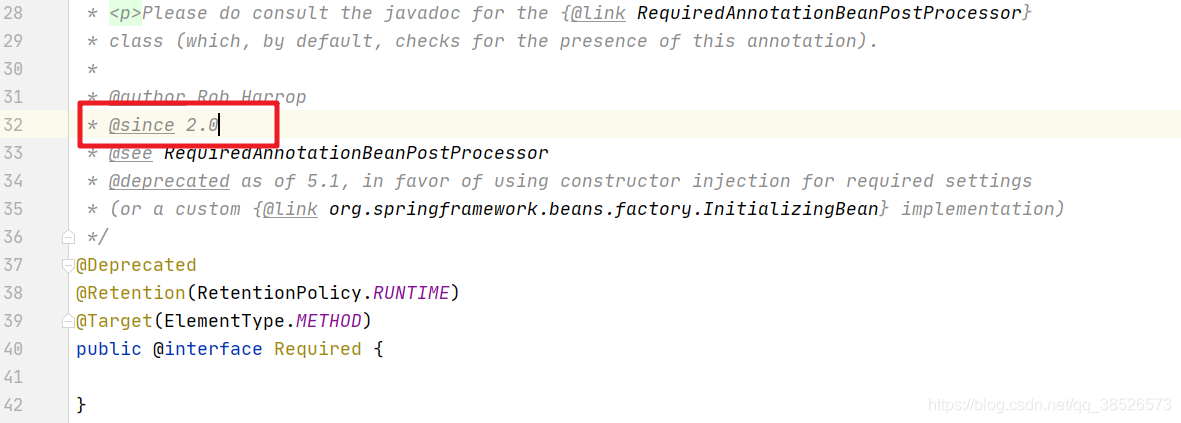
@Required
如果你在某个java类的某个set方法上使用了该注释,那么该set方法对应的属性在xml配置文件中必须被设置,否则就会报错!!!
public class UserService {
private String userName;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
@Required
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
如果在xml文件中我们不设置对应的属性就会给出错误的提示。
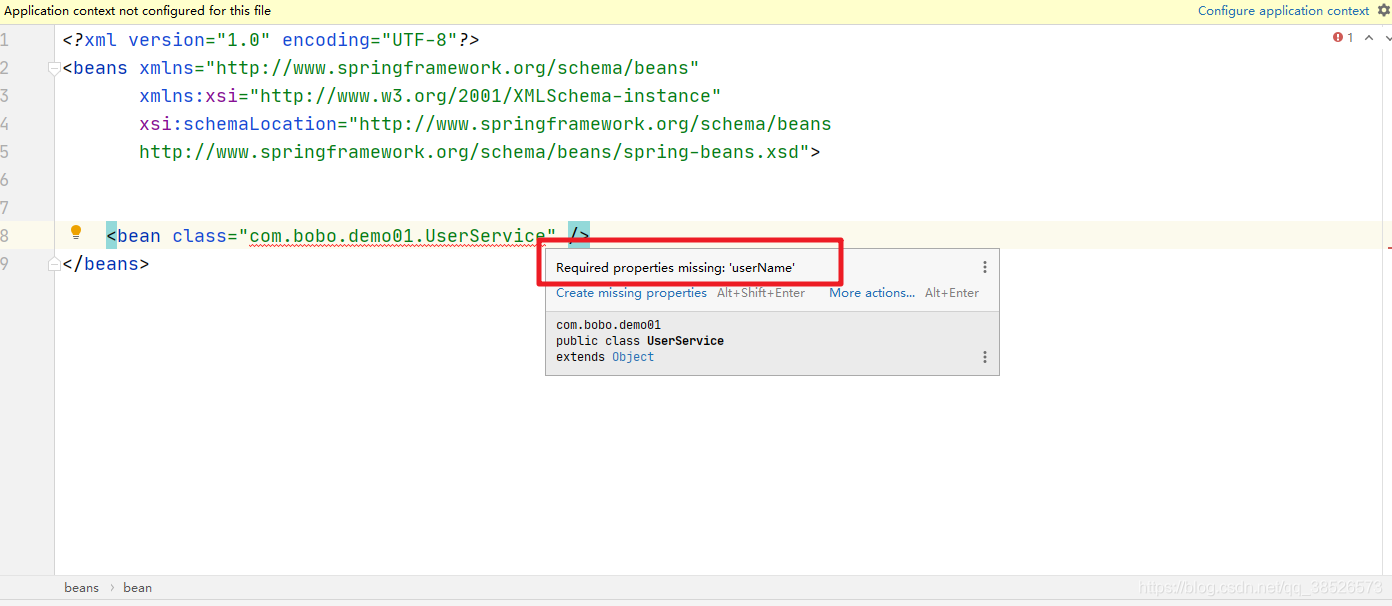
设置好属性后就没有了错误提示了
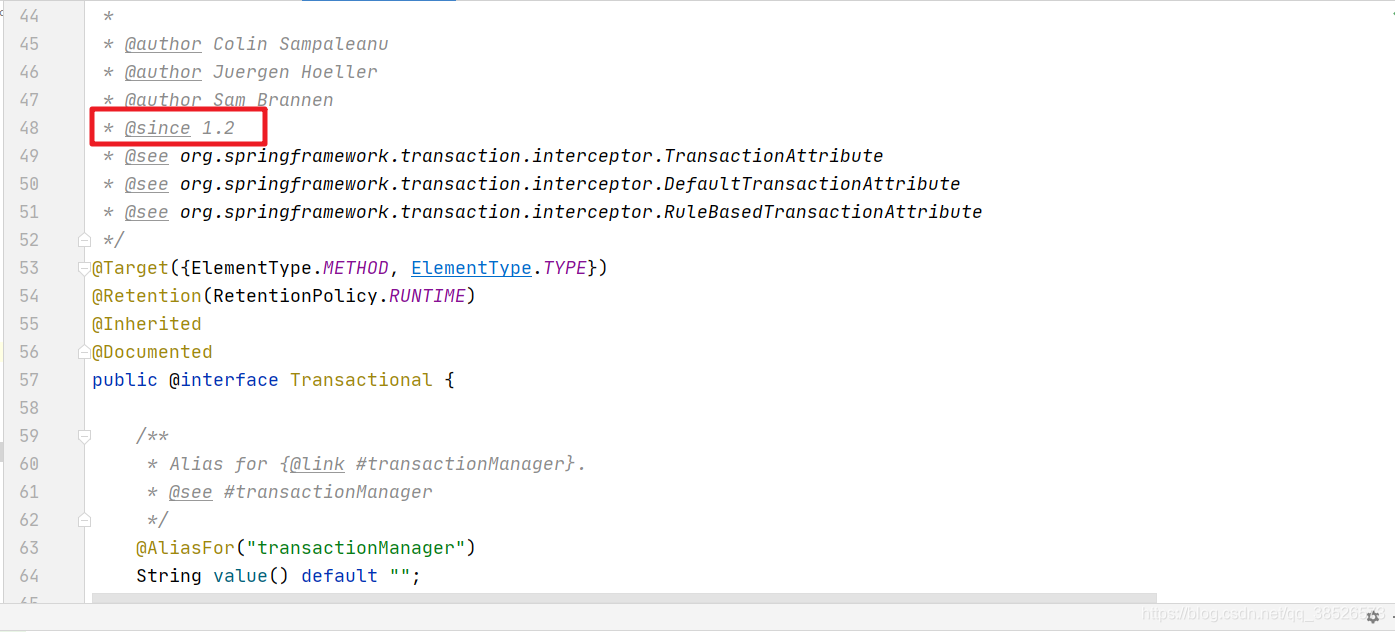
源码中可以看到@Required从2.0开始提供
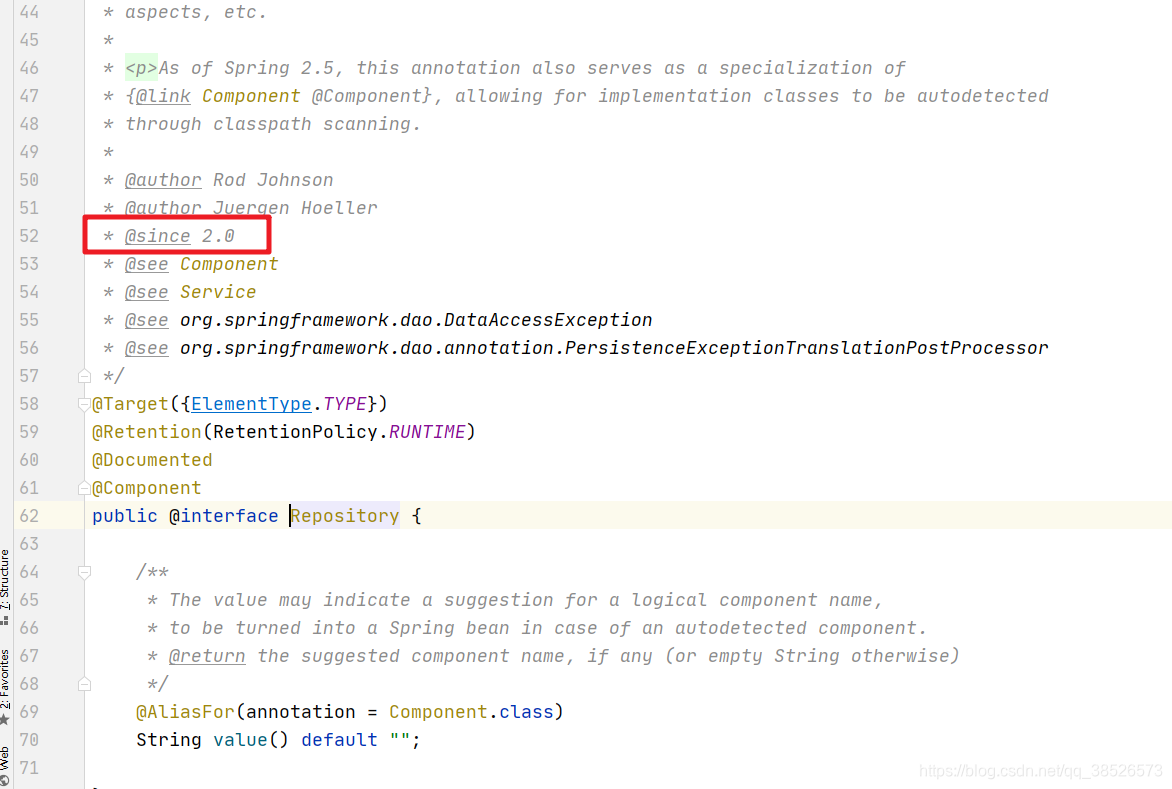
@Repository
@Repository 对应数据访问层Bean.这个注解在Spring2.0版本就提供的有哦,大家可能没有想到。
@Aspect
@Aspect是AOP相关的一个注解,用来标识配置类。
Spring2.5 之后
在2007年11月19日,Spring更新到了2.5版本,新增了很多常用注解,大大的简化配置操作。
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Autowired | 依赖注入 |
| @Qualifier | 配置@Autowired注解使用 |
| @Component | 声明组件 |
| @Service | 声明业务层组件 |
| @Controller | 声明控制层组件 |
| @RequestMapping | 声明请求对应的处理方法 |
在这些注解的作用下,我们可以不用在xml文件中去注册没有bean,这时我们只需要指定扫码路径,然后在对应的Bean头部添加相关的注解即可,这大大的简化了我们的配置及维护工作。案例如下:
我们在配置文件中只需要配置扫码路径即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bobo" />
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
持久层代码:
@Repository
public class UserDao {
public void query(){
System.out.println("dao query ..." );
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
业务逻辑层代码
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao dao;
public void query(){
dao.query();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
控制层代码:
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService service;
public void query(){
service.query();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
测试代码
public class Demo02Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext02.xml");
UserController acBean = ac.getBean(UserController.class);
acBean.query();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
虽然在Spring的2.5版本提供了很多的注解,也大大的简化了我们的开发,但是任然没有摆脱XML配置驱动。
3 Spring 3.x
在2009年12月16日发布了Spring3.0版本,这是一个注解编程发展的里程碑版本,在该版本中全面拥抱Java5。提供了@Configuration注解,目的就是去xml化。同时通过@ImportResource来实现Java配置类和XML配置的混合使用来实现平稳过渡。
/**
* @Configuration 标注的Java类 相当于 application.xml 配置文件
*/
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
/**
* @Bean 注解 标注的方法就相当于 <bean></bean> 标签
也是 Spring3.0 提供的注解
* @return
*/
@Bean
public UserService userService(){
return new UserService();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
在Spring3.1 版之前配置扫描路径我们还只能在 XML 配置文件中通过component-scan 标签来实现,在3.1之前还不能够完全实现去XML配置,在3.1 版本到来的时候,提供了一个 @ComponentScan注解,该注解的作用是替换掉 component-scan标签,是注解编程很大的进步,也是Spring实现无配置话的坚实基础。
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan的作用是指定扫码路径,用来替代在XML中的<component-scan>标签,默认的扫码路径是当前注解标注的类所在的包及其子包。
定义UserService
@Service
public class UserService {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
创建对于的Java配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class JavaConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaConfig.class);
System.out.println("ac.getBean(UserService.class) = " + ac.getBean(UserService.class));
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
输出的结果
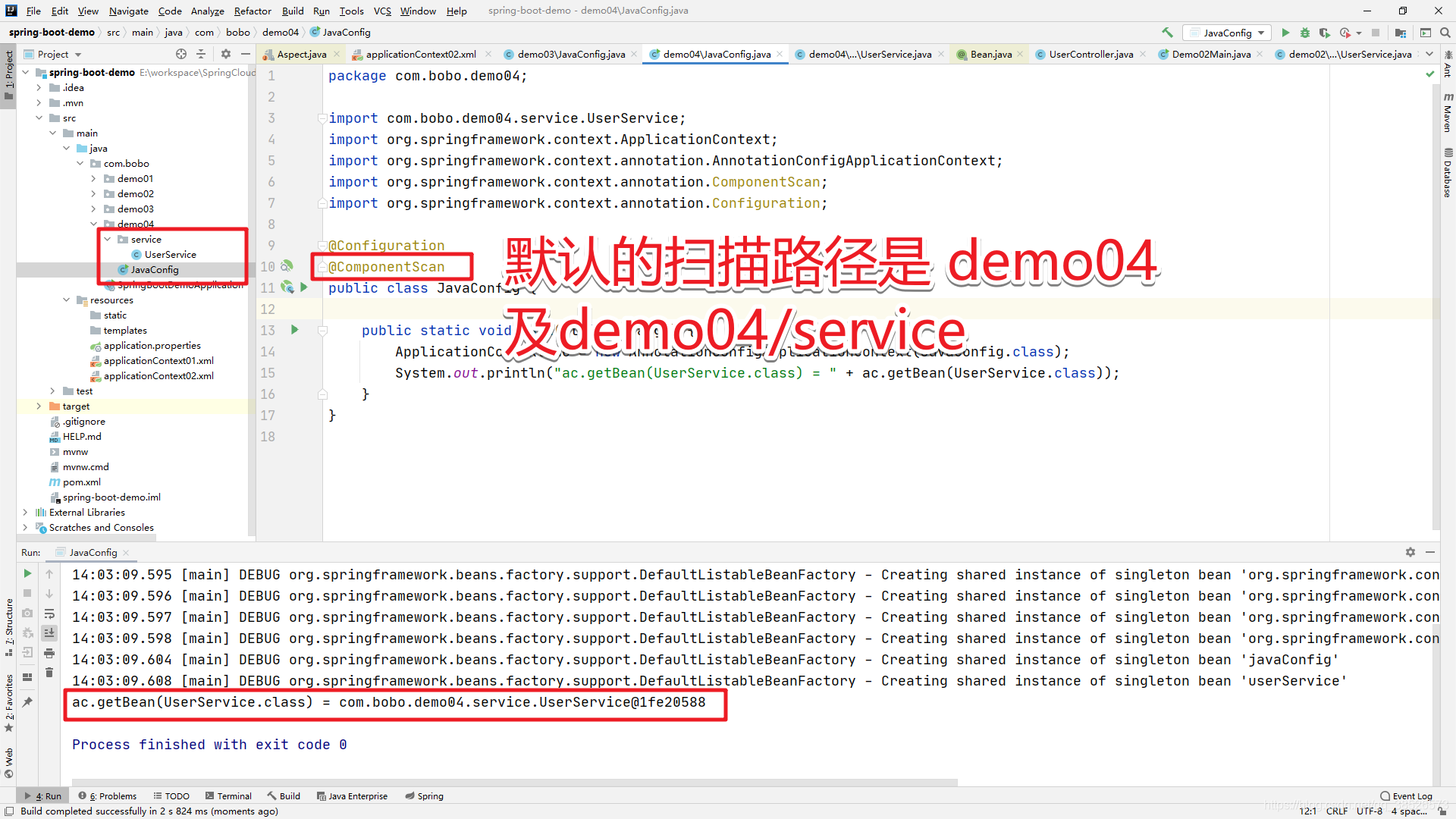
当然也可以指定特定的扫描路径
@Configuration
// 指定特定的扫描路径
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.bobo.demo04"})
public class JavaConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaConfig.class);
System.out.println("ac.getBean(UserService.class) = " + ac.getBean(UserService.class));
