碰到的问题
使用vagrant启动虚拟机时,出现如下警告:
vagrant up default: Warning: Authentication failure. Retrying...
原因分析
授权失败主要原因:
-
虚拟机获取不到物理机的公钥(有疑问的小伙伴,建议先了解一下SSH)
解决方案
-
将公钥复制到虚拟机vagrant用户家目录下的authorized_keys文件中
-
Vagrantfile中指定物理机当前用户的私钥路径
步骤一、确认物理机中已经生成了公钥和私钥
以windows系统为例,查看当前登录用户的文件夹下是否包含.ssh文件夹,以及.ssh文件夹下是否包含id_rsa(私钥)、id_rsa.pub(公钥)两个文件
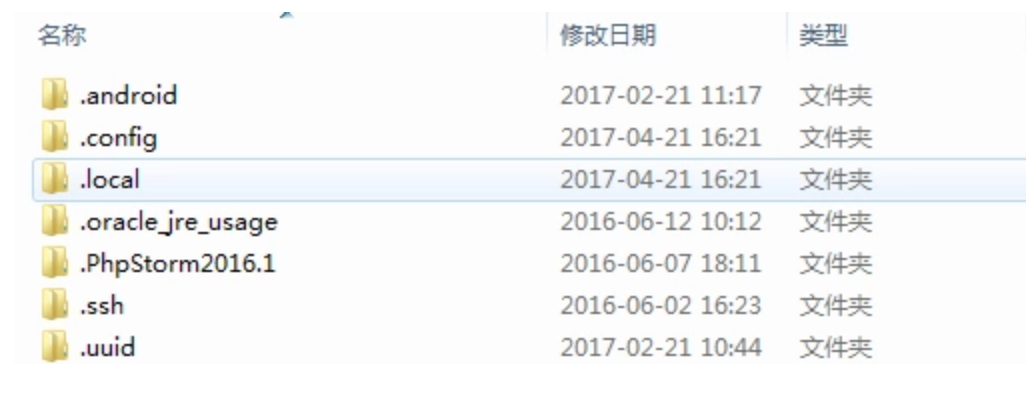
.ssh文件夹文件如下: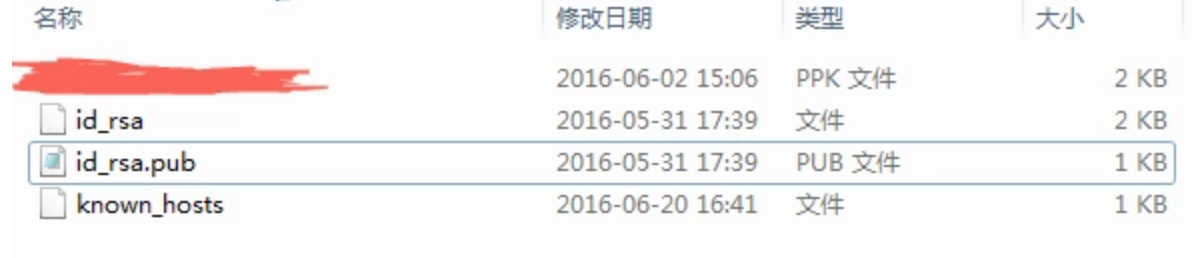
注意:必须打开 【显示隐藏的文件、文件夹或驱动器】才能看到.ssh文件夹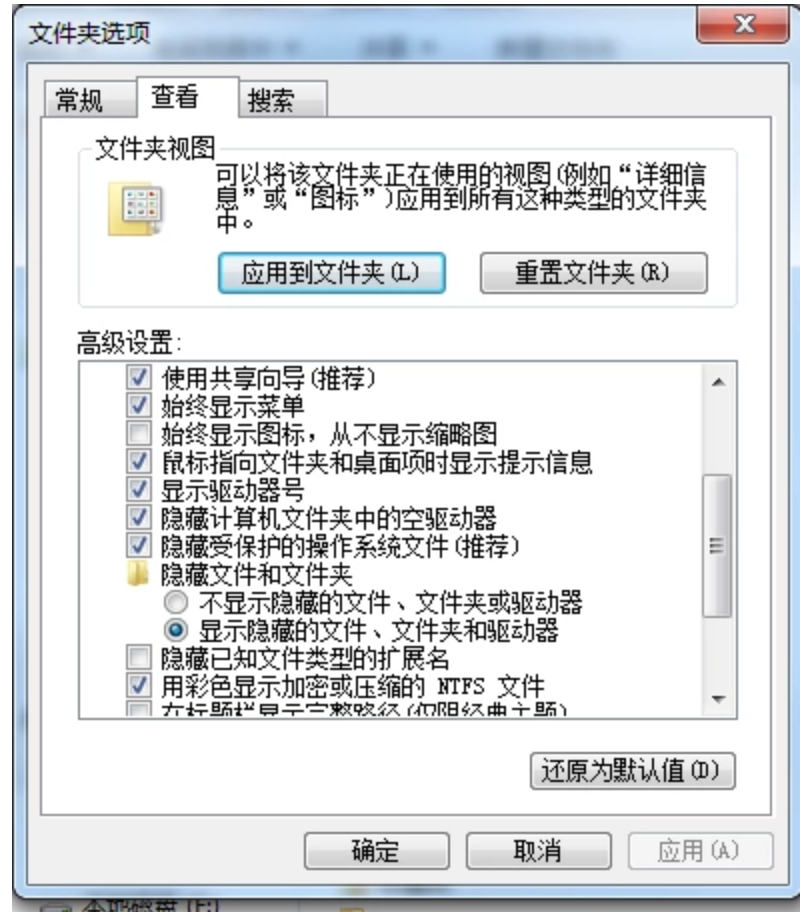
如果已经包含id_rsa(私钥)、id_rsa.pub(公钥)两个文件则可跳过步骤一。如果没有两个文件则继续往下看
生成公钥和私钥有多种方法,我们使用最常用的办法。开发者一般都会安装git。直接使用git bash生成一下就好了
进入git安装目录
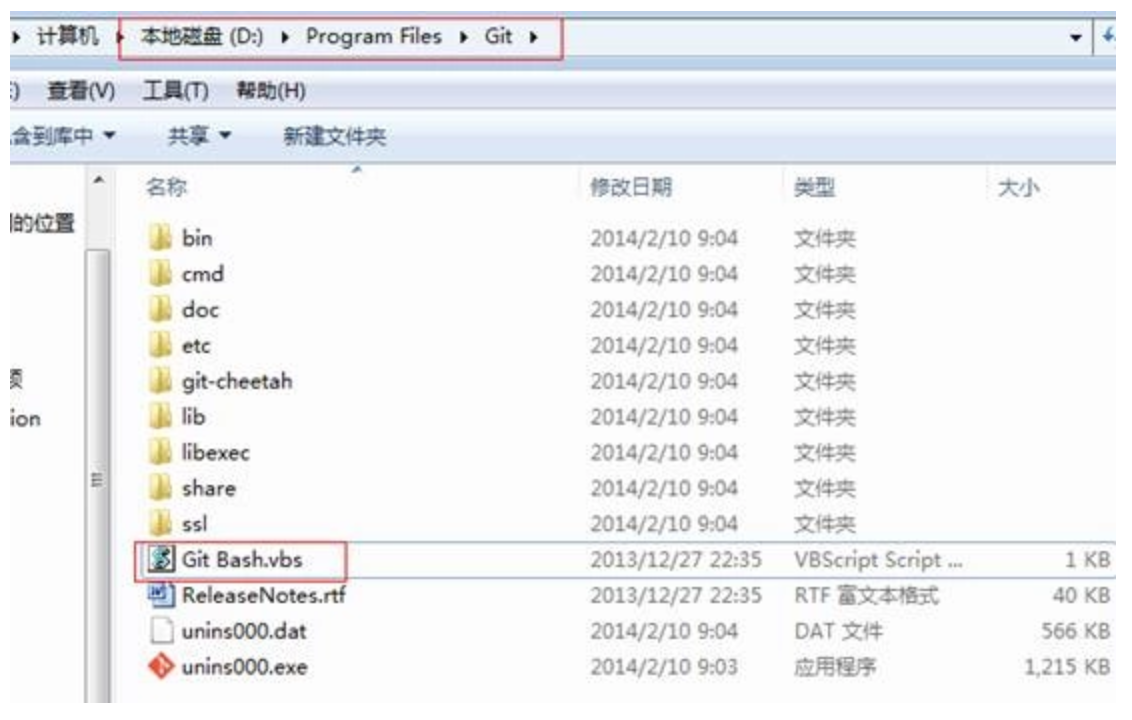
运行git-bash.vbs

执行ssh-keygen
一路回车,完成后,记住下面的地址

进入该路径,发现有两个文件:

这两个文件的含是:首先,他们是1对的,两者缺1不可,id_rsa 是私钥,id_rsa.pub是公钥
步骤二、将公钥复制到authorized_keys文件中
小伙伴可能奇怪,vagrant都报错了,怎么还能进入虚拟机?没错!其实此时虚拟机已经启动完毕了,只不过此时不能接受vagrant的命令,也无法设置共享目录。
