mybatis教程1(基本使用)
一、什么是 MyBatis ?
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
二、mybatis和hibernate的比较
| mybatis | hibernate |
|---|---|
| 半自动ORM框架 | 全自动ORM框架 |
| 必须写SQL | 可以不写SQL |
| 事务处理 | 事务处理 |
| 缓存都支持 | 缓存都支持,二级缓存比mybatis更好 |
三、入门案例
1.创建maven工程,添加对应jar包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.27</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2.创建全局配置文件
该配置文件包含了对 MyBatis 系统的核心设置,包含获取数据库连接实例的数据源(DataSource)和决定事务作用域和控制方式的事务管理器TransactionManager)。XML 配置文件的详细内容后面再探讨,这里先给出一个简单的示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?characterEncoding=utf-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
配置允许其他用户连接mysql:
grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '123456' with grant option;
flush privileges;
- 1
- 2
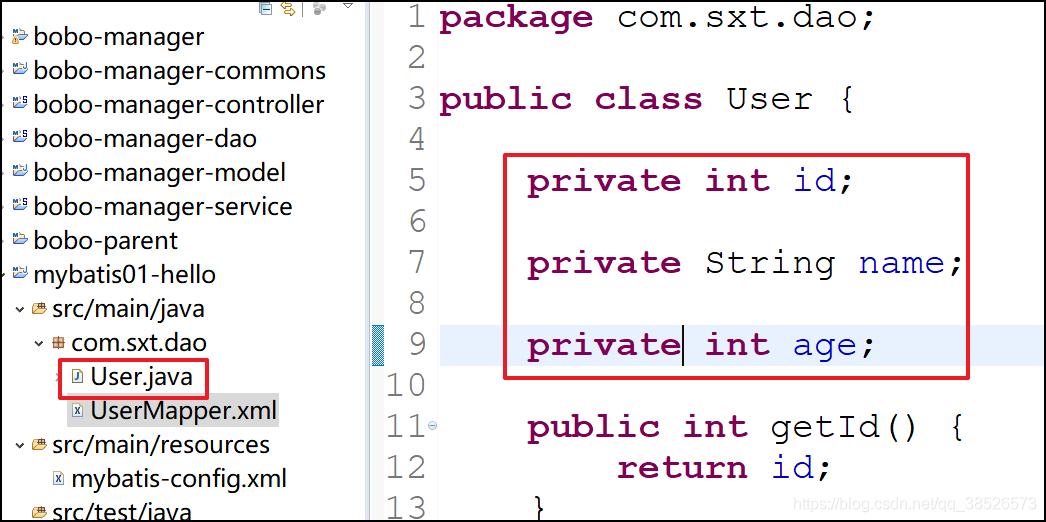
3.定义User对象
4.创建映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="dpb">
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.sxt.dao.User">
insert into t_user(name,age)values(#{name},#{age})
</insert>
<delete id="deleteUserById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from t_user where id=#{id}
</delete>
<update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.sxt.dao.User">
update t_user set name = #{name} where id=#{id}
</update>
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="com.sxt.dao.User">
select * from t_user where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
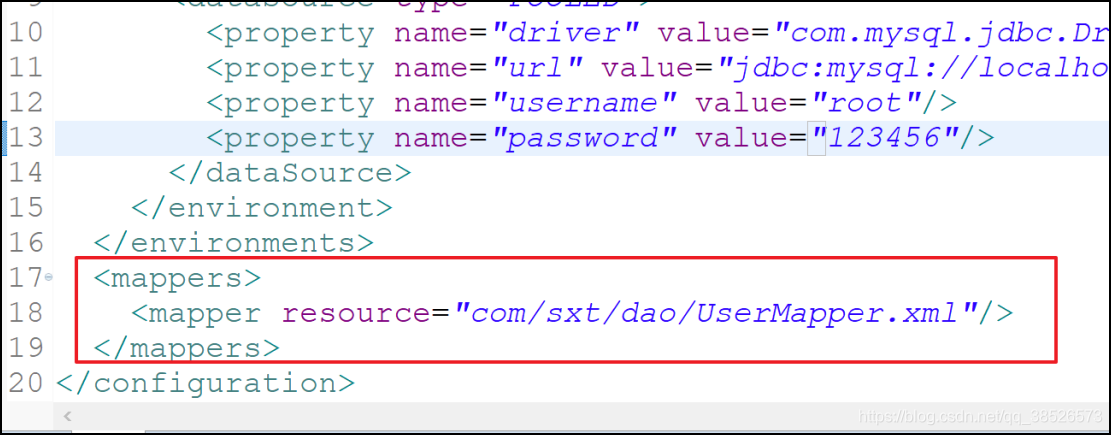
5.将映射文件添加到主配置文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 注册映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/sxt/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
6.测试
@Test
public void add() throws IOException {
// 1.通过Resources对象加载配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 2.获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream );
// 3.通过SqlSessionFactory对象获取SQLSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setName("dpb");
user.setAge(22);
// dpb.addUser 是映射文件中 namespace的内容加 id的内容,定位要执行的SQL
int count = session.insert("dpb.addUser", user);
System.out.println("影响的行数:"+count);
// 需要显示的提交
session.commit();
session.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
7.查询,修改,删除操作
public class Test02 {
private SqlSession sqlSession;
@Before
public void before() throws IOException {
// 1. 加载配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 2. 根据配置文件获取一个SqlSessionFactory对象,这个对象相当于连接工厂
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
// 3. 获取一个sqlsession,sqlsession类似于之前学过的Connection
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
@After
public void after() {
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void test1() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(7);
user.setName("里斯1");
int update = sqlSession.update("dpb.updateUserById", user);
System.out.println(update);
}
@Test
public void test2() {
int delete = sqlSession.delete("dpb.deleteUserById", 7);
System.out.println(delete);
}
@Test
public void test3() {
User user = (User) sqlSession.selectOne("dpb.getUserById", 8);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
四、案例优化
1.获取SqlSessionFactory对象的方式
SqlSessionFactory在一个服务中只需要有一个实例就可以了,此时可以通过单例的模式获取
/**
* 工具类 对外提供SqlSessionFactory的单例对象
* @author dengp
*
*/
public class DbUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory factory ;
public static SqlSessionFactory getInstace(){
if(factory ==null){
InputStream in = null;
try{
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (DbUtils.class) {
if(factory ==null){
factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
}
}
}
return factory;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
2.整理CRUD操作
public interface UserMapper {
public int addUser(User user);
public int updateById(User user);
