Spring中IoC基于注解方式操作bean管理
前言:
- 注解是代码特殊标记,格式:@注解名称(属性名称=属性值, 属性名称=属性值…)
- 使用注解,注解作用在类上面,方法上面,属性上面
- 使用注解目的:简化 xml 配置
一.Spring中针对Bean管理创建对象提供的注解
以下四个注解功能是一样的,都可以用来创建 bean 实例
- @Component
- @Service
- @Controller
- @Repository
步骤:
1.开启组件扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描
1.扫描包上层目录
2.如果扫描多个包,多个包使用逗号隔开
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="iocbean.byannotation"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2.创建类,在类上面添加可以创建对象的注解
//在注解里面 value 属性值可以省略不写,
// 如果不写默认值是类名称的首字母小写 例如:Person --> person
@Component(value = "person") //相当于xml配置<bean id="person" class="iocbean.byannotation.Person"></bean>
public class Person {
private String name;
private String age;
private String gender;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
测试代码:
public class DemoTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("iocbean/byannotation/bean.xml");
Person person = context.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
输出结果:
Person{name='null', age='null', gender='null'}
Process finished with exit code 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
二.组件扫描细节配置
- use-default-filters=“false” 表示现在不使用默认 filter,自己配置 filter ;context:include-filter ,设置扫描哪些内容
- context:exclude-filter: 设置哪些内容不进行扫描
其中type有annotation,aspectj,assignable,custom,regex几种类型。
其意义如下:
- annotation:注解类型
- assignable_type:annotation:指定的类型
- aspectj:按照Aspectj的表达式,基本上不会用到
- regex:按照正则表达式
- custom:自定义规则
配置文件示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描
1.扫描包上层目录
2.如果扫描多个包,多个包使用逗号隔开
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="iocbean.byannotation"></context:component-scan>
<!--示例 1
use-default-filters="false" 表示现在不使用默认 filter,
自己配置 filter context:include-filter ,设置扫描哪些内容
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="iocbean.byannotation" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"></context:include-filter>
</context:component-scan>
<!--示例 2
下面配置扫描包所有内容 context:exclude-filter: 设置哪些内容不进行扫描
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="iocbean.byannotation">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"></context:exclude-filter>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
三.注解方式实现属性注入
1. @Autowired:根据属性类型进行自动装配
@Component
public class Student {
// 添加注入属性注解
@Autowired
//定义 Person 类型属性
// 不需要添加 set 方法
private Person person;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"person=" + person +
'}';
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
2.@Qualifier:根据名称进行注入
@Qualifier 注解的使用需和上面@Autowired 一起使用
//添加注入属性注解
@Autowired //根据类型进行注入
@Qualifier(value = "person")//根据名称进行注入
//定义 Person 类型属性
// 不需要添加 set 方法
private Person person1;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.@Resource:可以根据类型注入,可以根据名称注入
其实@Resource并不是Spring的注解,它的包是javax.annotation.Resource,需要导入,但是Spring支持该注解的注入。
@Resource这个注解属于J2EE的,默认按照名称进行装配,名称可以通过name属性进行指定。
- 如果没有指定name属性,当注解写在字段上时,默认取字段名进行名称查找。
- 如果没有指定name属性,当注解写在setter方法上时,默认取属性名进行装配。
- 如果没有指定name属性,当找不到与名称匹配的bean时才按照类型进行装配。
- 需要注意的是,如果name属性一旦指定,就只会按照名称进行装配。
推荐使用:@Resource注解在字段上,且这个注解是属于J2EE的,减少了与spring的耦合。最重要的这样代码看起就比较优雅。
要注意的是高版本JDK在使用@Resource注解时装配失败,改用@Autowired() 和@Qualifier("")后bean装配成功。在使用Spring注解开发中,使用@Resource报空指针异常时有两个解决方案:
- 使用jdk8
- 导入一个新的javax.annotation的jar包
例如本人JDK12版本中javax.annotation.*包内容如下:
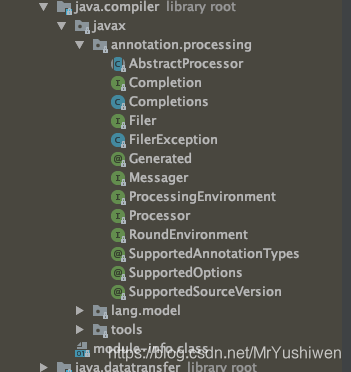
可以看到没有Resource注解类,然后本人重新导入javax.annotation-api-1.3.2.jar,完成后如下:
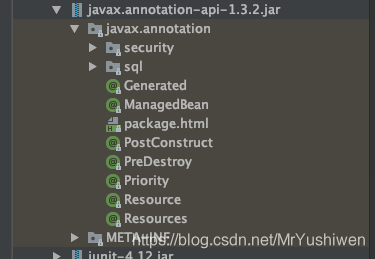
这样我们就可以使用@Resource注解了
代码示例:
@Resource//根据类型进行注入
private Person person;
@Resource(name = "person1") //根据名称进行注入
private Person person3;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4.@Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "19")
private String age;
- 1
- 2
- 3
5.@Autowired(required=false)
默认情况下必须要求依赖对象必须存在,如果要允许null 值,可以设置它的required属性为false,
即有些时候依赖对象不存在,会注入失败,当我们没有加上required=false时会出现异常,当我们加上参数(required=false)时,如果注入失败,此时会自动注入null值,不会发生报错当情况。
代码示例:
@Autowired(required = false)
private Person person;
@Autowired(required = false) //根据类型进行注入
@Qualifier(value = "person1")//根据名称进行注入
private Person person1;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
四.配置类
创建配置类,替代 xml 配置文件
//作为配置类,替代xml配置文件
@Configuration
//定义扫描的路径,从中找出标识了需要装配的类自动装配到spring的bean容器中
@ComponentScan("iocbean.byannotation/complete_annotation")
public class SpringIocConfig {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Person类:
@Component
public class Person {
@Value("Mr.Yu")
private String name;
@Value("21")
private String age;
@Value("男")
private String gender;
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person类构造器");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
Student类:
@Component
public class Student {
@Autowired(required = false)
private Person person;
@Autowired(required = false)
@Qualifier("person")
private Person person1;
@Resource
private Person person2;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student类构造器");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"person=" + person +
", person1=" + person1 +
", person2=" + person2 +
'}';
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
测试代码:
public class DemoTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringIocConfig.class);
Student student = context.getBean("student", Student.class);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
输出结果:
Person类构造器
Student类构造器
Student{person=Person{name='Mr.Yu', age='21', gender='男'}, person1=Person{name='Mr.Yu', age='21', gender='男'}, person2=Person{name='Mr.Yu', age='21', gender='男'}}
Process finished with exit code 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:Mr.Yushiwen,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/MrYushiwen/article/details/111301755
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)