iOS逆向之深入解析MachO文件
【摘要】
MachO文件简介
一、什么是MachO文件?
Mach-O其实是Mach Object文件格式的缩写,它是Mac以及iOS上一种用于可执行文件、目标代码、动态库的文件格式,类似于Windows上面的...
MachO文件简介
一、什么是MachO文件?
- Mach-O其实是Mach Object文件格式的缩写,它是Mac以及iOS上一种用于可执行文件、目标代码、动态库的文件格式,类似于Windows上面的PE格式(Portable Executable),linux上的elf格式(Executable and Link Format)。
- 它是一种用于可执行文件、目标代码、动态库的文件格式,作为.out格式的替代,MachO提供了更强的扩展性。
二、Mach-O文件格式
- 目标文件.o
- 库文件:.a .dylib .Framework
- 可执行文件
- dyld(动态链接器)
- .dsym(符号表:Relese环境运行生成)
三、查看文件类型
- $ file xxx.xx
系统架构
一、iPhone不同的型号对应的架构
| 手机型号 | 架构 |
|---|---|
| 32位模拟器 | i386 |
| 64位模拟器 | x86_64 |
| iPhone4、iPhone4S | armv7 |
| iPhone5、iPhone5C | armv7s |
| iPhone5s——iPhoneX | arm64 |
| iPhone XS、iPhone XS Max、iPhoneXR、iPhone11… | arm64e |
二、Xcode中指令集相关选项(Build Setting)
- Architectures
指定工程被编译成可支持哪些指令集类型,支持的指令集越多,就会编译出包含多个指令集代码的数据包,对应生成二进制 .ipa 包会变大。 - Valid Architectures
限制可能被支持的指令集的范围,即:Xcode编译出来的二进制包类型最终从这些类型产生,而编译出哪种指令集的包,将由Architectures与Valid Architectures的交集来确定 - Build Active Architecture Only
