【线程池工具类】打卡学习Java线程池(案例详解)
【辰兮要努力】:hello你好我是辰兮,很高兴你能来阅读,昵称是希望自己能不断精进,向着优秀程序员前行!
博客来源于项目以及编程中遇到的问题总结,偶尔会有读书分享,我会陆续更新Java前端、后台、数据库、项目案例等相关知识点总结,感谢你的阅读和关注,希望我的博客能帮助到更多的人,分享获取新知,大家一起进步!
吾等采石之人,应怀大教堂之心,愿大家奔赴在各自的热爱里…
一、初识线程池
hello 本期给大家分享线程池在Java项目中的真实案例,欢迎打卡!
线程池入门参考:Java工作一年了,不会还不懂Java线程池的使用吧?(代码详解)

线程池优点
1、降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
2、提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。
3、提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制地创建,不仅会消耗系统资源。
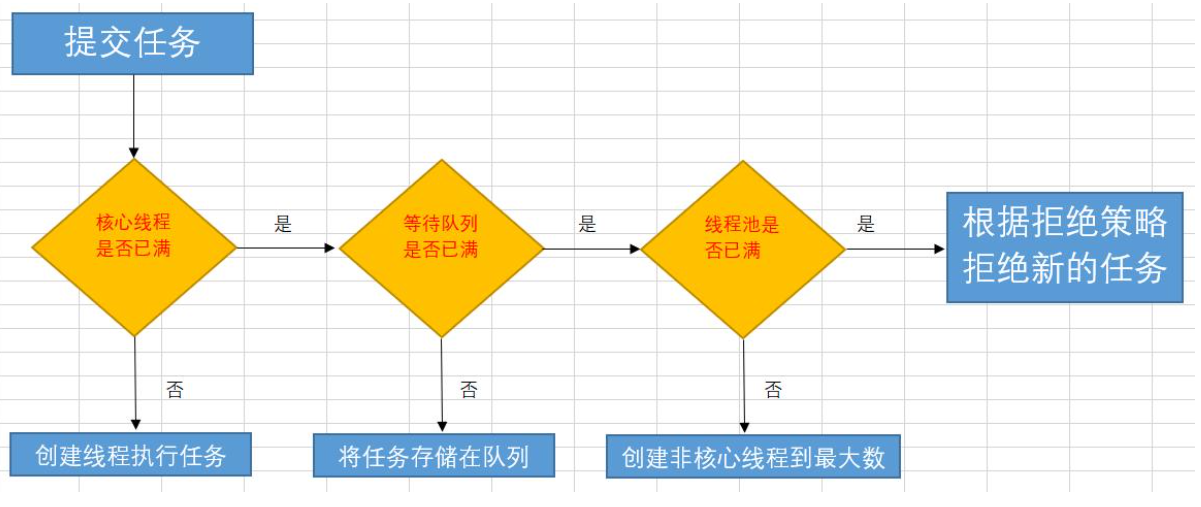
线程池创建线程的流程和执行任务的流程我们一定要搞懂
二、进阶线程池
初学者是否有个这样的疑惑,实际项目中我们到底如何写线程池帮助我们创建线程执行任务?

