Spring快速入门
引言
最近几天一直在忙着学习数据结构和算法,关于JavaEE的框架也有一阵子没更新了。那么今天就来聊一聊Spring框架吧,针对该框架写一篇快速入门的文章。
Spring简介
Spring框架是由于软件开发的复杂性而创建的。Spring使用的是基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。然而,Spring的用途不仅仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合性角度而言,绝大部分Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。
- 目的:解决企业应用开发的复杂性
- 功能:使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,并提供了更多的企业应用功能
- 范围:任何Java应用
Spring是一个轻量级控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
配置Bean
首先来说一说在Spring框架中如何去配置Bean。
通过一个简单案例感受一下:
首先得导入Spring框架的jar包,然后创建一个类:
package com.itcast.spring.bean;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void hello() {
System.out.println("hello:" + name);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
在传统的写法中,我们要想调用HelloWorld类的hello()方法,我们需要手动创建HelloWorld的实例,然后调用setName()方法给name赋值,接着调用hello()方法。但是有了Spring框架之后,对于对象的创建和属性的赋值都不需要我们操心,框架能够帮助我们完成。所以接下来创建Spring框架的配置文件applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.HelloWorld">
<property name="name" value="Spring"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
对于这段简单的配置,可以解释一下。bean是beans下的一个子节点,配置的是一个bean类的信息,然后是bean节点下的属性:
- id:标识容器中的bean,id是唯一的
- class:bean的全类名,因为框架是通过反射的方式在IOC容器中创建bean的实例,所以你需要提供类的全路径,这在很多框架中都能得到体现
然后是property,该节点配置的是bean类中的属性信息,name即为属性名,但是需要注意的是,这个name值是根据setXXX()方法进行匹配的,如果没有setXXX()方法或者setXXX()方法和类中的属性名不一致,将会导致异常产生。而value就是属性的值。
配置好后,我们编写测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
首先通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext去构造ApplicationContext 对象,传入配置文件名,接着通过getBean()方法得到HelloWorld实例,传入的是在配置文件中bean的id属性值。
运行结果:
hello:Spring
- 1
需要注意的是,在bean类中你必须提供一个无参的构造方法,因为反射的实现需要无参构造。
到这里,一个入门的Spring案例就完成了。
Spring容器
接下来,我们细细地研究一下。
在SpringIOC容器读取bean配置创建bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化,只有在容器实例化后,才可以从IOC容器中获取bean实例并使用。
在Spring中提供了两种类型的IOC容器实现:
- BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现
BeanFactory是Spring框架的基础设施,面向Spring本身 - ApplicationContext:提供了更多的高级特性,是BeanFactory的子接口
ApplicationContext面向使用Spring框架的开发者,几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用ApplicationContext而非底层的BeanFactory
但无论使用何种方式,配置文件的写法都是一样的。
ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,它有两个实现类:
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下加载配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统中加载配置文件
所以获得ApplicationContext的实例可以有两种方式,刚才的案例中使用的就是第一种方式。
获得了Spring容器后,我们是如何去获得bean实例的呢?
通过getBean()方法:
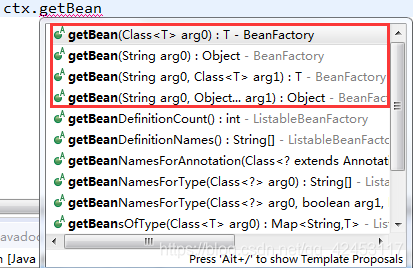
可以看到,ApplicationContext提供了多个getBean()方法的重载,所以对于bean实例的获取,除了通过id属性值获取以外,还可以通过bean的类型获取:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
helloWorld.hello();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
这样也能获取到bean的实例,而且有一个好处就是不用强制类型转换了。
属性值的注入
在Spring框架中,有两种方式可以对bean类的属性进行赋值:
- 属性注入
属性注入在开始的案例中已经使用到了,就是通过bean节点下的property节点进行注入,它通过setXXX()方法注入属性值,属性注入是实例应用开发中最常用的注入方式 - 构造方法注入
构造方法注入顾名思义就是通过构造方法注入属性值,它通过bean节点下的constructor-arg节点进行注入
对于构造方法注入属性值,有必要单独提取出来讲解一下,我们来看一个案例。
创建一个bean类:
package com.itcast.spring.bean;
public class Car {
private String brand;
private String corp;
private double price;
private int maxSpeed;
public Car(String brand, String corp, double price) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.corp = corp;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", corp=" + corp + ", price=" + price + ", maxSpeed=" + maxSpeed + "]";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
然后配置一下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 通过构造方法注入bean的属性值 -->
<bean id="car" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="ShangHai"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="250000"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
接下来编写测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:
Car [brand=Audi, corp=ShangHai, price=250000.0, maxSpeed=0]
- 1
因为是通过构造方法注入属性值,所以可以不需要setXXX()方法,从配置中可以知道,属性值是通过配置的顺序进行注入的,那么接下来我们修改一下Car类:
package com.itcast.spring.bean;
public class Car {
private String brand;
private String corp;
private double price;
private int maxSpeed;
public Car(String brand, String corp, double price) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.corp = corp;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String brand, String corp, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.corp = corp;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", corp=" + corp + ", price=" + price + ", maxSpeed=" + maxSpeed + "]";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
我们在Car类中新增了一个构造方法,然后我们重新配置一下bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="car2" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="BMW"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="BeiJing"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="240"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
我们想通过这三个属性值来得到一个Car的实例,接下来编写测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car2");
System.out.println(car);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:
Car [brand=BMW, corp=BeiJing, price=240.0, maxSpeed=0]
- 1
问题就出现了,我明明是想通过第二个构造方法构造对象,传入的240是maxSpeed的值,但它仍然使用了第一个构造方法,所以仅仅靠参数顺序来注入是不合理的。
不过不用担心,Spring为我们提供了类型匹配来区分不同的构造方法,修改配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="car2" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="BMW" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="BeiJing"