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
@Import
@Import注解只能用在类上,作用是快速的将实例导入到Spring的IoC容器中,将实例导入到IoC容器中的方式有很多种,比如@Bean注解,@Import注解可以用于导入第三方包。具体的使用方式有三种。
静态导入
静态导入的方式是直接将我们需要导入到IoC容器中的对象类型直接添加进去即可。
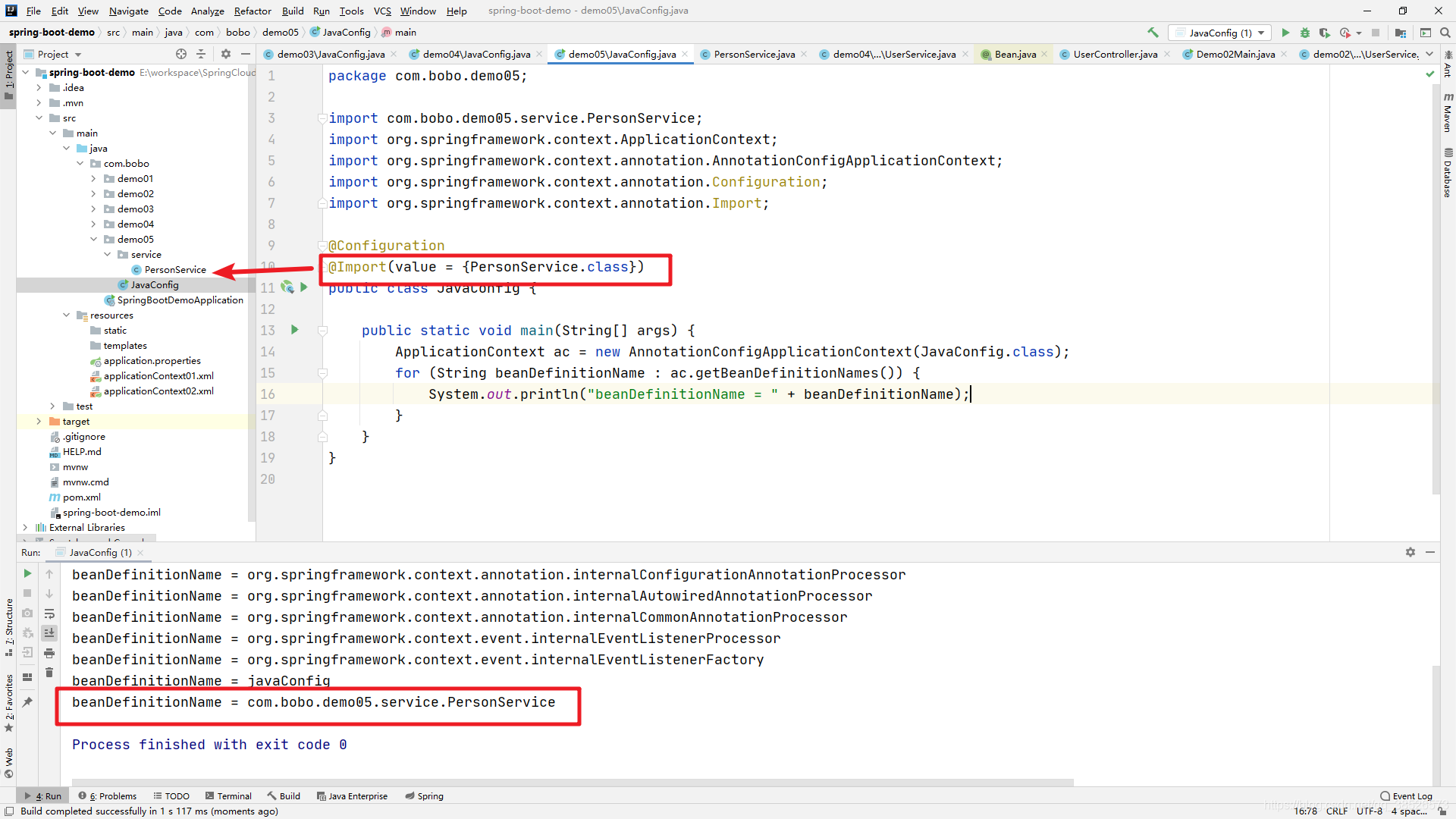
这种方式的好处是简单,直接,但是缺点是如果要导入的比较多,则不太方便,而且也不灵活。
ImportSelector
@Import注解中我们也可以添加一个实现了ImportSelector接口的类型,这时不会将该类型导入IoC容器中,而是会调用ImportSelector接口中定义的selectImports方法,将该方法的返回的字符串数组的类型添加到容器中。
定义两个业务类
public class Cache {
}
public class Logger {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
定义ImportSelector接口的实现,方法返回的是需要添加到IoC容器中的对象对应的类型的全类路径的字符串数组,我们可以根据不同的业务需求而导入不同的类型,会更加的灵活些。
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{Logger.class.getName(),Cache.class.getName()};
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
导入测试案例
@Configuration
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
public class JavaConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaConfig.class);
for (String beanDefinitionName : ac.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionName = " + beanDefinitionName);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