public int deleteById(int id);
public User queryById(int id);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
public class UserDao implements UserMapper {
@Override
public int addUser(User user) {
return DBUtils.getInstall().openSession().insert("com.sxt.dao.UserMapper.addUser", user);
}
@Override
public int updateById(User user) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return DBUtils.getInstall().openSession().update("com.sxt.dao.UserMapper.updateById", user);
}
@Override
public int deleteById(int id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return DBUtils.getInstall().openSession().delete("com.sxt.dao.UserMapper.deleteById", id);
}
@Override
public User queryById(int id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return DBUtils.getInstall().openSession().selectOne("com.sxt.dao.UserMapper.queryById", id);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sxt.dao.UserMapper">
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.sxt.bean.User">
insert into t_user(name,age)values(#{name},#{age})
</insert>
<delete id="deleteById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from t_user where id=#{id}
</delete>
<update id="updateById" parameterType="com.sxt.bean.User">
update t_user
set name=#{name},age=#{age}
where id=#{id}
</update>
<select id="queryById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer"
resultType="com.sxt.bean.User">
select * from t_user where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
/**
* 代理方式
*/
@Test
public void test(){
UserMapper mapper = (UserMapper) Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserMapper.class.getClassLoader()
, new Class[]{UserMapper.class},new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(UserMapper.class.getName()+"."+method.getName());
Object id = null;
for (Object object : args) {
System.out.println(object);
id = object;
}
// 实现逻辑
return DBUtils.getInstall().openSession().selectOne(UserMapper.class.getName()+"."+method.getName(), id);
}
} );
System.out.println(mapper.queryById(5));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
 可行!!!
可行!!!
五、mybatis接口的使用方式
通过前面UserDao的设计,可以发现,UserDao中的代码都是模板化代码,都可以通过配置自动生成,因此,在实际开发中,Mapper可以按照如下方式设计
1.定义Mapper接口
Mapper接口中,只需要声明方法名,方法参数、方法返回等信息
public interface UserMapper {
public int addUser(User user);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.定义映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- 使用接口 代理的方式 namespace必须和接口的全路径名称一致 -->
<mapper namespace="com.sxt.dao.UserMapper">
<!-- id必须和接口声明的方法一致 -->
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.sxt.bean.User">
insert into t_user(name,age)values(#{name},#{age})
</insert>
</mapper>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
3.测试
@Test
public void add() throws IOException {
// 1.通过Resources对象加载配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 2.获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream );
// 3.通过SqlSessionFactory对象获取SQLSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setName("dpb");
user.setAge(22);
//通过Java动态代理自动提供了UserMapper的实现类
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
int count = mapper.addUser(user);
System.out.println("影响的行数:"+count);
session.commit();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
注意:
使用mapper接口方式必须满足:
| 序号 | 注意点 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 映射文件的namespace的值必须是接口的全路径名称 比如:com.dpb.dao.UserMapper |
| 2 | 接口中的方法名在映射文件中必须有一个id值与之对应。 |
| 3 | 映射文件的名称必须和接口的名称一致 |
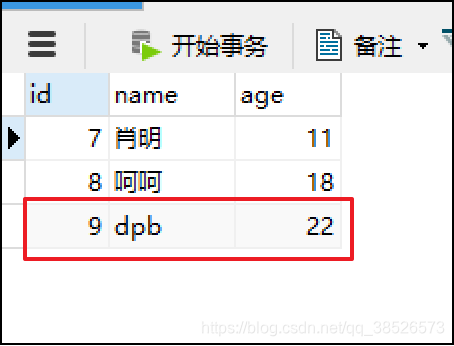
数据添加成功
文章来源: dpb-bobokaoya-sm.blog.csdn.net,作者:波波烤鸭,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:dpb-bobokaoya-sm.blog.csdn.net/article/details/86557327
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)