type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="240" type="int"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
其它地方不用修改,重新运行一下测试代码,结果如下:
Car [brand=BMW, corp=BeiJing, price=0.0, maxSpeed=240]
- 1
这样就达到了我们想要的结果。
对于属性值的注入,还可以通过子节点下的value节点进行注入,效果是一样的。
引用类型属性值的注入
对字面值的注入有了一定的了解之后,我们单独看一下引用类型的属性值该如何注入:
先创建一个bean类:
package com.itcast.spring.bean;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Car car;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
在配置文件中配置一下Person类:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="car2" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="BMW" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="BeiJing"
type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="240" type="int"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tony"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="car" ref="car2"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
对于引用类型Car,我们可以通过property节点的ref属性指向对car的引用,因为上面我配置了一个id为car2的bean,所以这里直接通过id引用指向它。
编写测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) ctx.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行效果:
Person [name=Tony, age=18, car=Car [brand=BMW, corp=BeiJing, price=0.0, maxSpeed=240]]
- 1
和上面类似,也可以使用子节点ref进行配置。
<bean id="person" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tony"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="car">
<ref bean="car2"/>
</property>
</bean>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
我们还可以在属性或构造器里包含一个bean的声明,这样的bean称为内部bean,无法被外部访问。
<bean id="person" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tony"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="car">
<bean class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="ShangHai" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="250000" type="double"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Spring和Struts、Hibernate框架一样,也支持级联属性。所以我们还可以通过级联属性赋值。
<property name="car.price" value="150000"></property>
- 1
可以通过这样的方式给Car类的属性赋值。
集合属性值注入
在引用类型中,又有一个特殊的群体,集合。包括Set、List、Map。
修改Person类代码:
package com.itcast.spring.bean;
import java.util.List;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<Car> cars;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", cars=" + cars + "]";
}
public List<Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
public void setCars(List<Car> cars) {
this.cars = cars;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
其中有一个集合类型Car,该如何在配置文件中进行配置呢?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 通过构造方法注入bean的属性值 -->
<bean id="car" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="Audi"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="ShangHai"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="250000"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="car2" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Car">
<constructor-arg value="BMW" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="BeiJing" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="240" type="int"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 如何配置集合属性 -->
<bean id="person2" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="Jack"></property>
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<property name="cars" >
<list>
<ref bean="car"/>
<ref bean="car2"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
编写测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) ctx.getBean("person2");
System.out.println(person);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:
Person [name=Jack, age=20, cars=[Car [brand=Audi, corp=ShangHai, price=250000.0, maxSpeed=0], Car [brand=BMW, corp=BeiJing, price=150000.0, maxSpeed=240]]]
- 1
对于Set和Map集合,Spring提供了set标签和map标签进行配置,配置原理相同,不作重复介绍。Map集合会有点特殊,因为它是以键值对的方式存储的,所以它是通过Map节点下的子节点entry进行配置的,entry节点包含key和value-ref属性,也简单配置一下给大家看看吧。
<map>
<entry key="aa" value-ref="car"></entry>
<entry key="bb" value-ref="car2"></entry>
</map>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
属性文件值注入
还有一种特殊类型,Properties,就是我们熟知的配置文件,在Spring中,同样可以通过配置直接将值注入到该属性中,看一个案例你们就会明白。
创建一个bane类:
package com.itcast.spring.bean;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DataSource {
private Properties properties;
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DataSource [properties=" + properties + "]";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
然后对该类进行配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.itcast.spring.bean.collection.DataSource">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="user">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql:///test</prop>
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
配置完成后,编写测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:
DataSource [properties={user=root, url=jdbc:mysql:///test, password=123456, driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver}]
- 1
实现过程非常简单,这样就将对数据库的配置注入到Properties属性中,关于对数据库的操作就可以通过这样进行封装。
鉴于是对Spring的快速入门,所以也没有去深入地介绍Spring的一些内容,关于Spring的快速入门,就说到这里,接下来还会出几篇Spring高级或者Spring一些其它的知识点。
推荐阅读
文章来源: blizzawang.blog.csdn.net,作者:·wangweijun,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blizzawang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/99833888
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)