ThreadLocal 基础入门学习(代码案例详解)
【辰兮要努力】:hello你好我是辰兮,很高兴你能来阅读,昵称是希望自己能不断精进,向着优秀程序员前行!
博客来源于项目以及编程中遇到的问题总结,偶尔会有读书分享,我会陆续更新Java前端、后台、数据库、项目案例等相关知识点总结,感谢你的阅读和关注,希望我的博客能帮助到更多的人,分享获取新知,大家一起进步!
吾等采石之人,应怀大教堂之心,愿我们奔赴在自己的热爱里…
一、基础入门
☕️业务场景:多线程访问同一个共享变量的时候容易出现并发问题,特别是多个线程对一个变量进行写入的时候,为了保证线程安全,一般使用者在访问共享变量的时候需要进行额外的同步措施才能保证线程安全性。
📝ThreadLocal的使用
当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
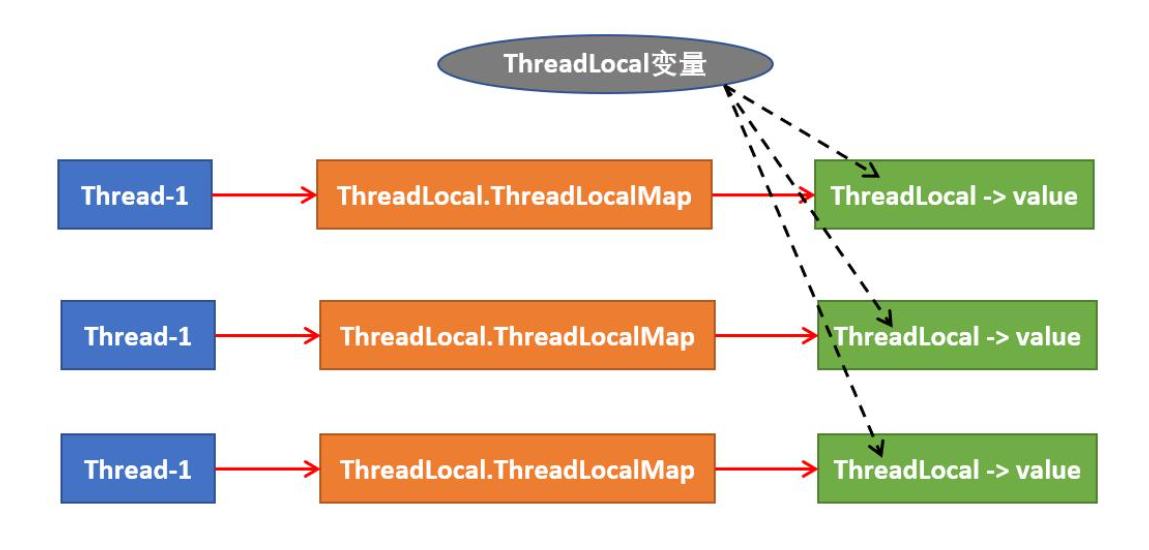
📣ThreadLocal原理:在ThreadLocal类中有一个Map集合,用于存储每一个线程的变量副本,Map中元素的键为线程对象,而值对应线程的变量副本
🎩经典的使用场景是为每个线程分配一个 JDBC 连接 Connection。这样就可以保证每个线程的都在各自的 Connection 上进行数据库的操作,不会出现 A 线程关了 B线程正在使用的 Connection;
二、案例应用
☕️ThreadLocal 结合线程池使用案例分享
/**
* @program: demo
* @description: ThreadLocal 结合线程池使用案例分享
* @author: 辰兮要努力
* @create: 2021-11-15 21:48
*/
public class ThreadLocalDemo {
/**
*
* ThreadLocal为变量在每个线程中都创建了一个副本,那么每个线程可以访问自己内部的副本变量。
* 变量:variable
*/
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocalVar = new ThreadLocal<String>();
static void print(String str) {
//打印当前线程中本地内存中本地变量的值
System.out.println(str + " :" + threadLocalVar.get());
//清除本地内存中的本地变量
threadLocalVar.remove();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorConfig.getThreadPoolInstance().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadLocalDemo.threadLocalVar.set("辰兮");
print("2021");
//打印本地变量
System.out.println("执行移除方法后 : " + threadLocalVar.get());
}
});
ExecutorConfig.getThreadPoolInstance().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadLocalDemo.threadLocalVar.set("辰兮要努力");
print("2022");
System.out.println("执行移除方法后 : " + threadLocalVar.get());
}
});
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
控制台输出
2022 :辰兮要努力
执行移除方法后 : null
2021 :辰兮
执行移除方法后 : null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
线程池帮助类
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* @program: ExecutorConfig
* @description: 线程池相关帮助类
* @author: 辰兮要努力
*/
public class ExecutorConfig {
/**
* 记录对应的日志
*/
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ExecutorConfig.class);
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor thPoolInstance = null;
/**
* 线程池
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
* @author 辰兮要努力
*/
public static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getThreadPoolInstance() {
if (thPoolInstance != null) {
return thPoolInstance;
}
synchronized (ExecutorConfig.class) {
if (thPoolInstance == null) {
try {
// 获取统一线程池
