Spring之Aware接口介绍
【摘要】
在Bean对象的生命周期的方法中有好几个接口是Aware接口的子接口,所以弄清楚Aware接口对于理解Spring框架还是很有帮助的。
文章目录
Aware接口1.Aware系列接口的共性2...
在Bean对象的生命周期的方法中有好几个接口是Aware接口的子接口,所以弄清楚Aware接口对于理解Spring框架还是很有帮助的。
Aware接口
Aware接口从字面上翻译过来是感知捕获的含义。单纯的bean(未实现Aware系列接口)是没有知觉的;实现了Aware系列接口的bean可以访问Spring容器。这些Aware系列接口增强了Spring bean的功能,但是也会造成对Spring框架的绑定,增大了与Spring框架的耦合度。(Aware是“意识到的,察觉到的”的意思,实现了Aware系列接口表明:可以意识到、可以察觉到)
接口的源码如下:
public interface Aware {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
可以发现该接口中并没有定义任何方法,所以这是个标识接口。该接口的子接口有如下:
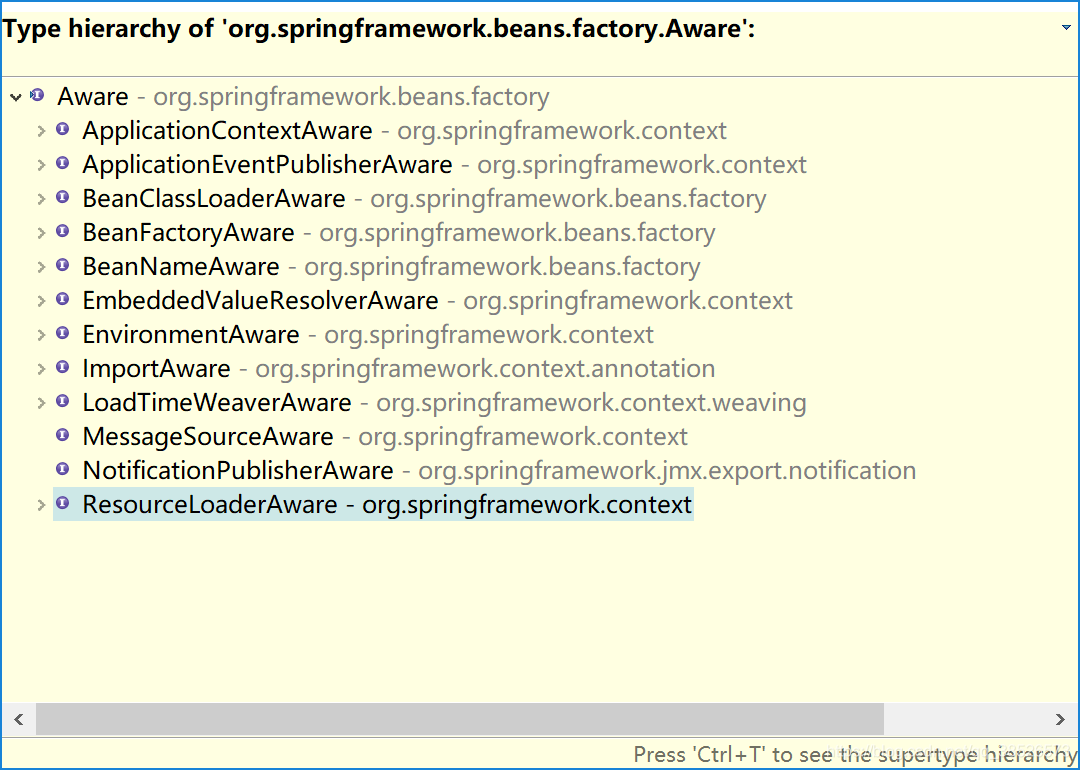
1.Aware系列接口的共性
- 都以“Aware”结尾
- 都是Aware接口的子接口,即都继承了Aware接口
- 接口内均定义了一个set方法
2.Aware子接口中的set方法
2.1ApplicationContextAware
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)
- 1
2.2BeanClassLoaderAware
void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader);
- 1
2.3BeanFactoryAware
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory)
- 1
2.4BeanNameAware
void setBeanName(String name);
- 1
…每个子接口都定义了set方法。而方法中的形参是接口Aware前面的内容,也就是当前Bean需要感知的内容。所以我们需要在Bean中声明相关的成员变量来接收。
3.举例说明
目标类
/**
* 实现了
* ApplicationContextAware
* BeanClassLoaderAware
* BeanFactoryAware
* BeanNameAware
* 接口
* @author dengp
*
*/
public class User implements ApplicationContextAware,BeanClassLoaderAware,BeanFactoryAware,BeanNameAware{
private int id;
private String name;
// 保存感知的信息
private String beanName;
// 保存感知的信息
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
// 保存感知的信息
private ApplicationContext ac;
// 保存感知的信息
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public BeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return beanFactory;
}
public ApplicationContext getAc() {
return ac;
}
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return classLoader;
}
public User(){
System.out.println("User 被实例化");
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getBeanName() {
return beanName;
}
/**
* 自定义的初始化方法
*/
public void start(){
System.out.println("User 中自定义的初始化方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", beanName=" + beanName + "]";
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println(">>> setBeanClassLoader");
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(">>> setApplicationContext");
this.ac = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println(">>> setBeanName");
this.beanName = name;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(">>> setBeanFactory");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
测试类
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = ac.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println("beanFactory:"+user.getBeanFactory());
System.out.println("beanName:"+user.getBeanName());
System.out.println("applicationContext:"+user.getAc());
System.out.println("classLoader:"+user.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(user);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
输出结果
User 被实例化
>>> setBeanName
>>> setBeanClassLoader
>>> setBeanFactory
>>> setApplicationContext
User 中自定义的初始化方法
beanFactory:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@4520ebad: defining beans [user]; root of factory hierarchy
beanName:user
applicationContext:org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@311d617d: startup date [Sun Mar 03 22:43:08 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy
classLoader:sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4aa298b7
User [id=0, name=波波烤鸭, beanName=user]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Aware系列接口,主要用于辅助Spring bean访问Spring容器
文章来源: dpb-bobokaoya-sm.blog.csdn.net,作者:波波烤鸭,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:dpb-bobokaoya-sm.blog.csdn.net/article/details/88095674
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)