指定是否只对当前连接设备所支持的指令集编译。当其值设置为YES,是为了debug的时候编译速度更快,它只编译当前的Architecture版本,而设置为no时,会编译所有的版本。 所以,一般debug的时候可以选择设置为YES,release的时候要改为NO。
三、生成多种架构
- 新建一个工程,真机运行,查看可执行文件仅是一个arm64架构的,将项目最低适配系统调为iOS9.0,真机运行 Relese环境:
~/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/TestDemo-aszxljwcoetyppfyxjarbzmhorsh
/Build/Products/Release-iphoneos/TestDemo.app file TestDemo
TestDemo: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [arm_v7:Mach-O executable arm_v7 ] [arm64:Mach-O executable arm64]
TestDemo (for architecture armv7): Mach-O executable arm_v7
TestDemo (for architecture armv54): Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 为什么要改为iOS9.0呢 ?是因为iPhone5c等armv7、armv7s架构不支持iOS11.0;
- 为什么要Relese环境运行呢 ?因为Xcode默认Debug只生成单一架构;
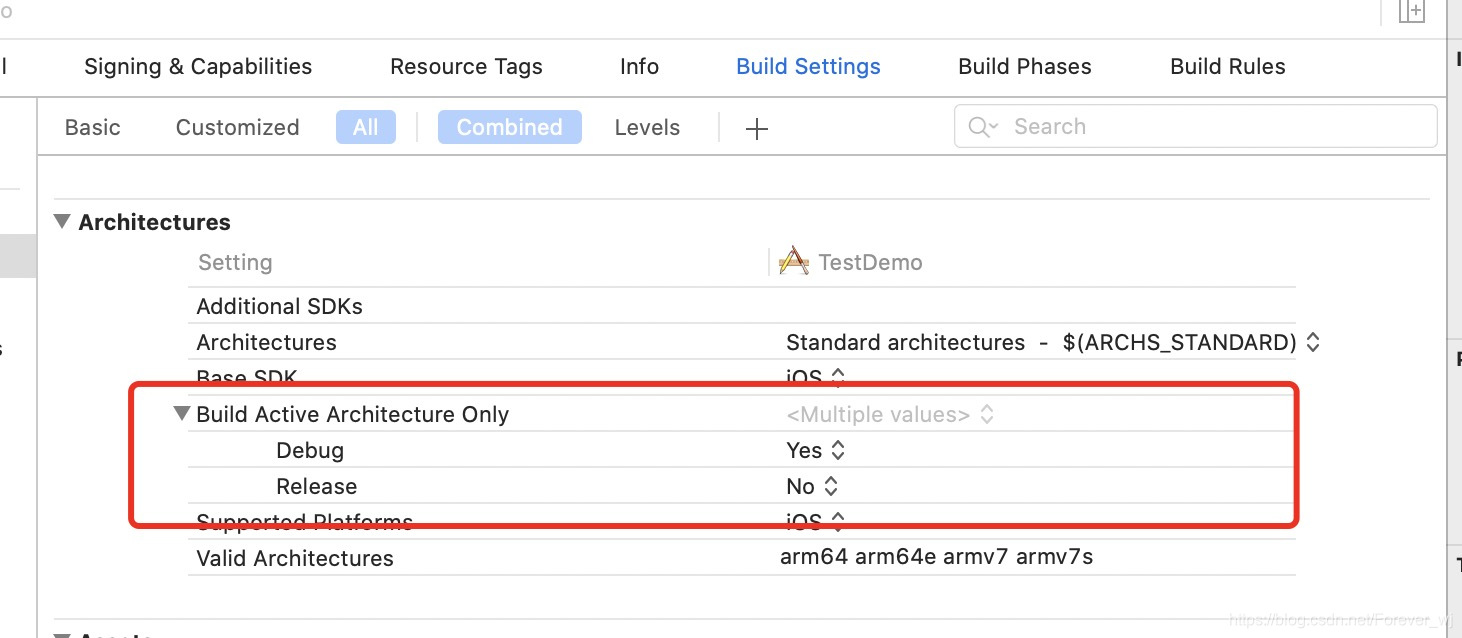
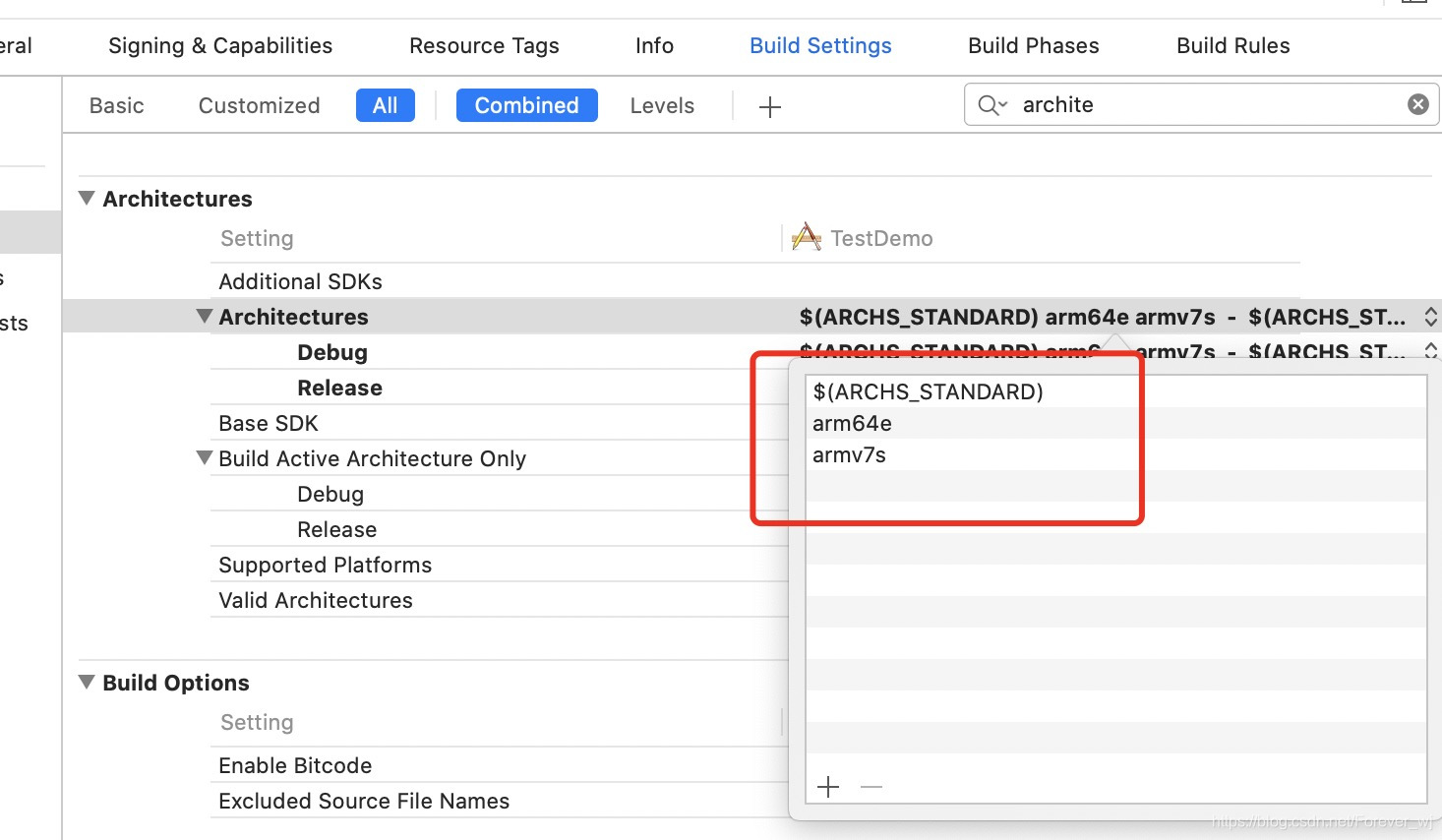
- 怎么生成所有架构 ?Xcode10中只包含了v7和64,需要在 Architectures 中添加:
通用二进制文件(Universal binary)
一、简介
- 通用二进制文件也被叫做胖二进制(Fat binary);