thPoolInstance = ApplicationContextHolder.getBean(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.class);
if (thPoolInstance == null) {
// 如果统一线程池还是为空,将启动本地创建线程,进行保护。
thPoolInstance = getThPoolInstance();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("getThreadPoolInstance -> create thread pool error", e);
} finally {
// 如果统一线程池还是为空,将启动本地创建线程,进行保护。
if (thPoolInstance == null) {
thPoolInstance = getThPoolInstance();
}
}
}
}
return thPoolInstance;
}
/**
* 获取本地线程池
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
* @author 辰兮要努力
* @date 2021-9-25 10:58:53
*/
private static ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getThPoolInstance() {
/**
* 如果对应的线程池不为空则直接返回,如果为空
*/
if (thPoolInstance != null) {
return thPoolInstance;
}
try {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数10:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
// 最大线程数15:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
executor.setMaxPoolSize(15);
// 缓冲队列25:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(25);
// 允许线程的空闲时间200秒:当超过了核心线程出之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(200);
// 线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便定位处理任务所在的线程池
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("chenXI-");
/**
* 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略:这里采用了CallerRunsPolicy策略, 当线程池没有处理能力的时候,
* 该策略会直接在 execute 方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务; 如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务
*/
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 设置线程池关闭的时候等待所有任务都完成再继续销毁其他的Bean
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 设置线程池中任务的等待时间,如果超过这个时候还没有销毁就强制销毁,以确保应用最后能够被关闭,而不是阻塞住。
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60 * 2);
executor.initialize();
thPoolInstance = executor;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("getThPoolInstance-> create thread pool error", e);
}
return thPoolInstance;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
帮助类:在spring环境中获取非spring容器管理的bean
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**
* @program: ApplicationContextHolder
* @description: 在spring环境中获取非spring容器管理的bean
* @author: 辰兮要努力
* @create: 2021-9-25 13:30:02
*/
public class ApplicationContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) throws BeansException {
applicationContext = ctx;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
