C++哈希-哈希封装实现unordered_map/unordered_set
【摘要】 三、哈希封装实现unordered_map/unordered_set这里使用哈希桶来封装实现map和set,哈希桶相对于哈希表来说没有哈希冲突,并且效率也十分好使用哈希封装map/set和使用红黑树来封装的思维具有很多相似的地方 1、哈希桶的改装注意:存储节点的数据类型对于set的K模型以及map的KV模型的兼容示例代码://哈希储存的数据类型template<class T>struc...
三、哈希封装实现unordered_map/unordered_set
这里使用哈希桶来封装实现map和set,哈希桶相对于哈希表来说没有哈希冲突,并且效率也十分好
使用哈希封装map/set和使用红黑树来封装的思维具有很多相似的地方
1、哈希桶的改装
- 注意:
- 存储节点的数据类型对于set的K模型以及map的KV模型的兼容
- 示例代码:
//哈希储存的数据类型
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;//对于不同的上层可以存对应的K类型以及pair<K,V>
HashNode* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
- 解释:
封装上层是set的话,则给底层哈希桶传入K类型,通过哈希桶再给底层的节点储存类型传入K类型
封装上层是map的话,则给底层哈希桶传入pair<K,V>,通过哈希桶再给底层的节点储存类型传入pair<K,V>
- 储存节点在不同封装的使用下进行对应的取出数据的key进行比较
- 示例代码:
//set上层
struct SetOfKey
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)const
{
return key;
}
};
typedef HashNode<K> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetOfKey> HT;
//map上层
struct MapOfKey
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)const
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef HashNode<pair<K, V>> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash, MapOfKey> HT;
- 解释:
上层封装中实现仿函数,给对应底层哈希传入对应使用的仿函数,便于进行使用对应的函数将储存数据的key继续取出比较
- 哈希桶的迭代器如何实现,对于当前位置的迭代器怎么找到下个位置
- 示例代码:
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
HT* _ht;
Node* _node;
HTIterator(Node* node, HT* ht)//不能加const,与成员变量不匹配
:_ht(ht)
, _node(node)
{}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const;
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const;
T& operator*();
T* operator->();
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//存在下个节点
_node = _node->_next;
else//找下一个桶
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t index = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_table.size();
//kot仿函数为了取出储存类型数据的key,hf仿函数是实现对key类型的取整值,便于进行取模
int i=index+1;
for (; i < _ht->_table.size(); i++)
{
if (_ht->_table[i])
{
_node = _ht->_table[i];
break;
}
}
if (i == _ht->_table.size())//走到最后*
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
friend struct HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT>;//*
public:
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Iterator;
//...
}
注:对于哈希桶来说只有正向迭代器(单向),主要是底层是一个单向的链表,找上个节点地址比较麻烦,对于反向并不是很强求
- 解释:
迭代器底层为哈希桶节点地址,同时还需要指向该哈希桶的指针,用来进行查找对应桶的下个节点地址,这里需要使用哈希的私有成员,所以我们需要让迭代器成为哈希桶的友元类,便于访问成员
在实现的时候,我们发现,实现的迭代器包含了哈希桶类型,而哈希桶也包含了迭代器类型,两个类型互相去查找对方类型,这里就需要进行前置声明,避免有一方找不到对方类型
- 示例代码:
//前置声明
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
HT* _ht;
Node* _node;
//...
Self& operator++();
};
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
friend struct HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT>;//*
public:
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Iterator;
Iterator begin()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i])
return Iterator(_table[i], this);
}
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}
Iterator end()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}
//...
}
- 哈希桶改装后完整代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//哈希储存的数据类型
