Nginx——配置文件详解
1、nginx参数详解
1.1、nginx.conf 配置文件全览
#---全局块开始----
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#----全局块结束----
#====events 块开始====
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
#====events 块结束====
#****http 块开始****
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
}
#****http 块结束****
1.1.1、第一部分:全局块
从配置文件开始到 events 之间的内容,主要会设置一些影响 nginx 服务器整体运行的配 置参数。主要包括配置运行 Nginx 服务器的用户(组)、允许生成的 worker process 数,进 程 PID 存放路径、日志存放路径和类型以及配置文件的引入等。
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
worker_processes 是 Nginx 服务器并发处理服务的关键配置,值越大,可以支持的并发处理 量也越多,但是会受到硬件、软件等设备的制约。
error_log 配置 nginx 日志文件的全路径名
pid 配置进程 PID 存放路径
1.1.2、第二部分:events 块
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
- events 块涉及的参数主要影响 Nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接,常用的设置包括是否开 启对多 work process 下的网络连接进行序列化,是否允许同时接受多个网络连接,选取哪种 事件驱动模型来处理连接请求,每个 work process 可以同时支持的最大连接数等。
- 上述的例子表示每个 work process 支持的最大连接数为 1024。这部分的配置对 Nginx 的性能影响比较大,在实际中应该灵活配置。
1.1.3、第三部分:http块{}
1.1.3.1、http全局块
http 全局块配置的指令包括文件引入、MIME-TYPE 定义、连接超时时间、单链接请求数上 限等。
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;#连接超时时间
#gzip on;#是否启动压缩
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
}
1.1.3.2、Server 块
这块和虚拟主机有密切关系,虚拟主机从用户角度看,和一台独立的硬件主机是完全一 样的,该技术的产生是为了节省互联网服务器硬件成本。
每个 http 块可以包括多个 server 块,而每个 server 块就相当于一个虚拟主机。而每个 server 块也分为全局 server 块,以及可以同时包含多个 location 块。
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;#监听的端口号
server_name localhost;#监听的域名
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {#路径中包含 /
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
##location ~ ¥.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /$.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
全局 server 块
最常见的配置是本虚拟主机的监听配置和本虚拟主机的名称或 IP 配置。
location 块
一个 server 块可以配置多个 location 块。
这块的主要作用是基于 Nginx 服务器接受到的请求字符串(例如 server_name/uri-string), 对虚拟主机名称(也可以是 IP 别名)之外的字符串(列如 前面的/uri-string)进行匹配,对 特定的请求进行处理。地址定向、数据缓存和应答控制等功能,还有许多第三方模块的配置 也在这里进行。
1.2、 工作模式与连接数上限
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
}
1. 用户与工作进程
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
[root@nginx1 conf]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 1170 0.0 0.0 22568 680 ? Ss 09:14 0:00 nginx: master process /opt/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nobody 1171 0.0 0.1 23020 1288 ? S 09:14 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 1174 0.0 0.0 103264 876 pts/0 S+ 09:14 0:00 grep nginx
[root@nginx1 conf]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 1170 0.0 0.0 22568 680 ? Ss 09:14 0:00 nginx: master process /opt/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nobody 1171 0.0 0.1 23020 1288 ? S 09:14 0:00 nginx: worker process
[root@nginx1 conf]# id nobody
uid=99(nobody) gid=99(nobody) groups=99(nobody)
[root@nginx1 conf]# cat /etc/passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
……
nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
2. use epoll;
参考事件模型,use [ kqueue | rtsig | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll ]; epoll 模型是 Linux 2.6 以上版本内核中的高性能网络 I/O 模型,如果跑在 FreeBSD上面,就用 kqueue 模型。
3. worker_connections 1024;
单个后台 worker process 进程的最大并发链接数。 并发总数是 worker_processes 和 worker_connections 的乘积,即 max_clients = worker_processes * worker_connections
在 设 置 了 反 向 代 理 的 情 况 下 , max_clients=worker_processes * worker_connections / 4
为什么上面反向代理要除以 4,应该说是一个经验值
根据以上条件,正常情况下的 Nginx Server 可以应付的最大连接数为:4 * 8000 = 32000
#worker_connections 值的设置跟物理内存大小有关
#因为并发受 IO 约束,max_clients 的值须小于系统可以打开的最大文件数
系统可以打开的最大文件数和内存大小成正比,一般 1GB 内存的机器上可以打开的文件数 大约是 10 万左右
#我们来看看 360M 内存的 VPS 可以打开的文件句柄数是多少:
#$ cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
#输出 34336 # 32000 < 34336,即并发连接总数小于系统可以打开的文件句柄总数,这样就在操 作系统可以承受的范围之内
#worker_connections 的值需根据 worker_processes 进程数目和系统可以 打开的最大文件总数进行适当地进行设置
#使得并发总数小于操作系统可以打开的最大文件数目
#其实质也就是根据主机的物理 CPU 和内存进行配置
#当然,理论上的并发总数可能会和实际有所偏差,因为主机还有其他的工作进程需 要消耗系统资源。
# ulimit -SHn 65535 设置可以打开的文件数量
1.3、开启零拷贝
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
sendfile 实际上是 Linux2.0+以后的推出的一个系统调用,web 服务器可以通过调整自 身的配置来决定是否利用 sendfile 这个系统调用。先来看一下不用 sendfile 的传统网 络传输过程:
read(file,tmp_buf, len);
write(socket,tmp_buf, len);
硬盘 >> kernel buffer >> user buffer>> kernel socket buffer >>协议栈