- 苹果公司提出的一种程序代码,能同时适用多种架构的二进制文件;
- 同一个程序包中同时为多种架构提供最理想的性能;
- 由于需要储存多种代码,通用二进制应用程序通常比单一平台二进制的程序要大;
- 由于两种架构有共通的非执行资源,所以并不会达到单一版本的两倍之多;
- 由于执行中只调用一部分代码,运行起来也不需要额外的内存;
二、拆分/合并架构
① 终端命令
- 架构查看
lipo -info + macho
- 1
- 架构合并
lipo -create macho_A macho_B -output(-o) macho_AB
- 1
- 架构分离
lipo macho -thin -arm64 -o macho_arm64
- 1
② 结论
- 胖二进制拆分后再重组会得到原始胖二进制;
- 通用二进制的大小可能大于子架构大小之和,也可能小于,也可能等于,取决于公共资源文件的多少;
MachO文件结构
一、苹果官方结构
主要组成可以大概分为三大块:
- Header部分(包含该二进制文件的一般信息):字节顺序、架构类型、加载指令的数量等。使得可以快速确认一些信息,比如当前文件用于32位还是64位,对应处理器是什么,文件类型是什么。
- Load commands 部分(一张包含很多内容的表);内容区包括区域的位置、符号表、动态符号表等。
- Data段:包含Segement的具体数据。
二、整体结构
- 使用 MachOView 打开会看到通用二进制文件由 Fat Header 和可执行文件组成(可执行文件是由 Header 、 Load commands 和 Data 组成):
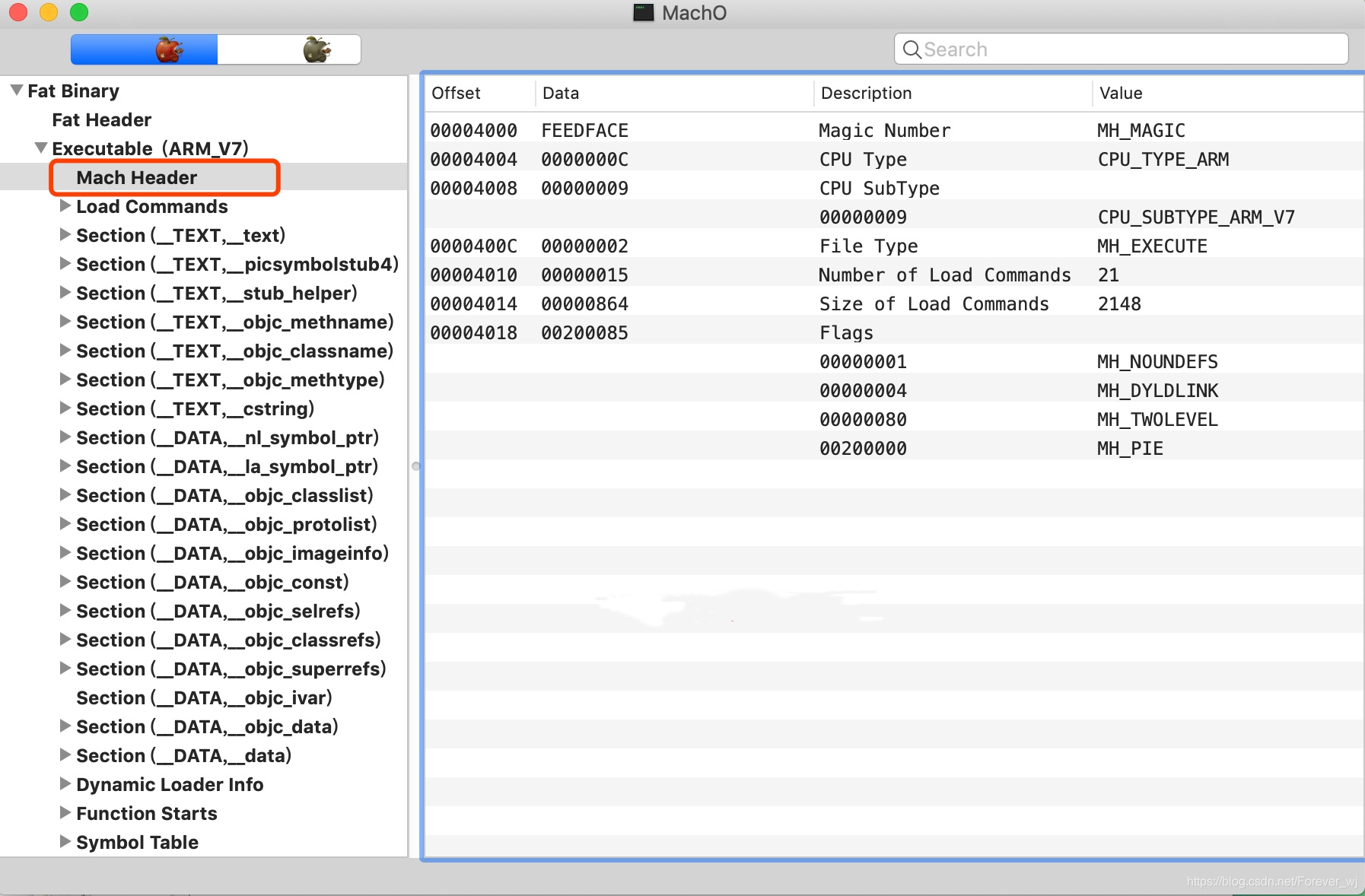
- 可执行文件是由 Header 、 Load commands 和 Data 组成:

- 可以使用otool命令来查看Mach-O文件,也可以使用MachOView这个工具查看刚刚生成的MachO文件,先cd到当前文件夹,然后:
$otool -f MachO
Fat headers
fat_magic 0xcafebabe
nfat_arch 3
architecture 0
cputype 12
cpusubtype 9