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;//对于不同的上层可以存对应的K类型以及pair<K,V>
HashNode* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
//取值比较仿函数及其特化
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
hash = hash * 131 + str[i];
}
return hash;
}
};
//获取下一个质数(接近二倍开辟)
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
static const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; ++i)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}
//前置声明
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
HT* _ht;
Node* _node;
HTIterator(Node* node, HT* ht)//不能加const,与成员变量不匹配
:_ht(ht)
, _node(node)
{}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)
_node = _node->_next;
else//找下一个桶
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t index = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_table.size();
int i=index+1;
for (; i < _ht->_table.size(); i++)
{
if (_ht->_table[i])
{
_node = _ht->_table[i];
break;
}
}
if (i == _ht->_table.size())//走到最后*
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
friend struct HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT>;//*
public:
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Iterator;
HashTable()
:_n(0)
{}
Iterator begin()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i])
return Iterator(_table[i], this);
}
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}
Iterator end()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}
HashTable(const HT& ht)//拷贝构造
:_n(ht._n)
{
if (ht._table.size() == 0)
return;
KeyOfT kot;
_table.resize(ht._table.size(), nullptr);
for (int i = 0; i < ht._table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(cur->_kv);
newnode->_next = _table[i];
_table[i] = newnode;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
HT& operator=(const HT& ht)
{
if (&ht != this)
{
HT temp(ht);
_table.swap(temp._table);
_n = ht._n;
}
return *this;
}
~HashTable()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;//置空
}
_n = 0;
}
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
//空哈希或者负载因子达到1
if (_table.size() == _n)
{
size_t newsize = _table.size() == 0 ? 10 : _table.size() * 2;
//size_t newsize = GetNextPrime(_table.size());//获取新大小
vector<Node*> newdata;
newdata.resize(newsize, nullptr);//开新的数组并扩容
//将原数组中的节点重新插入到新数组
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];//遍历数组
while (cur)//挂有节点
{
Node* next = cur->_next;//记录下一个节点
size_t index = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newsize;//重新计算下标
//头插到新位置
cur->_next = newdata[index];
newdata[index] = cur;
cur = next;//移动
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.swap(newdata);
}
//遍历查找
size_t index = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[index];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == kot(data))
return make_pair(Iterator(cur,this),false);
else
cur = cur->_next;
}
//头插
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
newnode->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(Iterator(newnode,this),true);
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
//空哈希