一个基于 socket 的服务,首先读硬盘数据,然后写数据到 socket 来完成网络传输的。
上面 2 行用代码解释了这一点,不过上面 2 行简单的代码掩盖了底层的很多操作。来看看 底层是怎么执行上面 2 行代码的:
1、系统调用 read()产生一个上下文切换:从 user mode 切换到 kernel mode,然 后 DMA 执行拷贝,把文件数据从硬盘读到一个 kernel buffer 里。
2、数据从 kernel buffer 拷贝到 user buffer,然后系统调用 read() 返回,这时 又产生一个上下文切换:从 kernel mode 切换到 user mode。
3、 系统调用 write()产生一个上下文切换:从 user mode 切换到 kernel mode,然 后把步骤 2 读到 user buffer 的数据拷贝到 kernel buffer
(数据第 2 次拷贝到 kernel buffer),不过这次是个不同的 kernel buffer,这个 buffer 和 socket 相关联。
4、系统调用 write()返回,产生一个上下文切换:从 kernel mode 切换到 user mode ,然后 DMA 从 kernel buffer 拷贝数据到协议栈。
上面 4 个步骤有 4 次上下文切换,有 4 次拷贝,我们发现如果能减少切换次数和拷贝次数 将会有效提升性能。在 kernel2.0+ 版本中,系统调用 sendfile() 就是用来简化上面 步骤提升性能的。sendfile() 不但能减少切换次数而且还能减少拷贝次数。
再来看一下用 sendfile()来进行网络传输的过程:
sendfile(socket,file, len);
硬盘 >> kernel buffer (快速拷贝到 kernelsocket buffer) >>协议栈
1、 系统调用 sendfile()通过 DMA 把硬盘数据拷贝到 kernel buffer,然后数据被 kernel 直接拷贝到另外一个与 socket 相关的 kernel buffer。
这里没有 user mode 和 kernel mode 之间的切换,在 kernel 中直接完成了从一个 buffer 到另一个 buffer 的拷贝。
2、DMA 把数据从 kernelbuffer 直接拷贝给协议栈,没有切换,也不需要数据从 user mode 拷贝到 kernel mode,因为数据就在 kernel 里。
简单说,sendfile 是个比 read 和 write 更高性能的系统接口, 不过需要注意的是, sendfile 是将 in_fd 的内容发送到 out_fd 。而 in_fd 不能是 socket , 也就是 只能文件句柄。 所以当 Nginx 是一个静态文件服务器的时候,开启 SENDFILE 配置项 能大大提高 Nginx 的性能。 但是当 Nginx 是作为一个反向代理来使用的时候, SENDFILE 则没什么用了,因为 Nginx 是反向代理的时候。 in_fd 就不是文件句柄而 是 socket,此时就不符合 sendfile 函数的参数要求了。
1.4、keepalive_timeout
keepalive_timeout 65;
测试时改为 0,便于看出负载切换的效果,部署到生产前进行优化来提高效率。
1.5、是否启用压缩
#gzip on;
压缩可以有效减少文件的大小,有利于网络传输。
1.6、autoindex
autoindex on; #开启目录列表访问,合适下载服务器,默认关闭。
1.7、nginx 虚拟主机演示

虚拟主机,就是将一台物理服务器虚拟为多个服务器来使用,从而实现在一台服务器上 配置多个站点,即可以在一台物理主机上配置多个域名。Nginx 中,一个 server 标签 就是一台虚拟主机,配置多个 server 标签就虚拟出了多台主机。Nginx 虚拟主机的实 现方式有两种:域名虚拟方式与端口虚拟方式。域名虚拟方式是指不同的虚拟机使用不同的 域名,通过不同的域名虚拟出不同的主机;端口虚拟方式是指不同的虚拟机使用相同的域名 不同的端口号,通过不同的端口号虚拟出不同的主机。基于端口的虚拟方式不常用。

- 修改 nginx.conf 文件
gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.sxthenhao.com;
location / {
root /mnt;
autoindex on;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.123.com;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
......
重新加载 nginx
[root@nginx1 conf]# service nginx reload
- 修改本机 hosts 文件(C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc)
192.168.20.11 nginx1 www.123.com www.sxthenhao.com
- 访问测试


自动提供了一个欢迎页面,由于/mnt 下什么也没有挂载,所以列表中什么也没有。 - 为/mnt 挂载,并重新测试
[root@nginx1 conf]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt

对比下图

1.8、 日志配置
Nginx 还可以作为日志服务器
[root@nginx1 logs]# pwd
/opt/nginx/logs
[root@nginx1 logs]# tail -f access.log
本地浏览器访问:http://www.123.com/2019-12-03maxwd19
先不管 404 的问题,查看日志多了一天记录
修改一下 http://www.123.com/2019-12-04maxwd20,日志又记录一条
当然日志格式我们也可以自定义
access_log 配置 http 下,多 server 公用,配置 http->某 server 下,仅对该 server 使用。
http://www.sxthenhao.com/2019-12-04maxwd20myfmt.log 日志记录多一条
http://www.123.com/2019-12-04maxwd20 日志记录 access.log 多一条(并没有 使用 myfmt.log)
1.9、 Location(重点)
参考:
http://tengine.taobao.org/nginx_docs/cn/docs/http/ngx_http_core_m odule.html
语法 location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
location @name { ... }
默认值 -
上下文 server, location
让我们用一个例子解释上面的说法:
location = / {
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
[ configuration B ]
}
location /documents/ {
[ configuration C ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
[ configuration D ]
}
location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
[ configuration E ]
}
请求" / “匹配配置 A,
请求” /index.html “匹配配置 B,
请求”/documents/document.html"匹配配置 C,
请求"/images/1.gif"匹配配置 D,
请求“/documents/1.jpg”匹配配置 E。


- 修改 nginx.conf 配置文件
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.sxthenhao.com;
access_log logs/myfmt.log myfmt;
location / {
root /mnt;
autoindex on;
}
location /aabb {
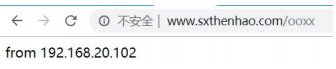
proxy_pass http://192.168.20.102/;#带上/访问该 url 对应的首页,
#不带/ 访问 http://192.168.20.102/aabb
}
}
- 重新加载 nginx
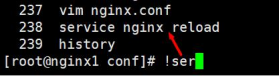
[root@nginx1 conf]# !ser
- 访问测试
http://www.sxthenhao.com/ooxx
- 修改 nginx.conf
location /ooxx {
proxy_pass http://www.baidu.com/;
}- 重启 nginx
- [root@nginx1 conf]# !ser
如果重启没有问题,直接跳步骤 7
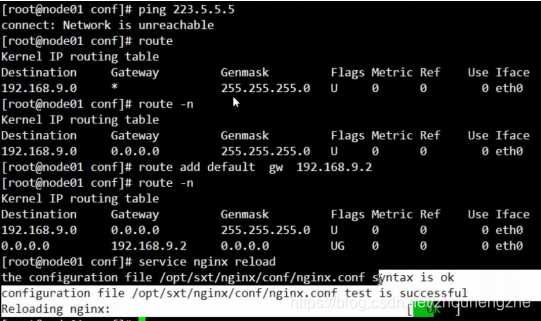
如果出现下图所示的错误:
找不到域名,也就是访问不到域名解析服务器。
解决办法:
- 访问测试 http://www.sxthenhao.com/ooxx
虽然访问到了百度,但是确实通过重定向的方式,以后发生的事情和我们的服务器就没有半 毛钱关系了。
优化配置 nginx.conf:
#尽量在服务器端跳转,不要在客户端跳转
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com/;
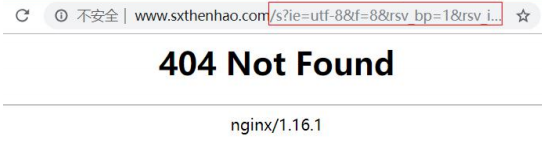
重启 nginx,再次测试,地址栏没有重定向,但是当我们查询(比如:ssd)时出现
修改 nginx.conf
location /ooxx {
proxy_pass http://www.baidu.com/;
}
location ~* /s.* {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com;
}
1.10、 Bug https protocol requires SSL support in
[root@nginx1 conf]# service nginx reload
nginx: [emerg] https protocol requires SSL support in /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:45
nginx: configuration file /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test failed
当初编译的时候没有启用 SSL 支持,在配置反向代理到 https 的网站时,编辑配置文件报 错,无法启动 nginx。
解决办法:先将 nginx.conf 备份/root/目录下,删除/opt/nginx 和/opt/apps/ nginx-1.16.1,然后在解压一份,最后编译安装。
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.16.1]# ./configure --prefix=/opt/nginx --with-http_ssl_module
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.16.1]# make && make install
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.16.1]# cd /opt/nginx/conf/
[root@nginx1 conf]# cp /root/nginx.conf ./
cp: overwrite `./nginx.conf'? yes
[root@nginx1 conf]# service nginx reload
nginx: the configuration file /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
Reloading nginx:
然后再访问 http://www.sxthenhao.com/ooxx

我是小白弟弟,一个在互联网行业的小白,立志成为一名架构师
https://blog.csdn.net/zhouhengzhe?t=1
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者











评论(0)