线程池工具类在项目中的创建有很多种写法,如下分享一种案例写法,欢迎实践

分享一下线程池的工具类
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* @program: ExecutorConfig
* @description: 线程池相关帮助类
* @author: 辰兮要努力
* @create: 2021-09-25 10:23
*/
public class ExecutorConfig {
/**
* 记录对应的日志
*/
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ExecutorConfig.class);
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor thPoolInstance = null;
/**
* 线程池
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
* @author 辰兮要努力
* @date 2021-9-25 10:58:57
*/
public static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getThreadPoolInstance() {
if (thPoolInstance != null) {
return thPoolInstance;
}
synchronized (ExecutorConfig.class) {
if (thPoolInstance == null) {
try {
// 获取统一线程池
thPoolInstance = ApplicationContextHolder.getBean(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.class);
if (thPoolInstance == null) {
// 如果统一线程池还是为空,将启动本地创建线程,进行保护。
thPoolInstance = getThPoolInstance();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("getThreadPoolInstance -> create thread pool error", e);
} finally {
// 如果统一线程池还是为空,将启动本地创建线程,进行保护。
if (thPoolInstance == null) {
thPoolInstance = getThPoolInstance();
}
}
}
}
return thPoolInstance;
}
/**
* 获取本地线程池
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
* @author 辰兮要努力
* @date 2021-9-25 10:58:53
*/
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getThPoolInstance() {
/**
* 如果对应的线程池不为空则直接返回,如果为空
*/
if (thPoolInstance != null) {
return thPoolInstance;
}
try {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数10:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
// 最大线程数15:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
executor.setMaxPoolSize(15);
// 缓冲队列25:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(25);
// 允许线程的空闲时间200秒:当超过了核心线程出之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(200);
// 线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便定位处理任务所在的线程池
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("chenXI-");
/**
* 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略:这里采用了CallerRunsPolicy策略, 当线程池没有处理能力的时候,
* 该策略会直接在 execute 方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务; 如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务
*/
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 设置线程池关闭的时候等待所有任务都完成再继续销毁其他的Bean
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 设置线程池中任务的等待时间,如果超过这个时候还没有销毁就强制销毁,以确保应用最后能够被关闭,而不是阻塞住。
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60 * 2);
executor.initialize();
thPoolInstance = executor;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("getThPoolInstance-> create thread pool error", e);
}
return thPoolInstance;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
在spring环境中获取非spring容器管理的bean
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**
* @program: ApplicationContextHolder
* @description: 在spring环境中获取非spring容器管理的bean
* @author: 辰兮要努力
* @create: 2021-9-25 13:30:02
*/
public class ApplicationContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) throws BeansException {
applicationContext = ctx;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
创建一个demo模拟一下一个接口处理多层业务
/**
* @program: ThreadPoolDemo
* @description: 模拟业务场景:相关使用案例
* @author: 辰兮要努力
* @create: 2021-09-25 10:43
*/
public class ThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 在一个业务逻辑层面模拟处理三个业务事情
* 如下业务1,2
*/
long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
//业务1:处理一下相关数据,同时计算出线程的执行时间
handleNum();
System.out.println("任务1执行完---------------");
//业务2:用线程池创建一个线程帮助我们处理相关业务,同时计算出线程的执行时间
ExecutorConfig.getThreadPoolInstance().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
/**
* 模拟一下新的业务逻辑
*/
handleNum();
// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
// 1000毫秒以内的随机数,模拟业务逻辑处理
System.out.println("任务2执行完---------------");
}
});
//业务:计算一下当前主线程的执行时间
long lastTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("主线程执行完-执行时间:"+ (lastTime1 - startTime1));
}
//创建一个方法模拟正常的业务逻辑,花费一定的时间
public static void handleNum(){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
i = i ++;
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long lastTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程执行时间:"+ (lastTime - startTime));
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
程序分析:程序在主线程中正常执行,我们利用线程池创建出了一个单独的线程帮助我们处理业务二
输出结果
main线程执行时间:3682
任务1执行完---------------
主线程执行完-执行时间:4034
chenXI-1线程执行时间:3353
任务2执行完---------------
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
我们可以将上述逻辑修改为传统的串行的执行方式,我们发现程序的运行时间和响应时间明显加长!
为什么我们会使用多线程呢?

保证应用程序的响应性能,即良好的用户体验。同时可以提高CPU的利用率。
如上当业务逻辑复杂且响应时间慢的情况下,我们可以考虑利用线程池开启线程帮助我们处理相关业务逻辑。(异步处理)
本期讲解到此结束,如上案例均可以在自己电脑实践
小伙伴们国庆假期愉快!爱生活、爱自己、爱你所在的每一天!
非常感谢你阅读到这里,如果这篇文章对你有帮助,希望能留下你的点赞👍 关注❤️ 分享👥 留言💬thanks!!!
2021年10月1日17:24:59 愿你们奔赴在自己的热爱里!
文章来源: blessing.blog.csdn.net,作者:辰兮要努力,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blessing.blog.csdn.net/article/details/120579223
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)