数据库SQL语句总结大全
一.数据库基础概念
数据库就是用来存储和管理数据的仓库!
二.SQL概述
SQL(Structured Query Language)是“结构化查询语言”,它是对关系型数据库的操作语言。通过SQL可以对数据库的数据进行增删改查。
1)分类

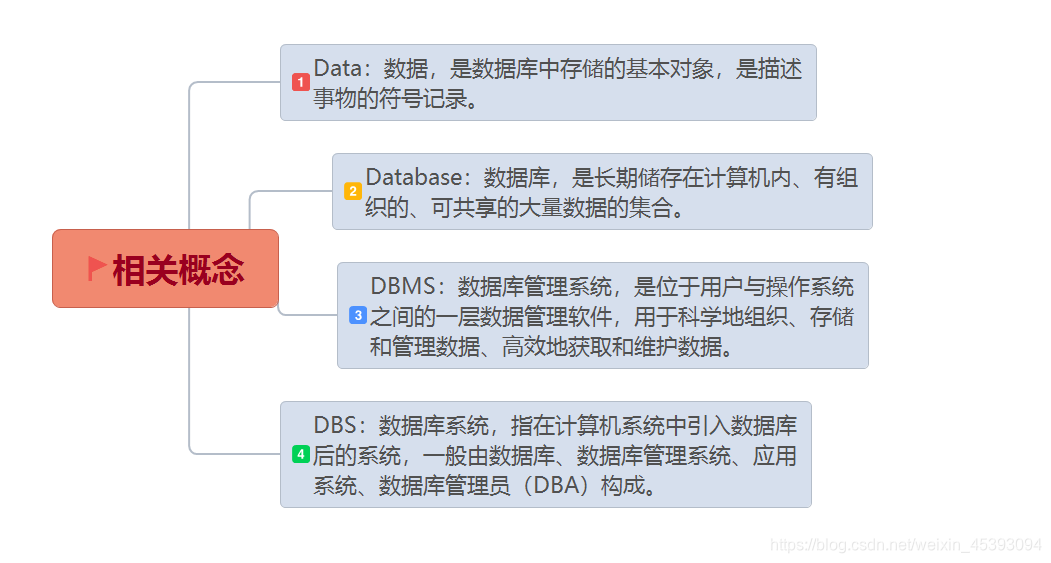
2)相关概念
- 数据库: 数据的仓库,保存数据的地方,一般一个项目对应一个数据库。
- 表: 数据库中实际保存数据的地方,数据会分类存储,如:学生表、教员表、班级表、院系表等。
- 行: 表中的一行记录(数据),如:学生表中一行就是一个学生的信息。
- 列(字段):每个类型数据的一部分信息,类似对象中的属性,如:学生表中学号、姓名、年龄等。
- 主键:一个特殊的列,用于唯一标识一行记录,每一行数据不能重复、不能为空,如:学生表的学号,一个表只能有一个主键。
3) 增删改案例
①DDL:数据定义语言
- 创建数据库
create database 数据库名;
例:
create database student default character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_general_ci;
① default character set 指定数据库的默认字符编码utf8和utf8mb4
②utf8占3个字节,不能支持特殊符号 utf8mb4占4个字节,兼容性好
③collate 是文字排序方式,utf8mb4_general_ci 是一般排序方式,忽略大小写
-
使用数据库
use 数据库名; -
删除数据库
①
sql drop database 数据库名;
②sql drop database if exists 数据库名; 存在数据库再删除
//如果数据库存在,删除数据库
drop database if exists student;
- 1
- 2
- 创建表
create table 表名
(
列名 数据类型 [约束],
列名 数据类型 [约束],
列名 数据类型 [约束]
...