capabilities 0x0
offset 16384
size 73568
align 2^14 (16384)
architecture 1
cputype 12
cpusubtype 11
capabilities 0x0
offset 98304
size 73568
align 2^14 (16384)
architecture 2
cputype 16777228
cpusubtype 0
capabilities 0x0
offset 180224
size 73888
align 2^14 (16384)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- header 包含了该二进制文件的字节顺序、架构类型、加载指令的数量等,使得可以快速确认一些信息,比如当前文件用于 32 位 还是 64 位 ,对应的处理器是什么、文件类型是什么;Xcode中 shift+command+O -> load.h -> 如下信息(mach_header_64(64位)对比mach_header(32位)只多了一个保留字段)
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* 魔数,快速定位64位/32位 */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu 类型 比如 ARM */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* cpu 具体类型 比如arm64 , armv7 */
uint32_t filetype; /* 文件类型 例如可执行文件 .. */
uint32_t ncmds; /* load commands 加载命令条数 */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* load commands 加载命令大小*/
uint32_t flags; /* 标志位标识二进制文件支持的功能 , 主要是和系统加载、链接有关*/
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved , 保留字段 */
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
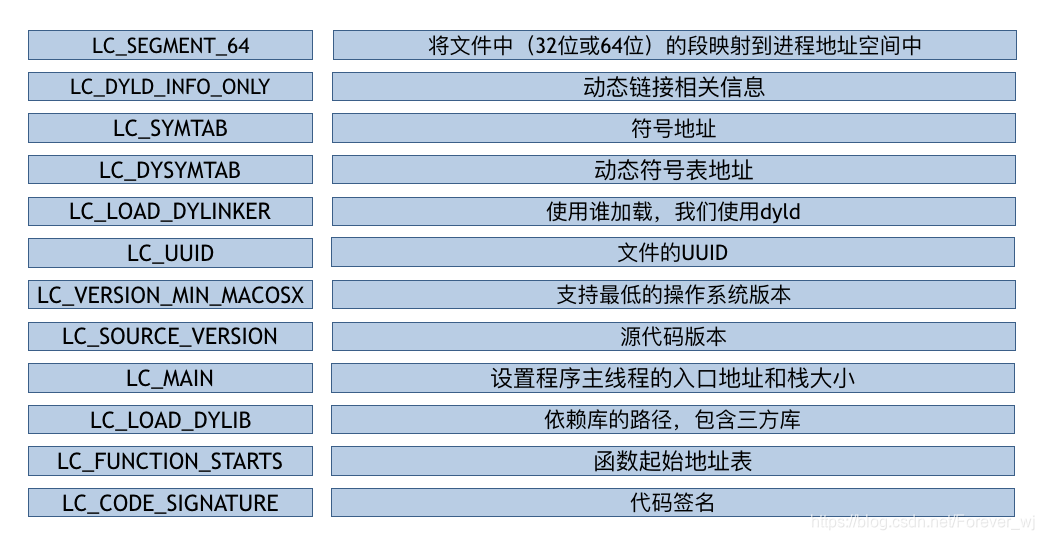
- load commands 是一张包括区域的位置、符号表、动态符号表等内容的表。它详细保存着加载指令的内容,告诉链接器如何去加载这个 Mach-O 文件。通过查看内存地址发现,在内存中 load commands 是紧跟在 header 之后的;
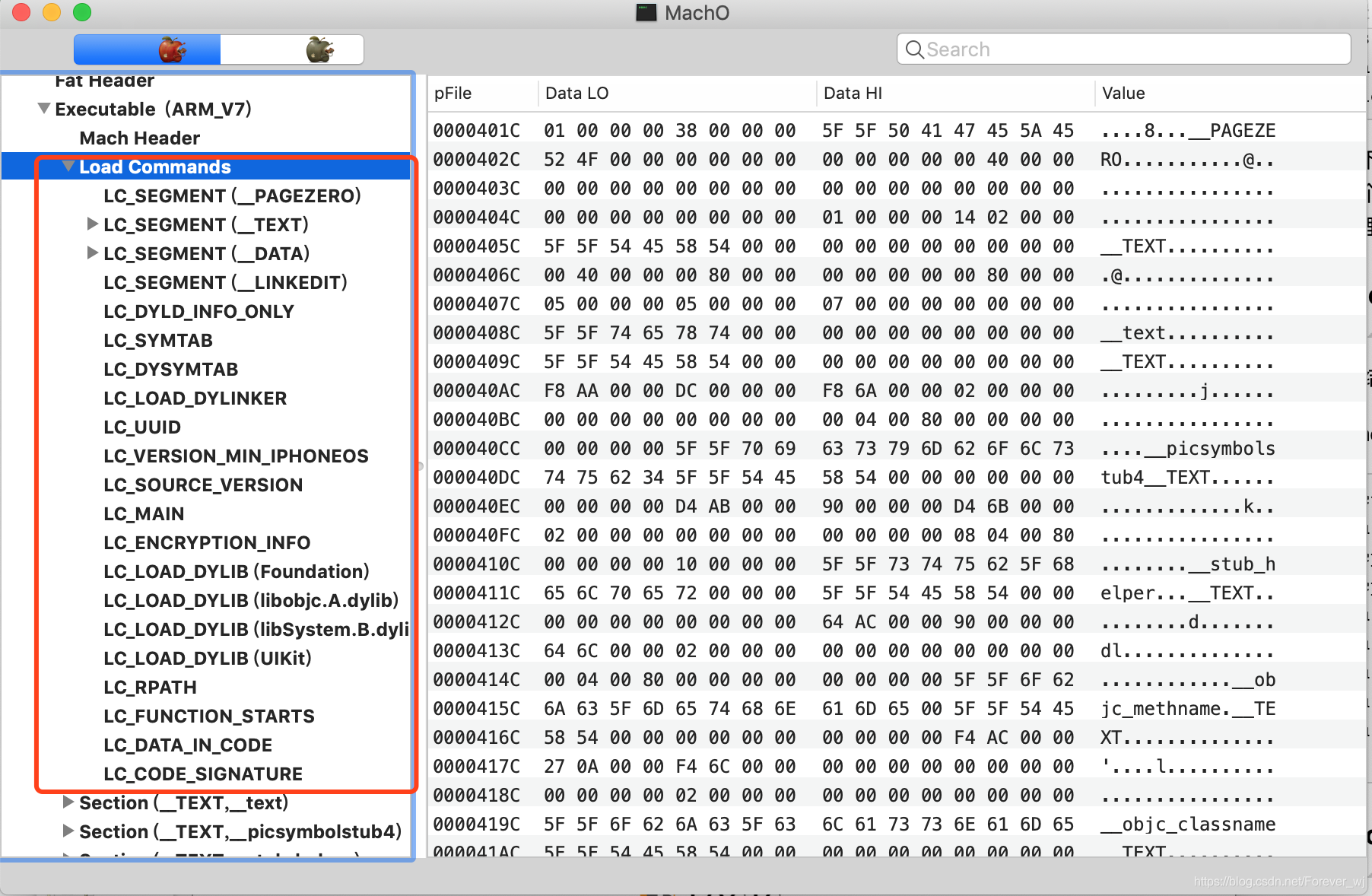
- load commands的详情:
/* Constants for the cmd field of all load commands, the type */
#define LC_SEGMENT 0x1 /* segment of this file to be mapped */
#define LC_SYMTAB 0x2 /* link-edit stab symbol table info */
#define LC_SYMSEG 0x3 /* link-edit gdb symbol table info (obsolete) */
#define LC_THREAD 0x4 /* thread */
#define LC_UNIXTHREAD 0x5 /* unix thread (includes a stack) */
#define LC_LOADFVMLIB 0x6 /* load a specified fixed VM shared library */
#define LC_IDFVMLIB 0x7 /* fixed VM shared library identification */
#define LC_IDENT 0x8 /* object identification info (obsolete) */
#define LC_FVMFILE 0x9 /* fixed VM file inclusion (internal use) */
#define LC_PREPAGE 0xa /* prepage command (internal use) */
#define LC_DYSYMTAB 0xb /* dynamic link-edit symbol table info */
#define LC_LOAD_DYLIB 0xc /* load a dynamically linked shared library */
#define LC_ID_DYLIB 0xd /* dynamically linked shared lib ident */
#define LC_LOAD_DYLINKER 0xe /* load a dynamic linker */
#define LC_ID_DYLINKER 0xf /* dynamic linker identification */
#define LC_PREBOUND_DYLIB 0x10 /* modules prebound for a dynamically */
/* linked shared library */
#define LC_ROUTINES 0x11 /* image routines */
#define LC_SUB_FRAMEWORK 0x12 /* sub framework */
#define LC_SUB_UMBRELLA 0x13 /* sub umbrella */
#define LC_SUB_CLIENT 0x14 /* sub client */
#define LC_SUB_LIBRARY 0x15 /* sub library */
#define LC_TWOLEVEL_HINTS 0x16 /* two-level namespace lookup hints */
#define LC_PREBIND_CKSUM 0x17 /* prebind checksum */
/*
* load a dynamically linked shared library that is allowed to be missing
* (all symbols are weak imported).