输出结果:
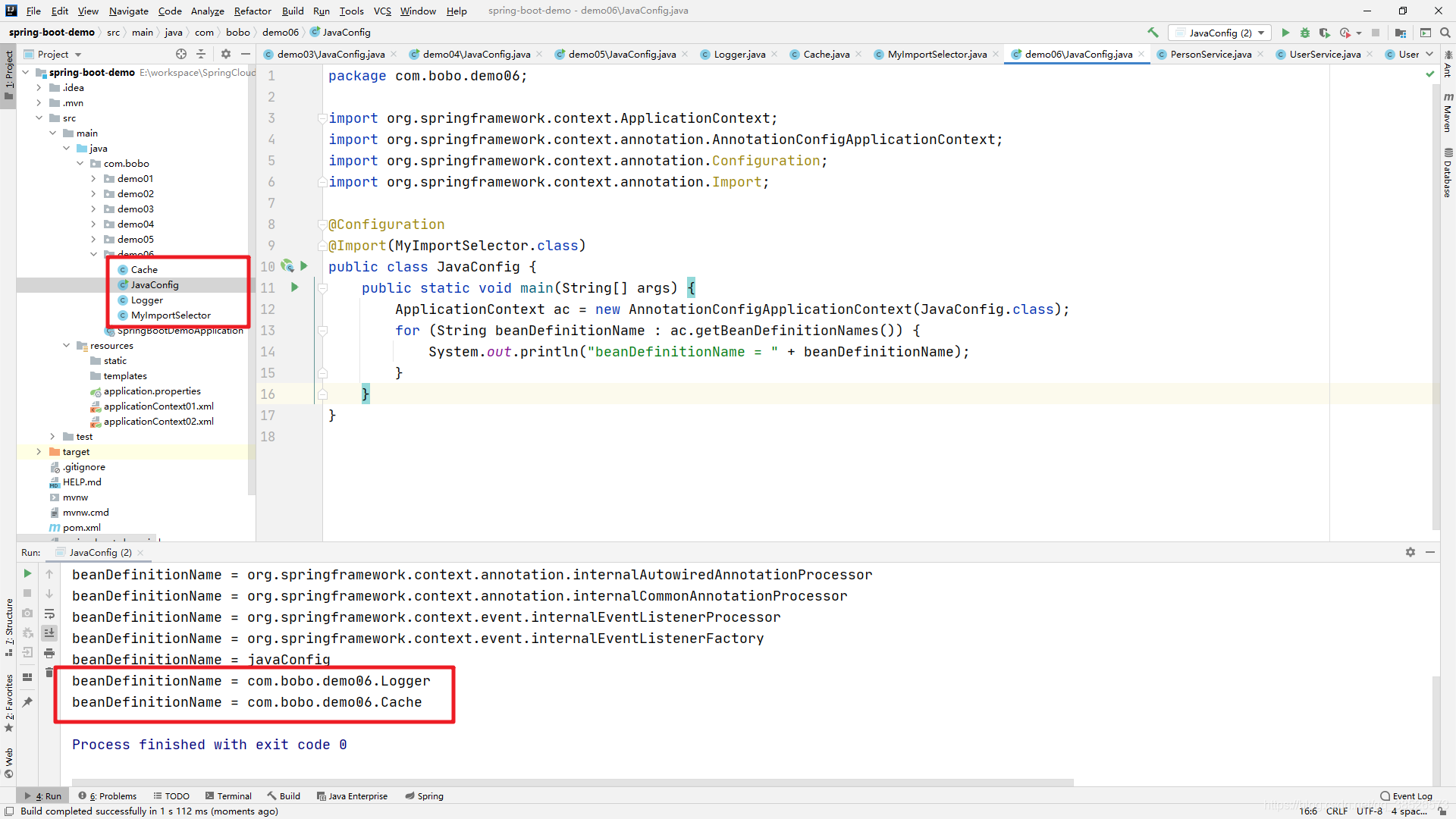
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
除了上面所介绍的ImportSelector方式灵活导入以外还提供了 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口,也可以实现,相比ImportSelector 接口的方式,ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 的方式是直接在定义的方法中提供了 BeanDefinitionRegistry ,自己在方法中实现注册。
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 将需要注册的对象封装为 RootBeanDefinition 对象
RootBeanDefinition cache = new RootBeanDefinition(Cache.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("cache",cache);
RootBeanDefinition logger = new RootBeanDefinition(Logger.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("logger",logger);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
测试代码
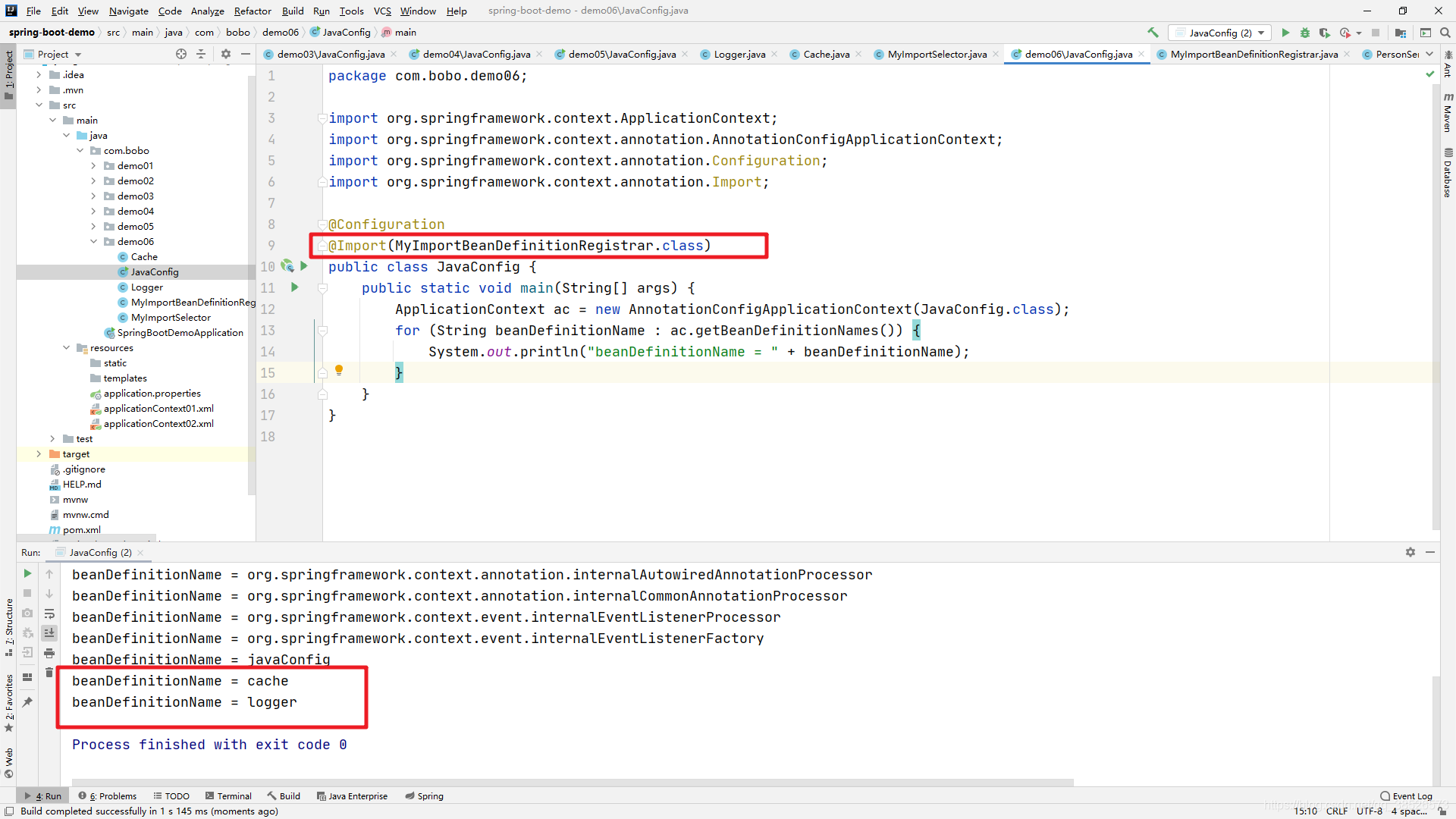
@Configuration
@Import(MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)
public class JavaConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaConfig.class);
for (String beanDefinitionName : ac.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionName = " + beanDefinitionName);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