你只需要用客户端工具(例如:Xshell)登录虚拟机
一般来说默认的用户名是vagrant,密码也是vagrant。
进入.ssh目录
查看是否有authorized_keys文件
-
[vagrant@localhost .ssh]$ pwd
-
/home/vagrant/.ssh
-
[vagrant@localhost .ssh]$ ls -al
-
total 8
-
drwx------ 2 vagrant root 28 Jul 26 2016 .
-
drwx------. 8 vagrant vagrant 4096 Nov 6 11:02 ..
-
-rw------- 1 vagrant vagrant 786 Jul 26 2016 authorized_keys
-
[vagrant@localhost .ssh]$
如果authorized_keys文件不存在,则自己手动创建一下。
注意authorized_keys 文件的权限是600,所有者是vagrant,所属组也是vagrant
-
[vagrant@localhost .ssh]$ touch authorized_keys
-
[vagrant@localhost .ssh]$ chmod 600 authorized_keys
复制公钥
如果已经存在authorized_keys文件,复制物理机公钥文件id_rsa.pub的内容,粘贴到authorized_keys文件中。每个公钥只占一行
注意:公钥内容只占一行
例如我的authorized_keys文件中有两个公钥
-
[vagrant@localhost .ssh]$ vim authorized_keys
-
1 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDlo4N35+9OM2UCAC82E4RtiqROZU/jI6bgg76QAA56cGdLwk4CNZzbn309nNRtO7tyBtWCyFx2AOn3Hd8hIFWiokMgxlf3eSjowT9dZqmbhGrYzAkPq r63rpHUX7M4FVjMLtoREqrGbBQZ7uZItViKeXXXl7bsGOUserLchzi+p3PJgjmw5j6ea+Kj2P7EThvcevoEPLcwGyckCTEiYo8nJ21K5bkmKCi2F8kaaJ9zbIeJ/2woayUkoZeufNo3A/gZx2bvHYAiFT 4RYLDwjrspq7pQS5Cs83YUGvolPKQfCrJRH3N+sNaeHx1NzEULMvQNxgEsFIVpi5k7OBIf4BY/ vagrant
-
2 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCov9Z/3qVWXkxLS6koRWxNu9lEt+e0+/6M+XCtDx7qWiCCZovNSCbKAHO3gwCV3myIyoiP/9bv2d0Sw18d/5BMYHWT4l85IZdF87no0Euu8Yt1w4BEU rCbL0jrDXHlVBhMyCeETr7BKDlM56meiNMo/PvNuN3qcp6tukLUXgrFRQ24hgg1mMvqQ0Km5UHYnHr+Vygc3udEVEEG5Px+04y6ap8gRZg7tKVgckdXZ7+1rNJtTXqR81uXXXbyown4eoccqsUTOK3iUs 2GdFwH/t3unbCSLu13UKDcLGG6hKG/x4aA1itIl3NdbzODgbte8UGXlifomayG+PTaf1tvb+n/ dc@GZ-Design003
步骤三、在物理机的Vagrantfile中添加以下内容
-
config.ssh.private_key_path = "C:/Users/dc/.ssh/id_rsa"
-
config.ssh.forward_agent = true
Vagrantfile全部配置内容如下:
