从thread类中,我们可以看到类中预先定义了三个优先级。
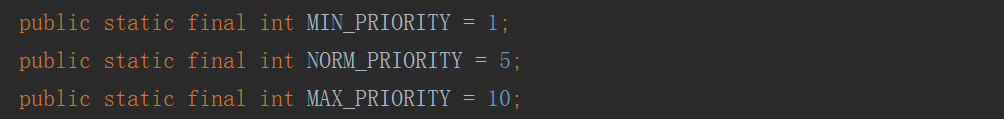
通过getpriority可以看到新建线程的默认等级。
-
public class ExtendsThread {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
MyThread c = new MyThread("线程C");
-
int priority = c.getPriority();
-
System.out.println(priority);
-
}
-
}
-
-
class MyThread extends Thread {
-
private String title;
-
public MyThread(String title) {
-
this.title = title;
-
}
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
for(int x = 0; x < 5 ; x++) {
-
System.out.println(this.title + "运行,x = " + x);
-
}
-
}
-
}
我们可以通过setpriority进行优先级设置。
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
MyThread a = new MyThread("线程A");
-
MyThread b = new MyThread("线程B");
-
MyThread c = new MyThread("线程C");
-
b.setPriority(1);
-
a.setPriority(10);
-
c.setPriority(10);
-
a.start();
-
b.start();
-
c.start();
-
}
我们查看运行结果。
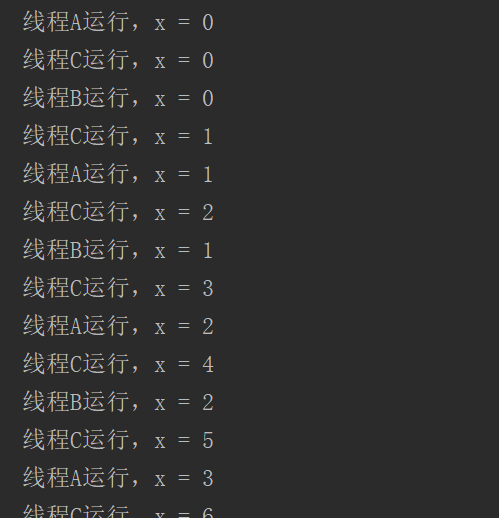
发现即使线程B设置的优先级很低,其仍然可以执行。
我们可以得到如下的结论:cpu分配资源,在控制台上并不能看出,而且,优先级低的并不代表一定要等到优先级高的运行完才能运行,只是cpu分配的资源少了而已。


评论(0)