输出结果
@EnableXXX
@Enable模块驱动,其实是在系统中我们先开发好各个功能独立的模块,比如 Web MVC 模块, AspectJ代理模块,Caching模块等。
案例说明,先定义好功能模块
/**
* 定义一个Java配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class HelloWorldConfiguration {
@Bean
public String helloWorld(){
return "Hello World";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
然后定义@Enable注解
/**
* 定义@Enable注解
* 在该注解中通过 @Import 注解导入我们自定义的模块,使之生效。
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(HelloWorldConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableHelloWorld {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
测试代码
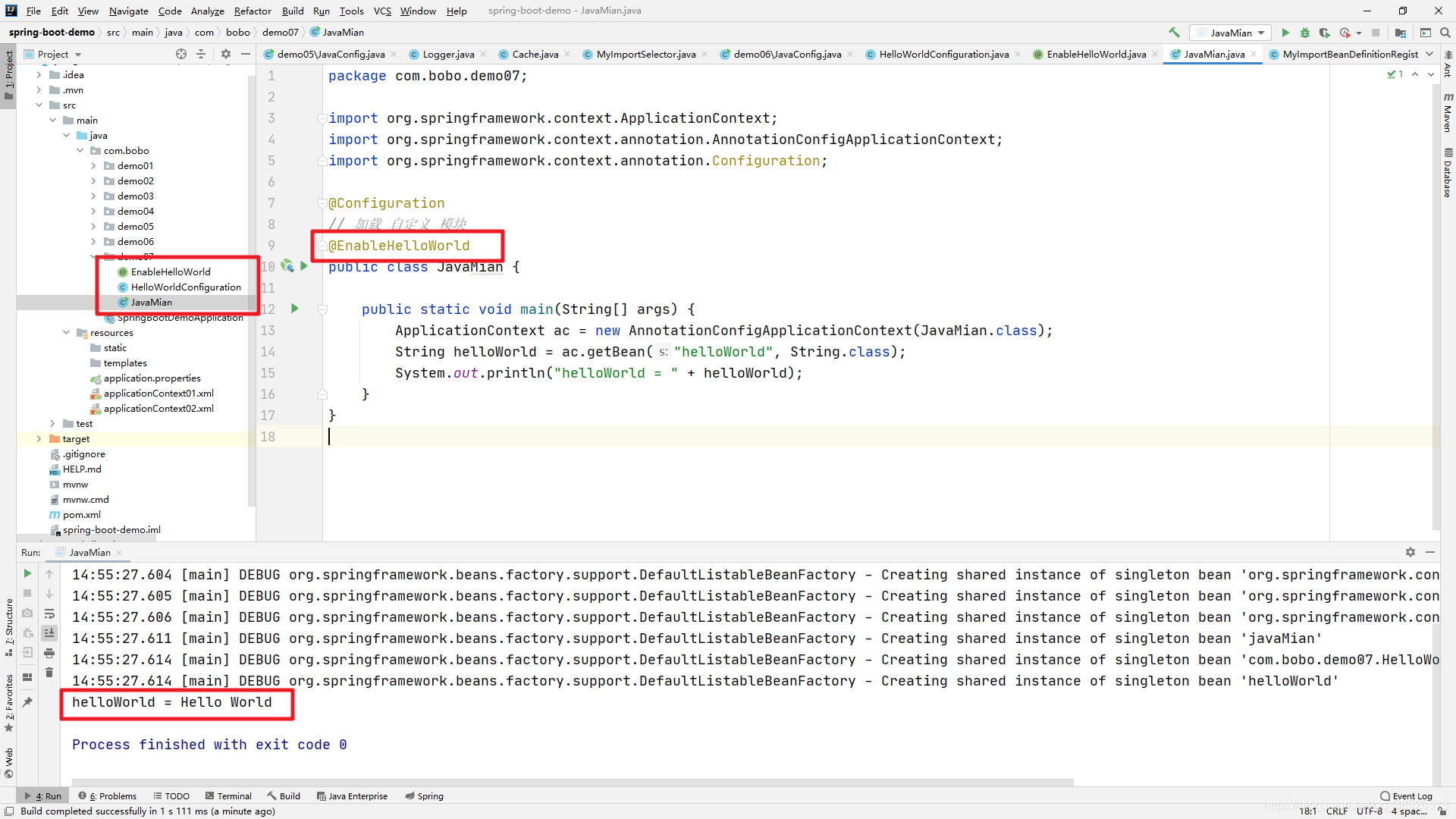
@Configuration
// 加载 自定义 模块
@EnableHelloWorld
public class JavaMian {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaMian.class);
String helloWorld = ac.getBean("helloWorld", String.class);
System.out.println("helloWorld = " + helloWorld);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
效果
4 Spring 4.x
2013年11月1 日更新的Spring 4.0 ,完全支持Java8.这是一个注解完善的时代,提供的核心注解是@Conditional条件注解。@Conditional 注解的作用是按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件就给容器注册Bean实例。