if (_table.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t index = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[index];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
return cur;
else
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//空哈希
if (_table.size() == 0)
return false;
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t index = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[index];
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
if (parent == nullptr)//头结点
_table[index] = cur->_next;
else
parent->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table;
size_t _n=0;
};
2、unordered_map的上层封装
只需要在底层哈希桶的接口以及迭代器的接口,进行进一步的封装接口,便于外部进行调用
- 实现代码:
namespace cole
{
template<class K,class V,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapOfKey
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)const
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef HashNode<pair<K, V>> Node;
public:
typedef HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash, MapOfKey> HT;
typedef typename HT::Iterator iterator;
//获取类型中的类型需要加typename进行修饰,告诉编译器在实例化后进行查找对应的类型
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
auto ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
Node* find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
HT _ht;
};
void test_unordered_map()
{
unordered_map<int, int> map;
int arr[] = { 1,2,22,34,3,4,54,4,2,6,18,48,56,16,45,16,23,156,49,153,45,81,6,6,16,16,151,84894,11,6 };
for (auto e : arr)
{
map.insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
for (auto& e : map)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
map[56] = 11;
auto ret = map.find(4);
cout << ret << endl;
cout << map[4] << endl;
map.erase(4);
cout << map[4] << endl;
cout << map[56] << endl;
for (auto e : arr)
{
map.erase(e);
}
for (auto& e : map)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
}
}
- 测试结果:
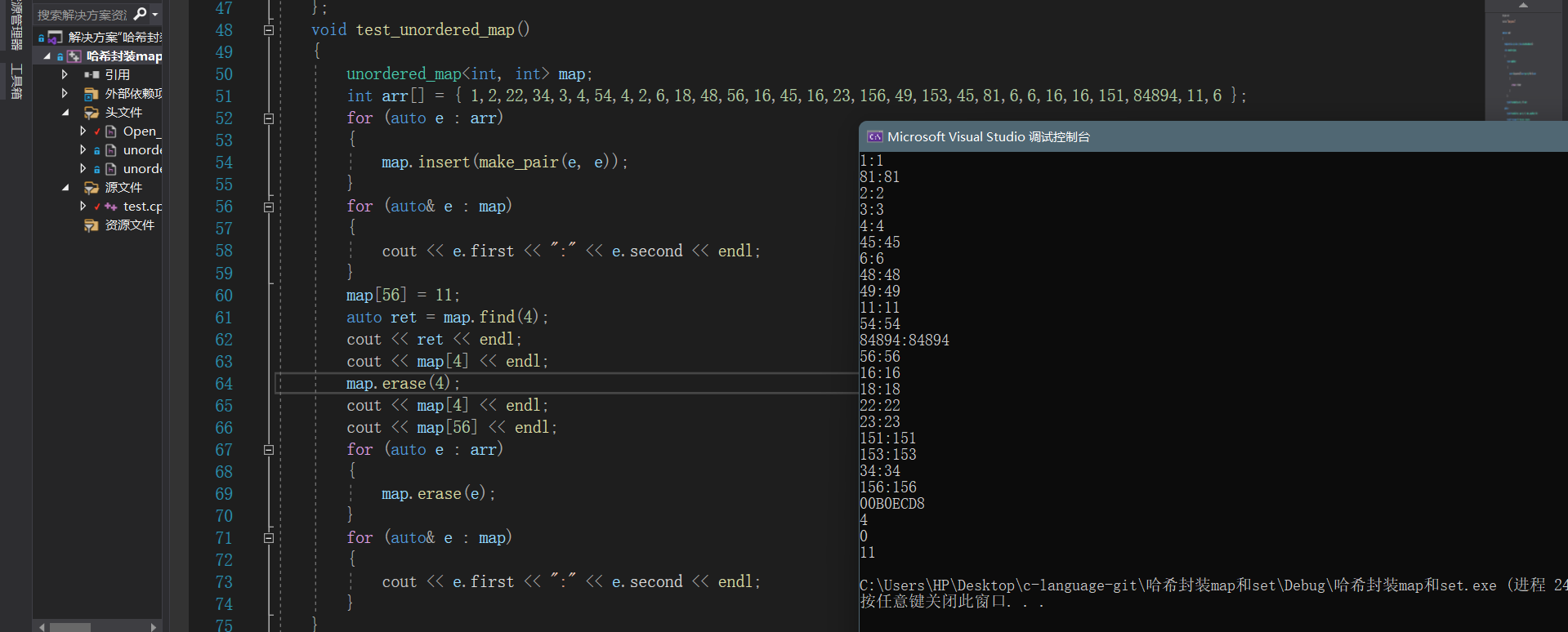
3、unordered_set的上层封装
同样的对于set来说,也只需要在底层哈希桶的接口以及迭代器的接口,进行进一步的封装接口,便于外部进行调用
- 实现代码:
namespace cole
{
template<class K , class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetOfKey
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)const
{
return key;
}
};
typedef HashNode<K> Node;
public:
typedef HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetOfKey> HT;
typedef typename HT::Iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
/*V& operator[](const K& key)
{
auto ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}*/
Node* find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
HT _ht;
};
void test_unordered_set()
{
unordered_set<int> set;
int arr[] = { 1,2,22,34,3,4,54,4,2,6,18,48,56,16,45,16,23,156,49,153,45,81,6,6,16,16,151,84894,11,6 };
for (auto e : arr)
{
set.insert(e);
}
for (auto& e : set)
{
cout << e << endl;
}
auto ret = set.find(4);
cout << ret << endl;
set.erase(4);
for (auto& e : set)
{
cout << e << endl;
}
for (auto e : arr)
{
set.erase(e);
}
for (auto& e : set)
{
cout << e<< endl;
}
}
}
- 测试结果:
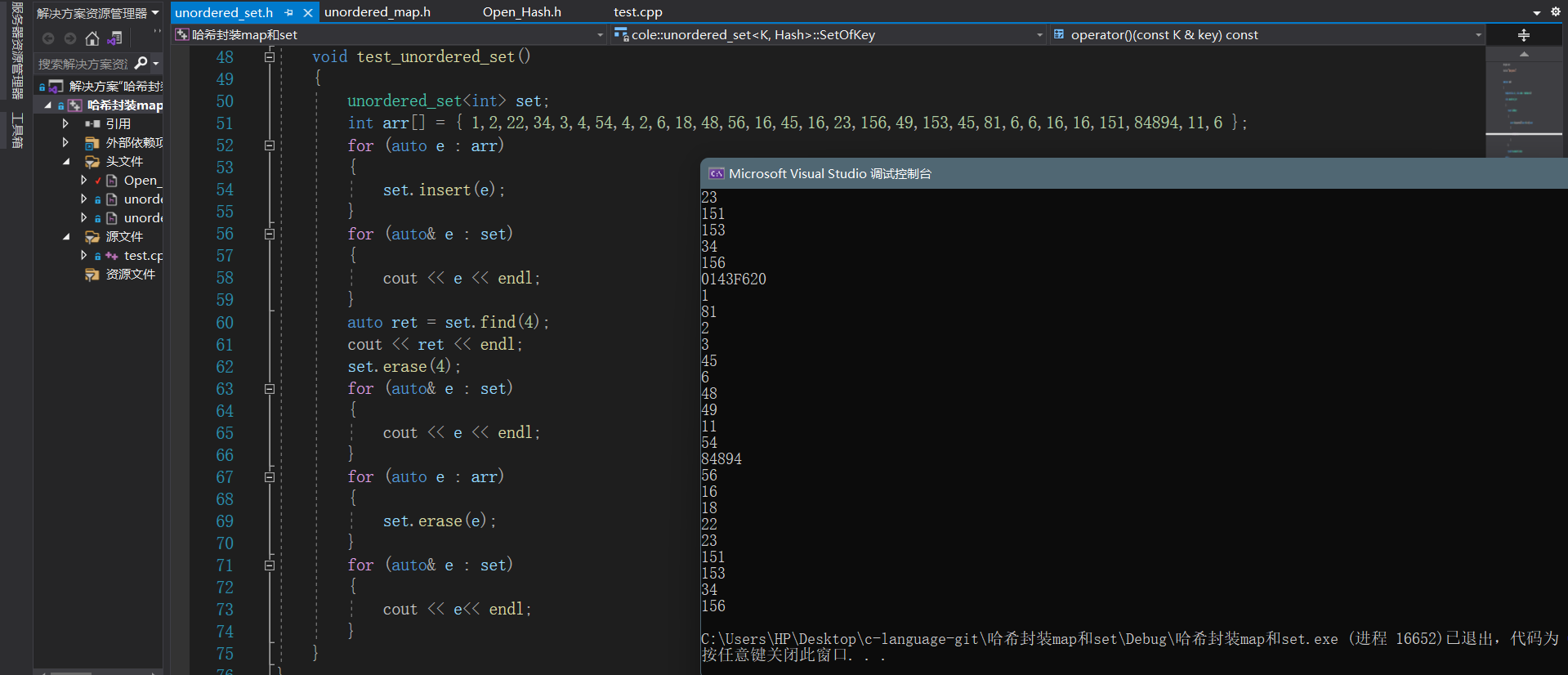
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)