【Groovy】Groovy 脚本调用 ( Java 类中调用 Groovy 脚本 )
前言
Java 类中调用 Groovy 脚本 , 与 Groovy 类中调用 Groovy 脚本 , 代码基本类似 ;
也是参考 groovy.lang.Script#evaluate 方法 , 创建 Binding 对象并设置 args 参数 , 创建 GroovyShell 对象并执行 Groovy 脚本 , 就可以在 Java 类中启动 Groovy 脚本 ;
一、Groovy 类中调用 Groovy 脚本
1、参考 Script#evaluate 方法分析 Groovy 类中调用 Groovy 脚本
可以参考 groovy.lang.Script 类的 evaluate 方法 , 通过 GroovyShell 在类方法中调用 Groovy 脚本 ;
在 evaluate 方法中 , 首先创建 GroovyShell 实例对象 , 然后执行该实例对象的 evaluate 方法 , 传入要调用的 Groovy 脚本对应的 File 对象 ;
public abstract class Script extends GroovyObjectSupport {
/**
* 一个助手方法,允许使用此脚本绑定作为变量范围动态计算groovy表达式
*
* @param file 要执行的 Groovy 脚本文件
*/
public Object evaluate(File file) throws CompilationFailedException, IOException {
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell(getClass().getClassLoader(), binding);
return shell.evaluate(file);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2、创建 Binding 对象并设置 args 参数
此处创建 GroovyShell 实例对象 涉及到传入 Binding 类型的参数 , 这个参数是 绑定作用域 变量 参数 ;
-
在 Groovy 脚本中 , 该变量本身就被封装在 Script 类中 , 可以直接调用 Binding binding 成员 ;
-
但是在 Java 类中 , 并没有该 Binding 成员变量 , 需要通过手动创建 Binding 实例对象 , 然后传入 GroovyShell 构造函数 ;
在 Binding 对象中的 Map variables 成员中 , 设置 args 参数 , 作为调用 Groovy 脚本的执行参数 ;
首先 , 要在 Java 类方法中 , 创建 Binding 对象 ,
// 注意这里创建 groovy.lang.Binding
Binding binding = new Binding();
- 1
- 2
然后 , 调用 Binding 对象的 setVariable 方法 , 设置 args 执行参数 ;
// 设置 args 参数到 Binding 中的 variable 成员中
binding.setVariable("args", new String[]{"arg0", "arg1"});
- 1
- 2
3、创建 GroovyShell 对象并执行 Groovy 脚本
首先 , 创建 GroovyShell 对象 , 在构造函数中 , 需要传入 Binding 对象 ;
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell(JavaClass.class.getClassLoader(), binding);
- 1
然后 , 设置要调用的 Groovy 脚本对应的 File 文件对象 ;
File file = new File("src/main/groovy/Script.groovy");
- 1
最后 , 调用 GroovyShell 对象的 evaluate 方法 , 执行 Groovy 脚本 ;
shell.evaluate(file);
- 1
4、代码示例
代码示例 :
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class JavaClass {
public void startScript() throws IOException {