@Conditional的定义为:
// 该注解可以在 类和方法中使用
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
/**
* 注解中添加的类型必须是 实现了 Condition 接口的类型
*/
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
Condition是个接口,需要实现matches方法,返回true则注入bean,false则不注入。
案例讲解:
/**
* 定义一个 Condition 接口的是实现
*/
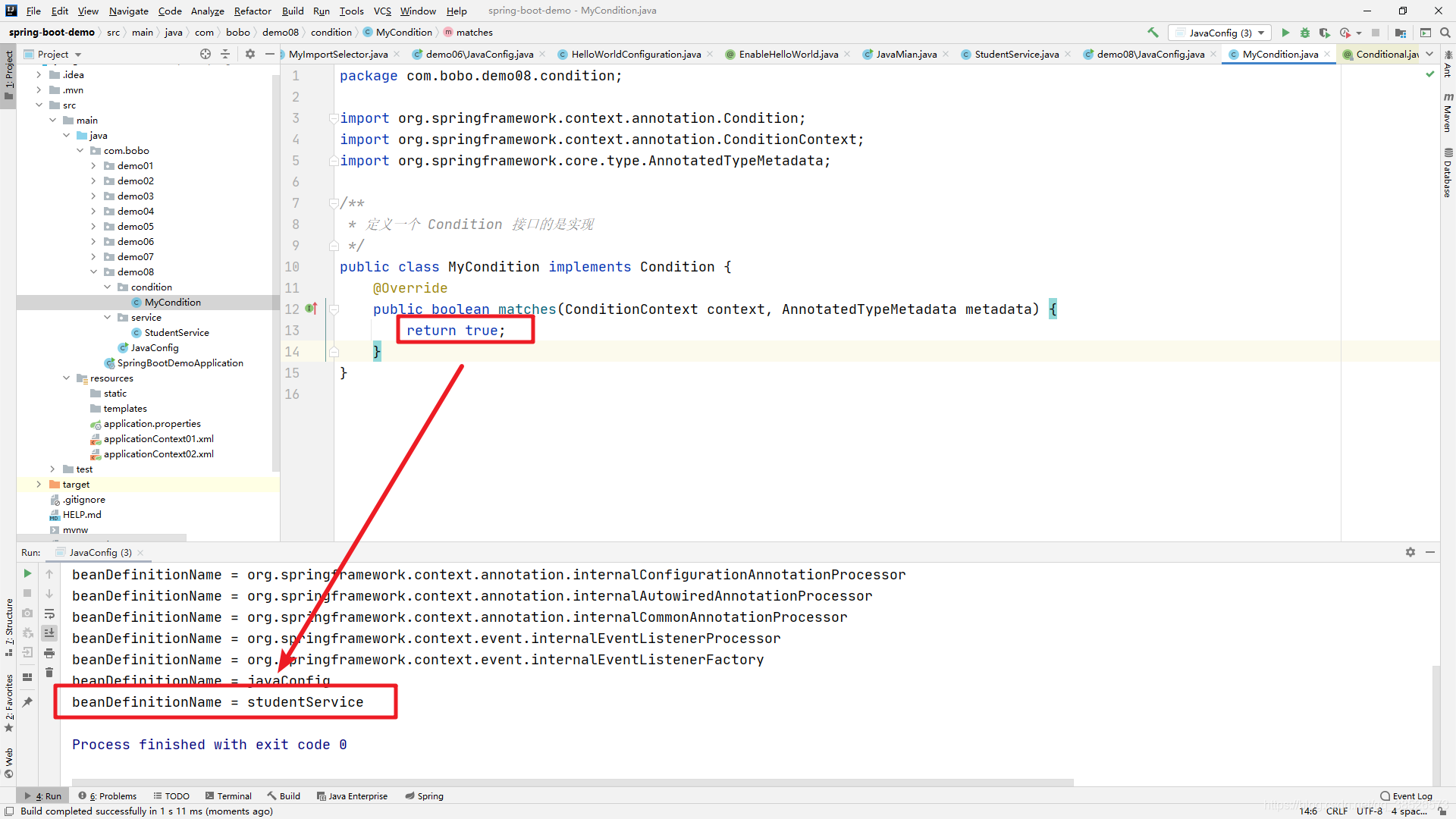
public class MyCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return false; // 默认返回false
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
创建Java配置类
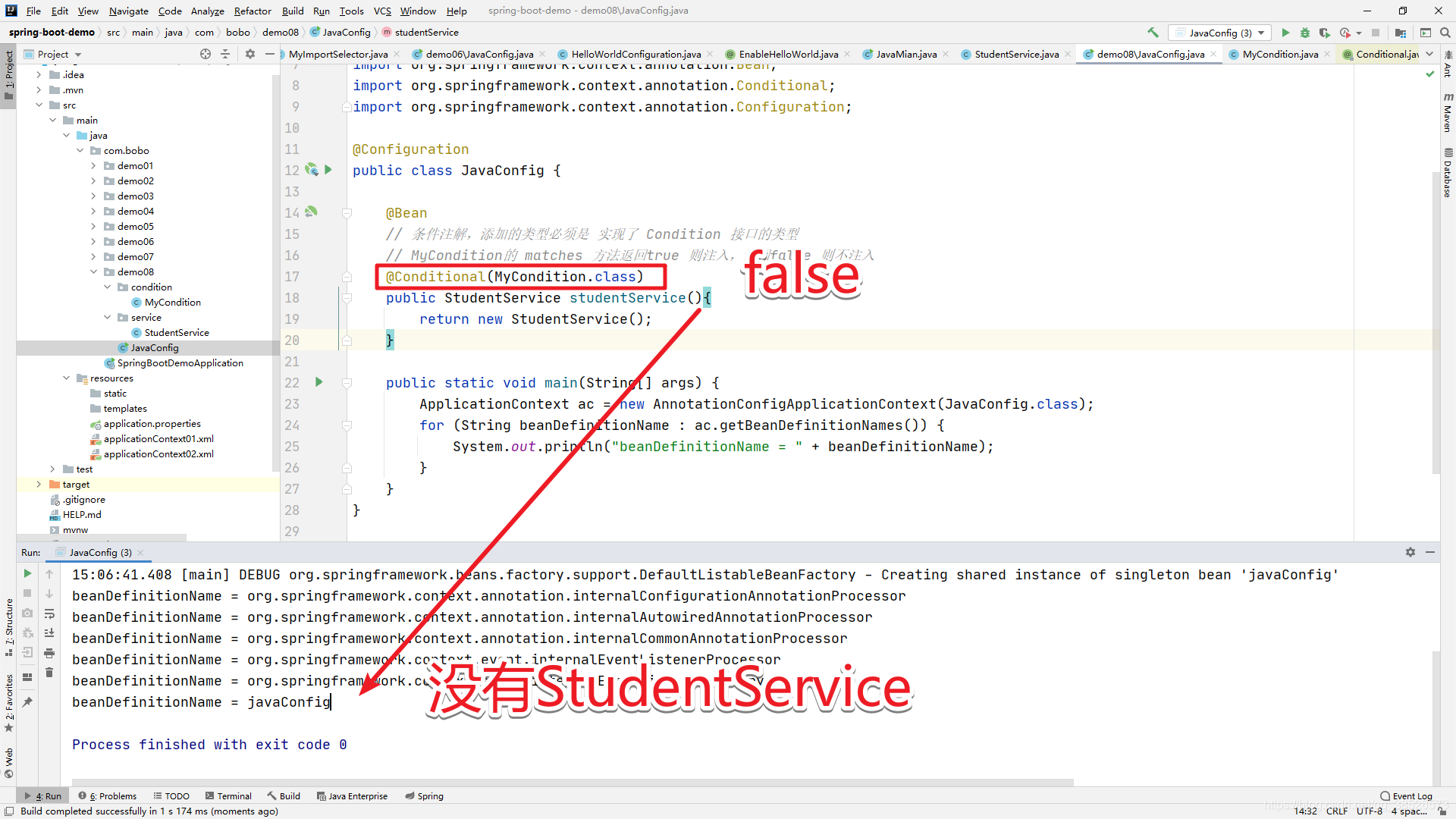
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean
// 条件注解,添加的类型必须是 实现了 Condition 接口的类型
// MyCondition的 matches 方法返回true 则注入,返回false 则不注入
@Conditional(MyCondition.class)
public StudentService studentService(){
return new StudentService();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaConfig.class);
for (String beanDefinitionName : ac.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionName = " + beanDefinitionName);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
测试:
但是将 matchs方法的返回结果设置为 true 则效果不同
所以@Conditional的作用就是给我们提供了对象导入IoC容器的条件机制,这也是SpringBoot中的自动装配的核心关键。当然在4.x还提供一些其他的注解支持,比如@EventListener,作为ApplicationListener接口编程的第二选择,@AliasFor解除注解派生的时候冲突限制。@CrossOrigin作为浏览器跨域资源的解决方案。
5 Spring 5.x
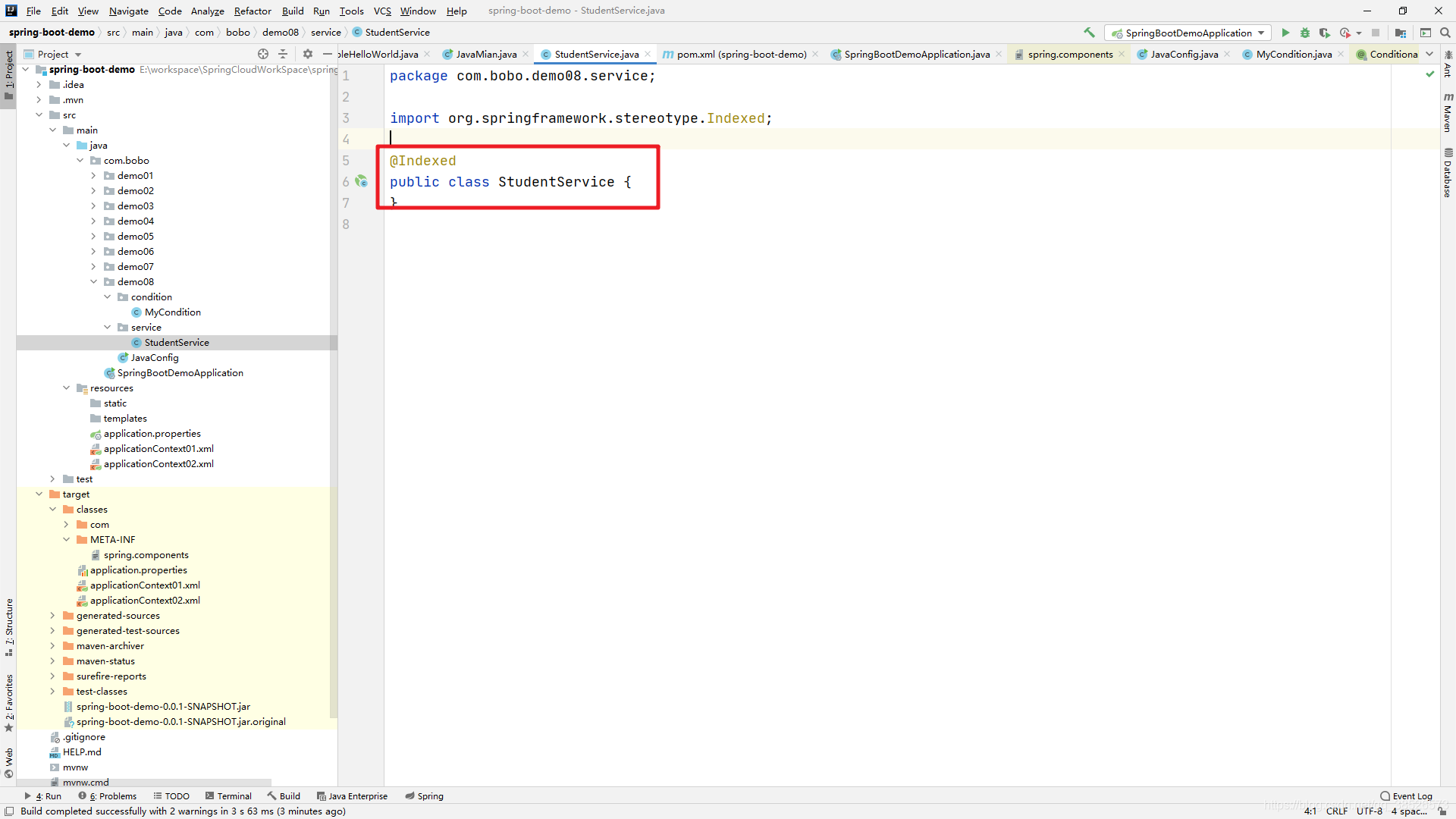
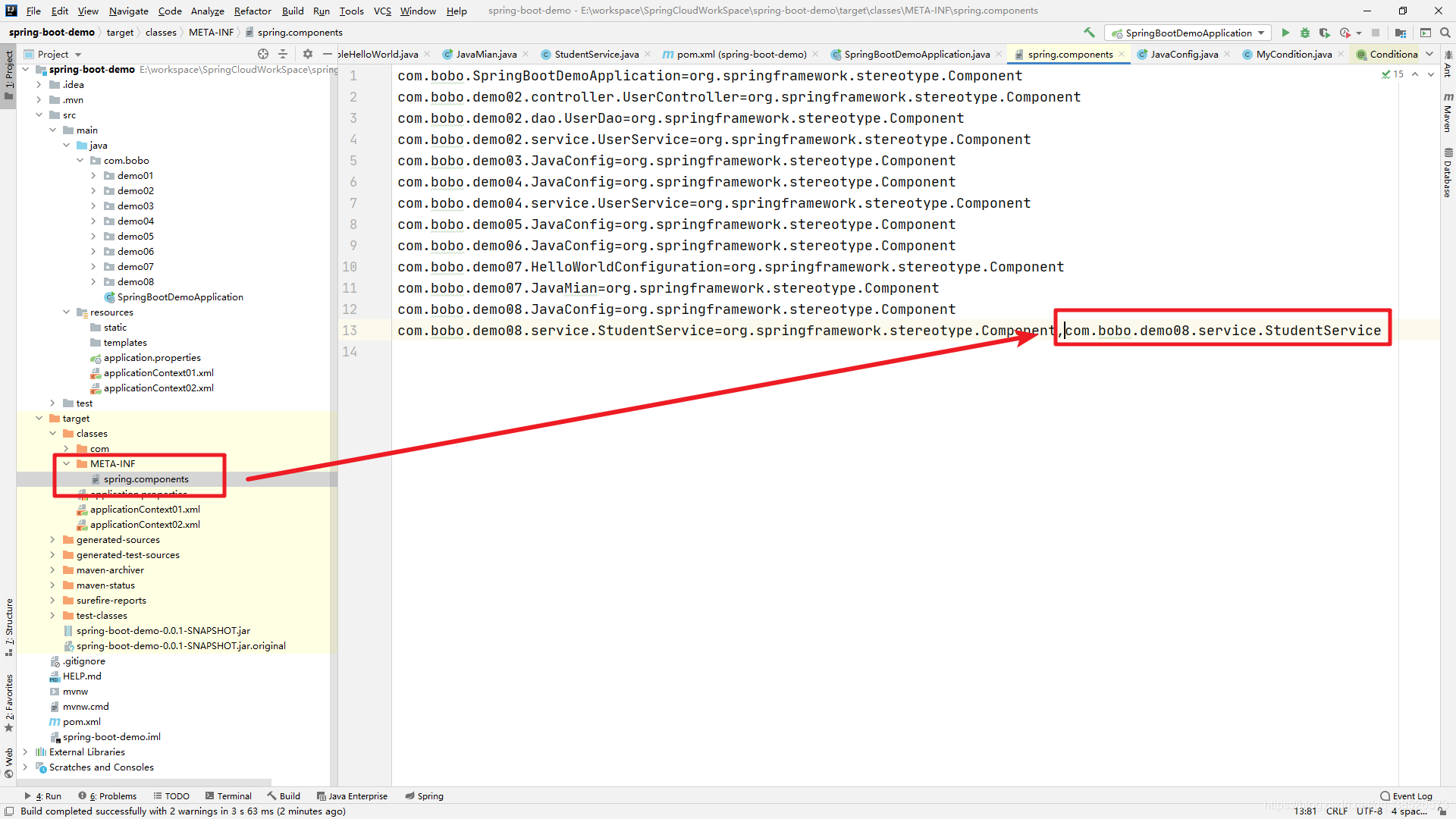
2017年9月28日,Spring来到了5.0版本。5.0同时也是SpringBoot2.0的底层。注解驱动的性能提升方面不是很明显。在Spring Boot应用场景中,大量使用@ComponentScan扫描,导致Spring模式的注解解析时间耗时增大,因此,5.0时代引入**@Indexed**,为Spring模式注解添加索引。
当我们在项目中使用了@Indexed之后,编译打包的时候会在项目中自动生成META-INT/spring.components文件。当Spring应用上下文执行ComponentScan扫描时,META-INT/spring.components将会被CandidateComponentsIndexLoader 读取并加载,转换为CandidateComponentsIndex对象,这样的话@ComponentScan不在扫描指定的package,而是读取CandidateComponentsIndex对象,从而达到提升性能的目的。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
使用@Indexed注解
好了,到这相信大家对于Spring的发展历程应该就比较清楚了,如果对你有帮助,欢迎关注点赞加收藏哦!!!

文章来源: dpb-bobokaoya-sm.blog.csdn.net,作者:波波烤鸭,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:dpb-bobokaoya-sm.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118730595
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)