);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
| 约束 | 概念解释 |
|---|---|
| 主键 | primary key (不能重复、不能为空、表只有一个) |
| 自增 | auto_increment(只能用于整型数据) |
| 非空 | not null(必须填写) |
| 唯一 | unique(不能重复) |
-- 创建学生表
create table tb_student
(
-- 学生编码,主键、自动增长
stu_id int primary key auto_increment,
stu_name varchar(20) not null,
stu_age int not null,
stu_gender varchar(1) not null,
stu_address varchar(200)
);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 删除表
①sql drop table 表名;
②sql drop table if exists 表名;
-- 存在学生表,先删除
drop table if exists tb_student ;
- 1
- 2
②DML:数据管理语言
-
单行插入
-
insert into 表名(列名,列名,列名,列名) values(值,值,值,值);
-- 插入学生信息
insert into tb_student(stu_name,stu_age,stu_gender,stu_address)
values('王五',20,'男','北京');
- 1
- 2
- 3
注意:列的个数和类型和值的个数、类型一致
自动增长的列不用插入。
- 多行插入
insert into 表名(列名,列名,列名,列名) values (值,值,值,值),(值,值,值,值),(值,值,值,值);
insert into tb_student(stu_name,stu_age,stu_gender,stu_address)
values('赵六',28,'男','北京'),('马七',25,'女','成都');
- 1
- 2
- 删除
全部删除: delete from 表名;带条件的删除 :delete from 表名 where 条件;清空表: truncate table 表名;- 更新
update 表名 set 列=值,列=值,列=值 [where 条件];
-- 更新马七的年龄和地址
update tb_student set stu_age = 19,stu_address='南京'
where stu_name = '马七';
- 1
- 2
- 3
③DQL:数据查询语言
-
查询表的所有记录
-
select * from 表名; -
*代表所有列,没有条件就查询所有行 -
查询部分列
-
select 列名,列名,列名 from 表名; -
给列加别名
-
select 列名 as 别名,列名 别名,列名 别名 from 表名; -
带条件的查询
-
select * from 表名 where 条件; -
例:查询编号为3的学生
select * from tb_student where stu_id = 3;
- 1
- 例:查询编号不为3的学生
!=和<>都表示不相等
select * from tb_student where stu_id != 3;
or
select * from tb_student where stu_id <> 3;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 例:查询年龄大于20的学生
select * from tb_student where stu_age > 20;
- 1
-
例:查询年龄在20到25之间的学生
-
sql 相当于Java的&&,表示两个条件同时成立 表示值在某个范围内,可以使用between 值1 and 值2;
select * from tb_student where stu_age >= 20 and stu_age <= 25;
select * from tb_student where stu_age between 20 and 25;
- 1
- 2
- 例:查询地址是武汉或上海的学生
条件1 or 条件2 相当于Java的||,表示两个条件只需要一个成立
select * from tb_student where stu_address = '武汉' or stu_address = '上海';
- 1
表示值在几个值之间任意一个,可以使用in(值1,值2)
select * from tb_student where stu_address in('武汉','上海');
- 1
- 例:查询年龄不在20到25之间的学生
not 条件 相当于Java的!,条件取反
select * from tb_student where stu_age not between 20 and 25;
- 1
- 按年龄排序
order by 列 [asc|desc] 写在查询语句最后,默认情况是升序
select * from tb_student order by stu_age;
select * from tb_student order by stu_age desc;
- 1
- 2
- 例:分页查询,一页显示4个学生,显示前5页学生
limit 开始位置, 长度limit 长度默认从第一行开始
select * from tb_student limit 0,4;
select * from tb_student limit 4,4;
select * from tb_student limit 8,4;
select * from tb_student limit 12,4;
select * from tb_student limit 16,4;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 例:查询年龄最大的学生
//先desc降序排列然后取第一个值
select * from tb_student order by stu_age desc limit 1;
- 1
- 2
-
模糊查询
-
like '模糊查询字符串' 两个通配符: % 任意长度的字符 _ 任意的一个字符 -
例:查询姓张的学生
select * from tb_student where stu_name like '张%';
- 1
- 例:查询姓名带小的学生
select * from tb_student where stu_name like '%小%';
- 1
- 查找第二位是3或5的手机号
列 regexp '正则表达式'
select * from tb_student where stu_tel regexp '^1[35]\\d{9}$';
- 1
- 统计(聚合)函数
count(*) 行数 max(列) 最大值 min(列) 最小值 sum(列) 总和 avg(列) 平均值
select count(*) 人数,max(stu_age) 最大年龄,min(stu_age) 最小年龄,sum(stu_age) 年龄总和,avg(stu_age) 平均年龄 from tb_student;
- 1
- 例:查询不同地区学生的平均年龄
group by 列 分组查询
select avg(stu_age) 平均年龄,stu_address 地区 from tb_student
group by stu_address;
- 1
- 2
- 例:查询男女学生各自人数
select count(*) 人数,stu_gender 性别 from tb_student group by stu_gender;
- 1
-
例:查询学生的平均年龄低于20的地区
-
where 在分组之前进行筛选 having 在分组之后进行筛选 where ——> group by ——> having
select avg(stu_age) 平均年龄,stu_address 地区 from tb_student
group by stu_address having avg(stu_age) < 25;
- 1
- 2

Don’t aim for success if you want it; just do what you love and believe in, and it will come naturally.
2020.02.28
文章来源: blessing.blog.csdn.net,作者:辰兮要努力,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blessing.blog.csdn.net/article/details/104533623
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)