// 注意这里创建 groovy.lang.Binding
Binding binding = new Binding();
// 设置 args 参数到 Binding 中的 variable 成员中
binding.setVariable("args", new String[]{"arg0", "arg1"});
// 执行 Groovy 脚本
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell(JavaClass.class.getClassLoader(), binding);
File file = new File("src/main/groovy/Script.groovy");
shell.evaluate(file);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new JavaClass().startScript();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
二、完整代码示例
1、调用者 Groovy 脚本的类
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
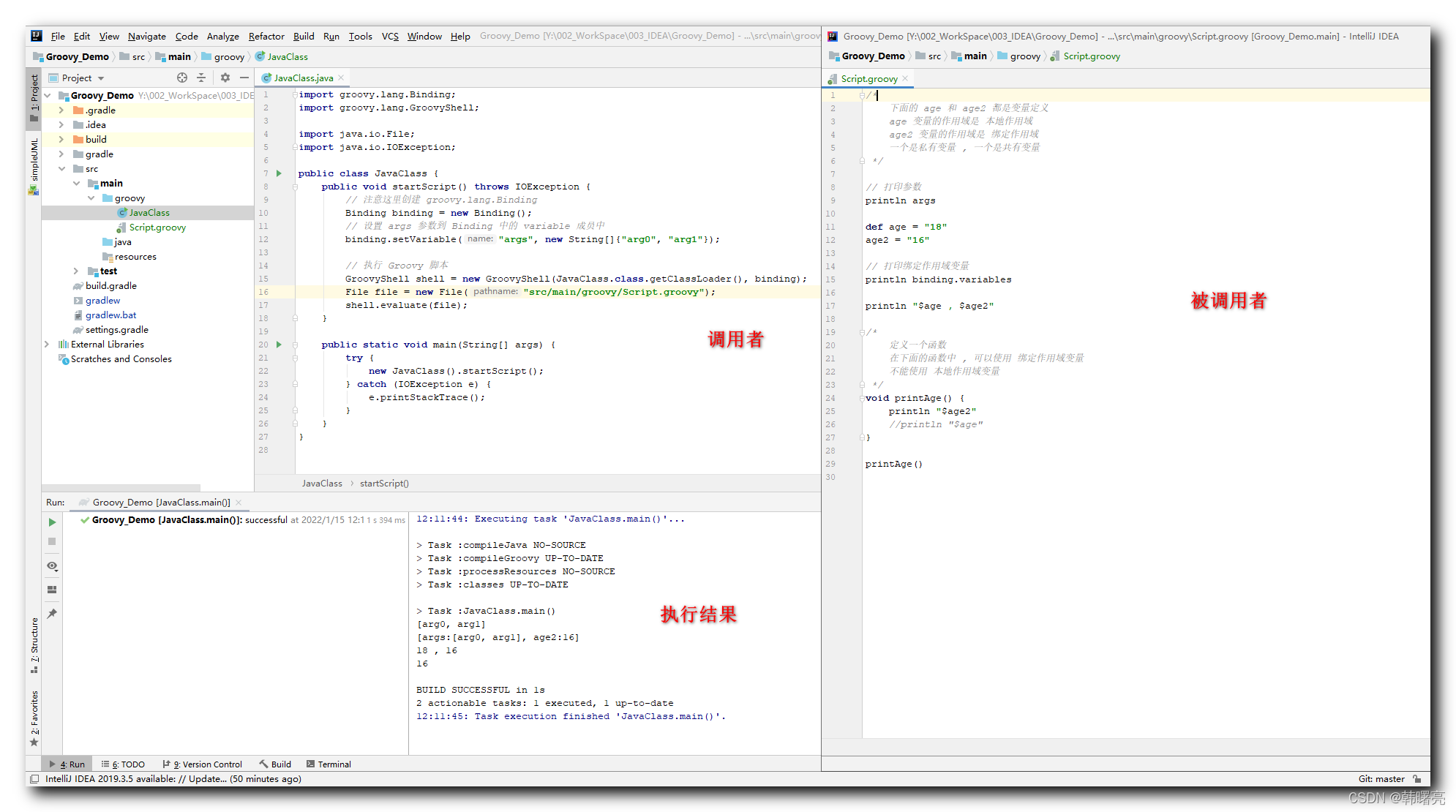
public class JavaClass {
public void startScript() throws IOException {
// 注意这里创建 groovy.lang.Binding
Binding binding = new Binding();
// 设置 args 参数到 Binding 中的 variable 成员中
binding.setVariable("args", new String[]{"arg0", "arg1"});
// 执行 Groovy 脚本
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell(JavaClass.class.getClassLoader(), binding);
File file = new File("src/main/groovy/Script.groovy");
shell.evaluate(file);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new JavaClass().startScript();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2、被调用者 Groovy 脚本
/*
下面的 age 和 age2 都是变量定义
age 变量的作用域是 本地作用域
age2 变量的作用域是 绑定作用域
一个是私有变量 , 一个是共有变量
*/
// 打印参数
println args
def age = "18"
age2 = "16"
// 打印绑定作用域变量
println binding.variables
println "$age , $age2"
/*
定义一个函数
在下面的函数中 , 可以使用 绑定作用域变量
不能使用 本地作用域变量
*/
void printAge() {
println "$age2"
//println "$age"
}
printAge()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
3、执行结果
上面的两个 Groovy 脚本都在相同目录 ;
[arg0, arg1]
[args:[arg0, arg1], age2:16]
18 , 16
16
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
文章来源: hanshuliang.blog.csdn.net,作者:韩曙亮,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:hanshuliang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/122501343
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)