-
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
-
-
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
-
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
-
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
-
# you're doing.
-
Vagrant.configure(2) do |config|
-
config.vm.box = "web"
-
config.ssh.private_key_path = "C:/Users/dc/.ssh/id_rsa"
-
config.ssh.forward_agent = true
-
# config.winnfsd.logging="on"
-
# config.winnfsd.uid=1
-
# config.winnfsd.gid=1
-
# config.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant",type:"nfs"
-
-
config.vm.define :web do |web|
-
web.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
-
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "web", "--memory", "2048", "--cpus","2"]
-
end
-
web.vm.box = "web"
-
web.vm.hostname = "web"
-
web.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant"
-
# web.vm.network:private_network, ip: "192.168.33.11"
-
web.vm.network "public_network"
-
end
-
config.vm.define :php do |php|
-
php.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
-
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "php", "--memory", "512"]
-
end
-
php.vm.box = "php"
-
php.vm.network:private_network, ip: "192.168.33.10"
-
# php.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
-
php.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant",type:"nfs"
-
php.winnfsd.logging="on"
-
php.winnfsd.uid=1
-
php.winnfsd.gid=1
-
php.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant"
-
end
-
config.vm.define :swoole do |swoole|
-
swoole.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
-
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "swoole", "--memory", "512"]
-
end
-
swoole.vm.box = "swoole"
-
# swoole.vm.network:private_network, ip: "192.168.33.12"
-
swoole.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.33.12"
-
# swoole.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant",type:"nfs"
-
swoole.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant"
-
end
-
config.vm.define :master do |master|
-
master.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
-
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "master", "--memory", "512"]
-
end
-
master.vm.box = "master"
-
master.vm.network "public_network"
-
master.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant"
-
end
-
config.vm.define :slave do |slave|
-
slave.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
-
v.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "slave", "--memory", "512"]
-
end
-
slave.vm.box = "slave"
-
slave.vm.network "public_network"
-
slave.vm.synced_folder "./","/vagrant"
-
end
-
end
-
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
-
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
-
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
-
-
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
-
# boxes at https://atlas.hashicorp.com/search.
-
-
-
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
-
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
-
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
-
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
-
-
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
-
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
-
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
-
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
-
-
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
-
# using a specific IP.
-
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
-
-
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
-
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
-
# your network.
-
# config.vm.network "public_network"
-
-
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
-
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
-
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
-
# argument is a set of non-required options.
-
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
-
-
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
-
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
-
# Example for VirtualBox:
-
#
-
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
-
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
-
# vb.gui = true
-
#
-
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
-
# vb.memory = "1024"
-
# end
-
#
-
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
-
# information on available options.
-
-
# Define a Vagrant Push strategy for pushing to Atlas. Other push strategies
-
# such as FTP and Heroku are also available. See the documentation at
-
# https://docs.vagrantup.com/v2/push/atlas.html for more information.
-
# config.push.define "atlas" do |push|
-
# push.app = "YOUR_ATLAS_USERNAME/YOUR_APPLICATION_NAME"
-
# end
-
-
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
-
# Puppet, Chef, Ansible, Salt, and Docker are also available. Please see the
-
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
-
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
-
# sudo apt-get update
-
# sudo apt-get install -y apache2
-
# SHELL
步骤四、重启虚拟机
在物理机的命令行重启虚拟机
vagrant reload XXXX
转载:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011925921


评论(0)