【Android】安卓开发常用的布局
【摘要】
前言
布局是安卓开发中很基础的部分,作为移动开发的初学者,我也在不断的学习进步中~
正文
文件的位置
一般都在layout文件夹内。
一个布局文件,一般对应一个Activity,在代码中...
前言
布局是安卓开发中很基础的部分,作为移动开发的初学者,我也在不断的学习进步中~
正文
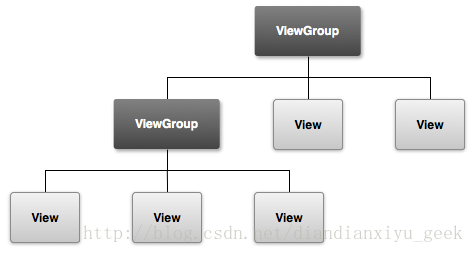
文件的位置
一般都在layout文件夹内。
一个布局文件,一般对应一个Activity,在代码中通过
setContentView(R.layout.first_layout);
- 1
将页面跟逻辑关联起来
布局的分类
常见的布局
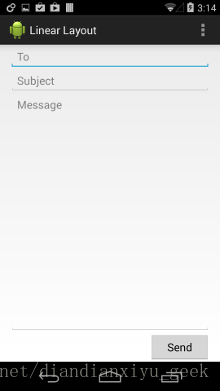
LinearLayout,线性布局方式
一种使用单个水平行或垂直行来组织子项的布局。它会在窗口长度超出屏幕长度时创建一个滚动条。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingRight="16dp"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/to" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/subject" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="top"
android:hint="@string/message" />
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:text="@string/send" />
</LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
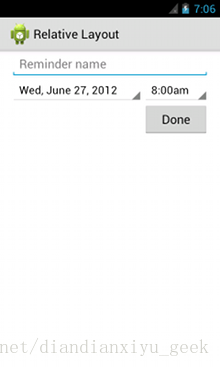
Relative Layout,相对布局
让您能够指定子对象彼此之间的相对位置(子对象 A 在子对象 B 左侧)或子对象与父对象的相对位置(与父对象顶部对齐)。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingRight="16dp" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/reminder" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/dates"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/name"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" />
<Spinner
android:id="@id/times"
android:layout_width="96dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/name"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="96dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/times"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="@string/done" />
</RelativeLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
WebView,网页布局
展示网页
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<WebView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/webview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
/>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
//加载网页
WebView myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview);
myWebView.loadUrl("http://www.example.com");
- 1
- 2
- 3
//网络访问权限
<manifest ... >
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
...
</manifest>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
使用适配器构建布局
如果你的元素是动态加载的,可以用下面的布局。
ListView,列表视图
显示滚动的单列列表。
public class ListViewLoader extends ListActivity
implements LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor> {
// This is the Adapter being used to display the list's data
SimpleCursorAdapter mAdapter;
// These are the Contacts rows that we will retrieve
static final String[] PROJECTION = new String[] {ContactsContract.Data._ID,
ContactsContract.Data.DISPLAY_NAME};
// This is the select criteria
static final String SELECTION = "((" +
ContactsContract.Data.DISPLAY_NAME + " NOTNULL) AND (" +
ContactsContract.Data.DISPLAY_NAME + " != '' ))";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Create a progress bar to display while the list loads
ProgressBar progressBar = new ProgressBar(this);
progressBar.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, Gravity.CENTER));
progressBar.setIndeterminate(true);
getListView().setEmptyView(progressBar);
// Must add the progress bar to the root of the layout
ViewGroup root = (ViewGroup) findViewById(android.R.id.content);
root.addView(progressBar);
// For the cursor adapter, specify which columns go into which views
String[] fromColumns = {ContactsContract.Data.DISPLAY_NAME};
int[] toViews = {android.R.id.text1}; // The TextView in simple_list_item_1
// Create an empty adapter we will use to display the loaded data.
// We pass null for the cursor, then update it in onLoadFinished()
mAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, null,
fromColumns, toViews, 0);
setListAdapter(mAdapter);
// Prepare the loader. Either re-connect with an existing one,
// or start a new one.
getLoaderManager().initLoader(0, null, this);
}
// Called when a new Loader needs to be created
public Loader<Cursor> onCreateLoader(int id, Bundle args) {
// Now create and return a CursorLoader that will take care of
// creating a Cursor for the data being displayed.
return new CursorLoader(this, ContactsContract.Data.CONTENT_URI,
PROJECTION, SELECTION, null, null);
}
// Called when a previously created loader has finished loading
public void onLoadFinished(Loader<Cursor> loader, Cursor data) {
// Swap the new cursor in. (The framework will take care of closing the
// old cursor once we return.)
mAdapter.swapCursor(data);
}
// Called when a previously created loader is reset, making the data unavailable
public void onLoaderReset(Loader<Cursor> loader) {
// This is called when the last Cursor provided to onLoadFinished()
// above is about to be closed. We need to make sure we are no
// longer using it.
mAdapter.swapCursor(null);
}
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
// Do something when a list item is clicked
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
GridView,网格视图
显示滚动的行列网格。
特别推荐
ConstraintLayout,约束布局
这种布局综合的大部分布局的优点,更容易的去调节元素的边距。
详情参考 https://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/constraint/ConstraintLayout.html
以后详细写下相关的文章。
不推荐的布局
由于版本的更新,下面的这些布局不再推荐。官方文档里也没有推荐这些布局了。
- AbsoluteLayout,绝对位置布局
- FrameLayout,帧布局
- TableLayout,表格布局
总结
布局部分,很容易去类比网页开发的部分。
html也是xml,所以对理解这些很方便。
持续的学习就是进步。
参考资料
- https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/devinzhang/archive/2012/01/19/2327535.html
- https://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/constraint/ConstraintLayout.html#GoneMargin
- https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/linear.html
- https://developer.android.com/guide/webapps/webview.html#UsingJavaScript
文章来源: coderfix.blog.csdn.net,作者:小雨青年,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:coderfix.blog.csdn.net/article/details/78923274
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)