首先我们要清楚一个概念 成员变量 和 局部变量
成员变量: 直接在类中声明的变量叫成员变量(又称全局变量)
局部变量:方法中的参数、方法中定义的变量和代码块中定义的变量统称为局部变量
三、源码学习
📖Java官方对ThreadLocal类的定义如下:
- ThreadLocal类用于提供线程内部的局部变量。
- 这种变量在多线程环境下访问(通过get和set方法访问)时能保证各个线程的变量相对独立于其他线程内的变量。
- ThreadLocal实例通常来说都是private static类型的,用于关联线程和线程上下文。
☕️ThreadLocal 底层源码学习
public T get() 返回当前线程所对应的线程局部变量
//ThreadLocal中的get方法
public T get() {
//获取到当前的线程对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//进而获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//如果此map存在
if (map != null) {
//以当前的ThreadLocal 为 key,调用getEntry获取对应的存储实体e
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
//找到对应的存储实体 e
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//如果map不存在,调用setInitialValue进行初始化
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
//调用initialValue获取初始化的值
T value = initialValue();
//获取当前线程对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//如果此map存在
if (map != null)
//存在则调用map.set设置此实体entry
map.set(this, value);
else
调用createMap进行ThreadLocalMap对象的初始化,并将此实体作为第一个值
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
public void set(T value)
public void set(T value) {
//获取到当前的线程对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//进而获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//如果ThreadLocalMap存在,则以当前的ThreadLocal为key,value作为值设置entry
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
//调用createMap进行ThreadLocalMap对象的初始化,并将此实体作为第一个值
createMap(t, value);
}
//创建一个与线程t关联的ThreadLocalMap
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
public void remove() 将当前线程局部变量的值删除,目的是为了减少内存的占用
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
//以当前ThreadLocal为key删除对应的实体entry
m.remove(this);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
移除当前线程存储的 Value 值。当 ThreadLocal 不在使用,最好在 finally 语句块中,调用 remove() 方法,释放去 Value 的引用,避免内存泄露。
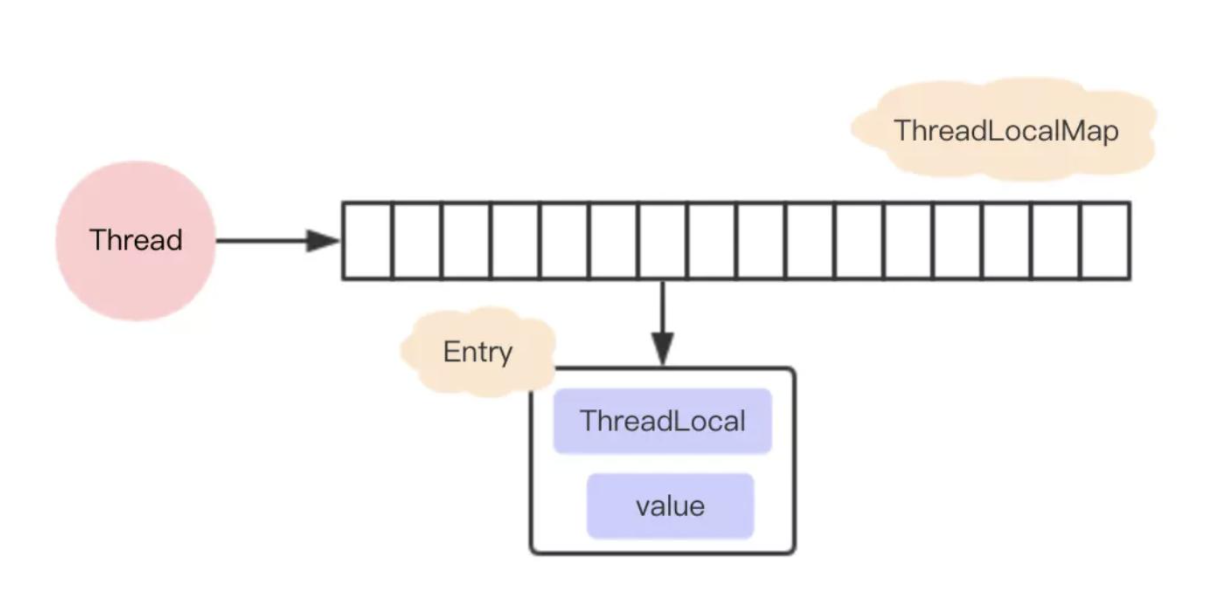
在getMap中,是调用当期线程t,返回当前线程t中的一个成员变量threadLocals。
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
📝ThreadLocal和synchronized对比
使用ThreadLocal代替synchronized来保证线程安全。同步机制采用了以时间换空间的方式,而ThreadLocal采用了以空间换时间的方式。
前者仅提供一份变量,让不同的线程排队访问,而后者为每一个线程都提供了一份变量,因此可以同时访问而互不影响。
📖☕️🌊📝📚🎩🚀📣
后续会继续总结ThreadLocal的应用案例,未来见……
📝非常感谢你阅读到这里,如果这篇文章对你有帮助,希望能留下你的点赞👍 关注❤️ 分享👥 留言💬thanks!!!
🚀 愿我们奔赴在自己的热爱里!
文章来源: blessing.blog.csdn.net,作者:辰兮要努力,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blessing.blog.csdn.net/article/details/123647272
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)