*/
#define LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB (0x18 | LC_REQ_DYLD)
#define LC_SEGMENT_64 0x19 /* 64-bit segment of this file to be
mapped */
#define LC_ROUTINES_64 0x1a /* 64-bit image routines */
#define LC_UUID 0x1b /* the uuid */
#define LC_RPATH (0x1c | LC_REQ_DYLD) /* runpath additions */
#define LC_CODE_SIGNATURE 0x1d /* local of code signature */
#define LC_SEGMENT_SPLIT_INFO 0x1e /* local of info to split segments */
#define LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB (0x1f | LC_REQ_DYLD) /* load and re-export dylib */
#define LC_LAZY_LOAD_DYLIB 0x20 /* delay load of dylib until first use */
#define LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO 0x21 /* encrypted segment information */
#define LC_DYLD_INFO 0x22 /* compressed dyld information */
#define LC_DYLD_INFO_ONLY (0x22|LC_REQ_DYLD) /* compressed dyld information only */
#define LC_LOAD_UPWARD_DYLIB (0x23 | LC_REQ_DYLD) /* load upward dylib */
#define LC_VERSION_MIN_MACOSX 0x24 /* build for MacOSX min OS version */
#define LC_VERSION_MIN_IPHONEOS 0x25 /* build for iPhoneOS min OS version */
#define LC_FUNCTION_STARTS 0x26 /* compressed table of function start addresses */
#define LC_DYLD_ENVIRONMENT 0x27 /* string for dyld to treat
like environment variable */
#define LC_MAIN (0x28|LC_REQ_DYLD) /* replacement for LC_UNIXTHREAD */
#define LC_DATA_IN_CODE 0x29 /* table of non-instructions in __text */
#define LC_SOURCE_VERSION 0x2A /* source version used to build binary */
#define LC_DYLIB_CODE_SIGN_DRS 0x2B /* Code signing DRs copied from linked dylibs */
#define LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO_64 0x2C /* 64-bit encrypted segment information */
#define LC_LINKER_OPTION 0x2D /* linker options in MH_OBJECT files */
#define LC_LINKER_OPTIMIZATION_HINT 0x2E /* optimization hints in MH_OBJECT files */
#define LC_VERSION_MIN_TVOS 0x2F /* build for AppleTV min OS version */
#define LC_VERSION_MIN_WATCHOS 0x30 /* build for Watch min OS version */
#define LC_NOTE 0x31 /* arbitrary data included within a Mach-O file */
#define LC_BUILD_VERSION 0x32 /* build for platform min OS version */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 部分字段说明:

- data 是MachO文件中最大的部分,其中 _TEXT段 、 _DATA段 能给到很多信息。load commands 和 data 之间还留有不少空间,给我们留下了注入代码的冲破口:
| _TEXT段名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| _text | 主程序代码 |
| _stubs、_stub_helper | 动态链接 |
| _objc_methodname | 方法名称 |
| _objc_classname | 类名称 |
| _objc_methtype | 方法类型 |
| _cstring | 静态字符串常量 |
| _DATA段名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| _got=Non-Lazy Symbol Pointers | 非懒加载符号表 |
| _la_symbol_ptr => Lazy Symbol Pointers | 懒加载符号表 |
| _objc_classlist | 方法名称 |
| … | … |
dyld
- dyld(the dynamic link editor)是苹果的动态链接器,是苹果操作系统的一个重要组成部分,在系统内容做好程序准备工作之后,交由dyld负责余下的工作。
- 系统库的方法由于是公用的,存放在共享缓存中,那么我们的MachO在调用系统方法时,dyld会将MachO里调用存放在共享缓存中的方法进行符号绑定。这个符号在 release环境 是会被自动去掉的,这也是经常使用收集 bug 工具时需要恢复符号表的原因。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:Serendipity·y,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/Forever_wj/article/details/107812834
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)