什么是栈
类似于链表,栈是一种简单的数据结构。在栈中,数据的取值顺序非常重要。
栈的生活例子
栈也有许多真实生活示例。考虑在食堂中彼此堆叠的板的简单示例。栈有点像洗碟子然后堆碟子,最先洗的一定是最上面的碟子,然后洗干净后,放到碟子的最下面。第一个放好的碟子永远是最后一个被取用的。可以简单地看到它遵循LIFO / FILO 原则。
栈的操作
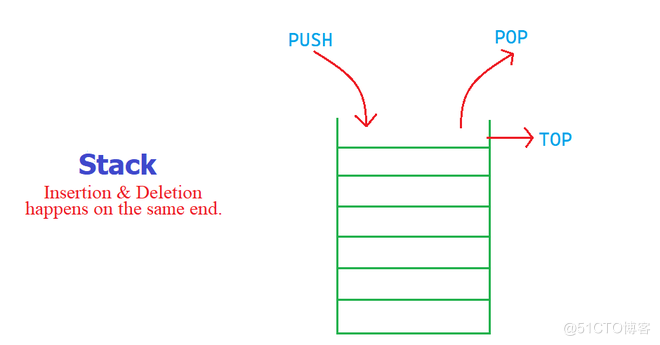
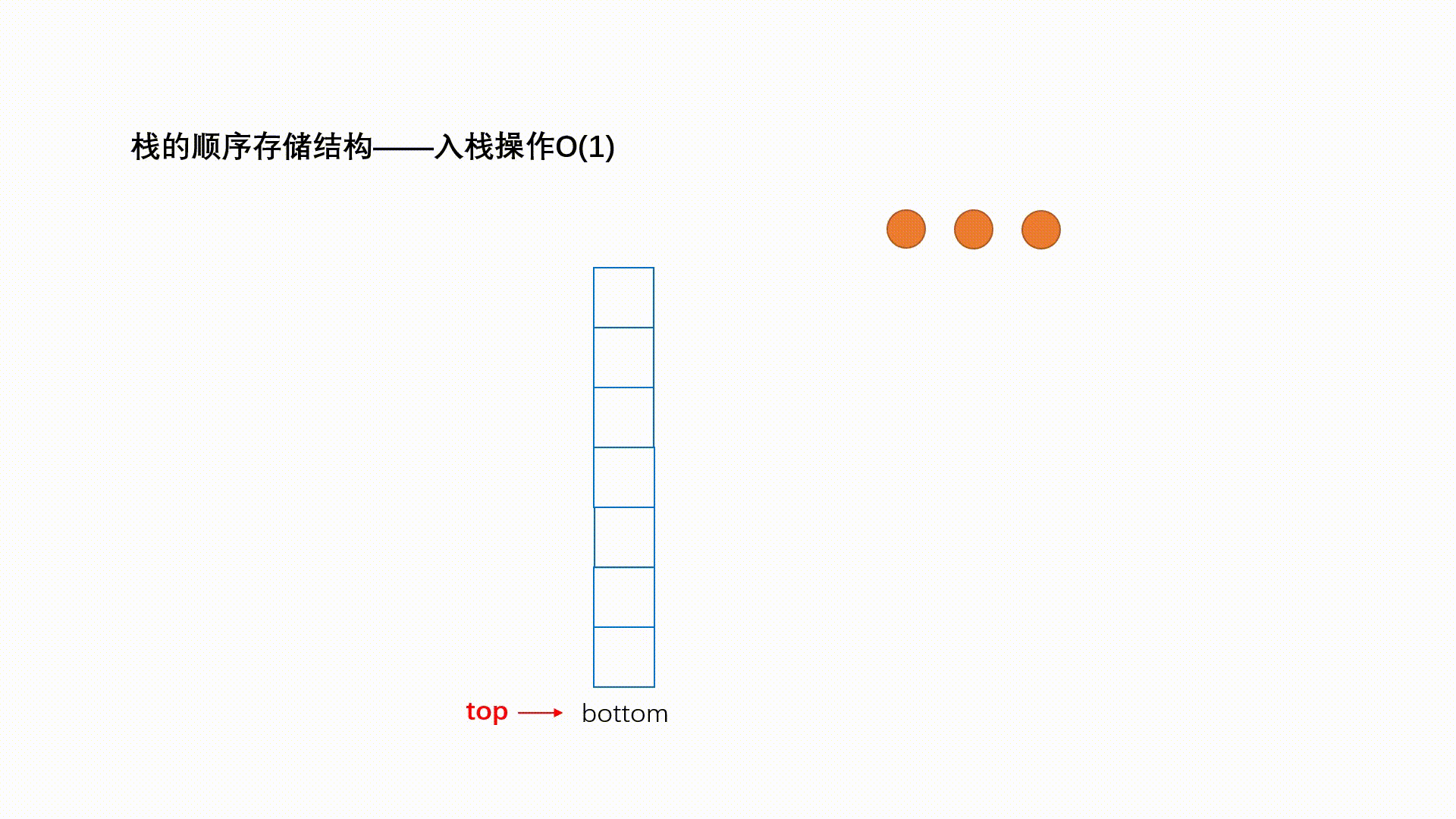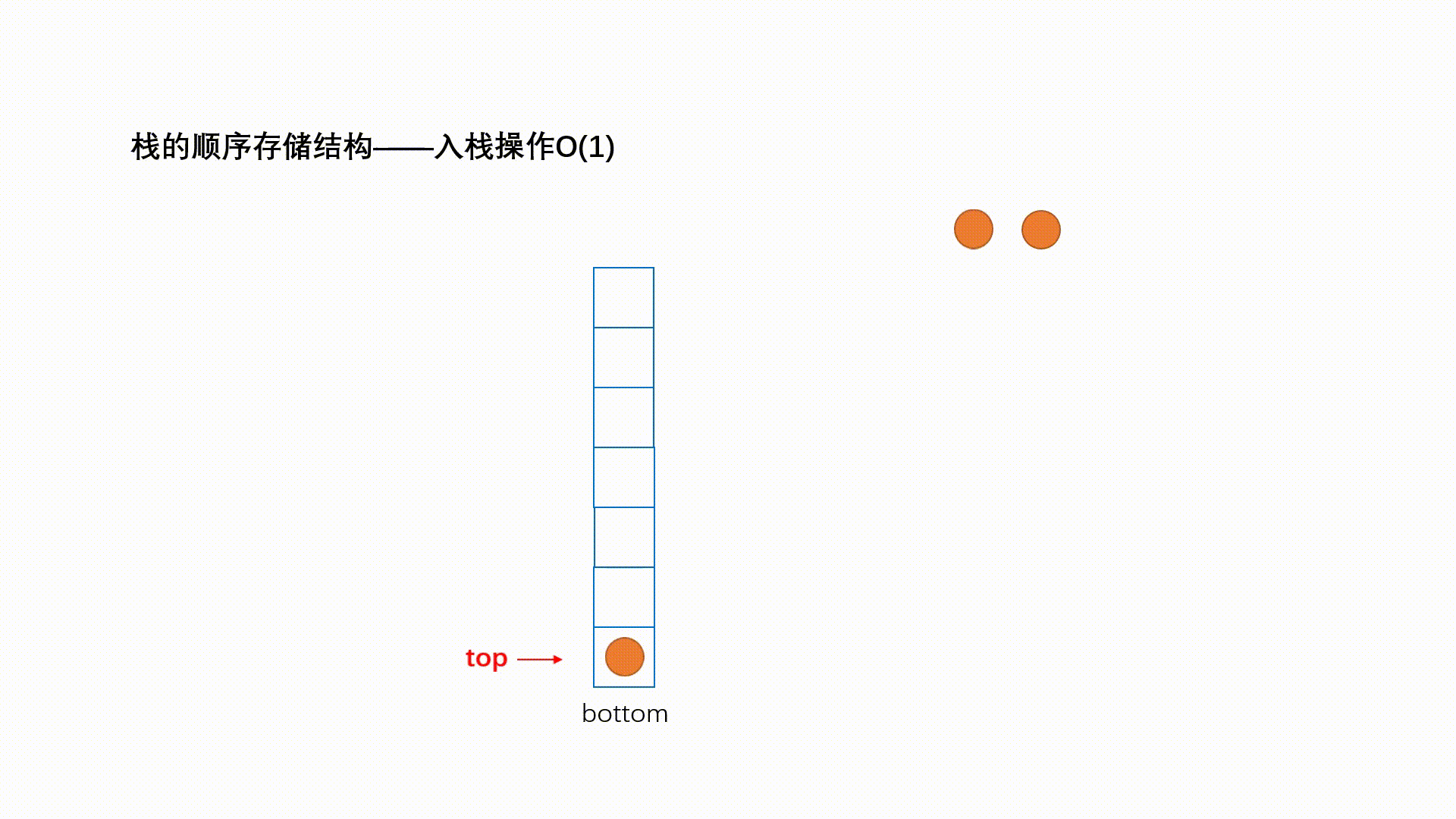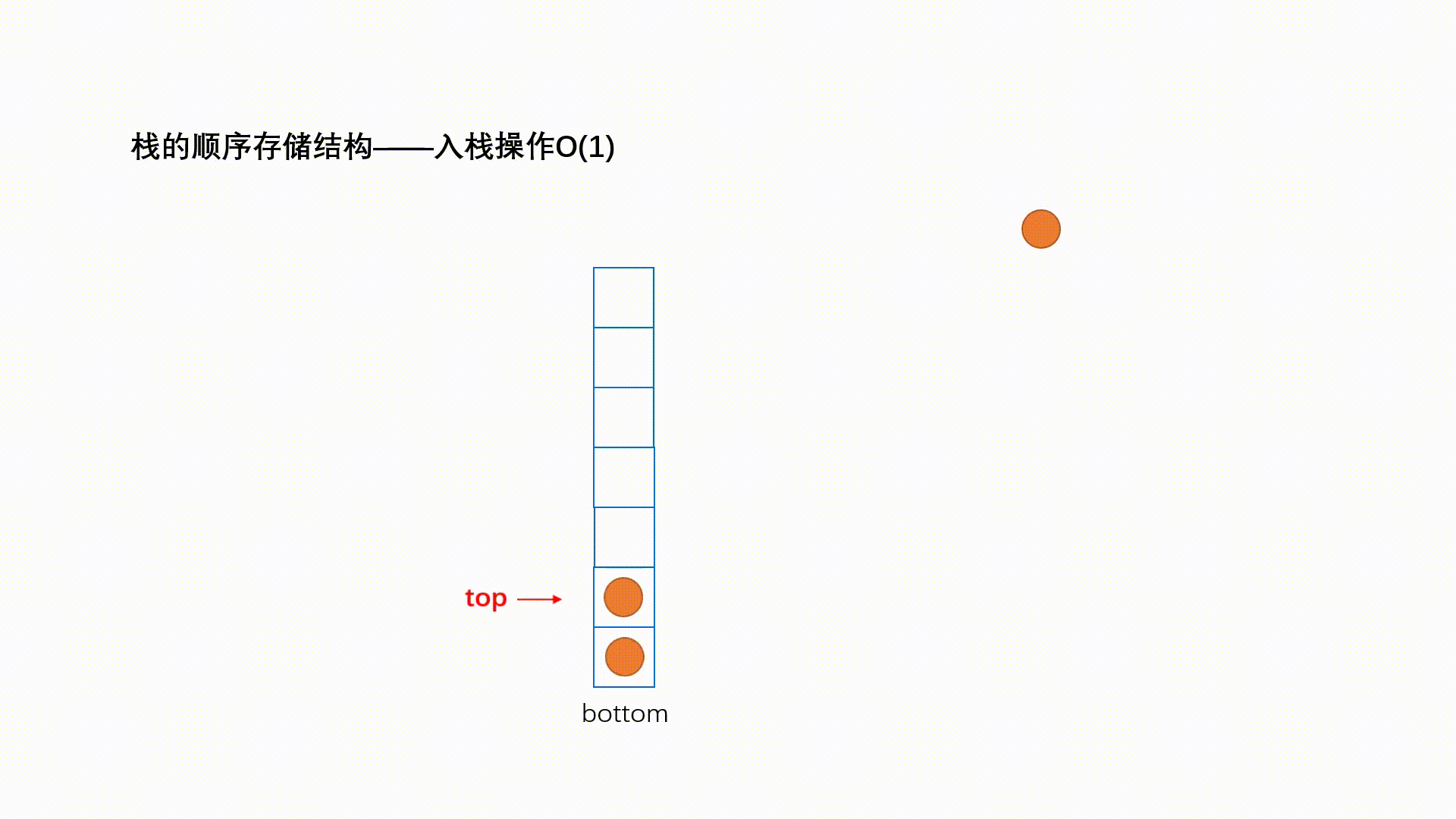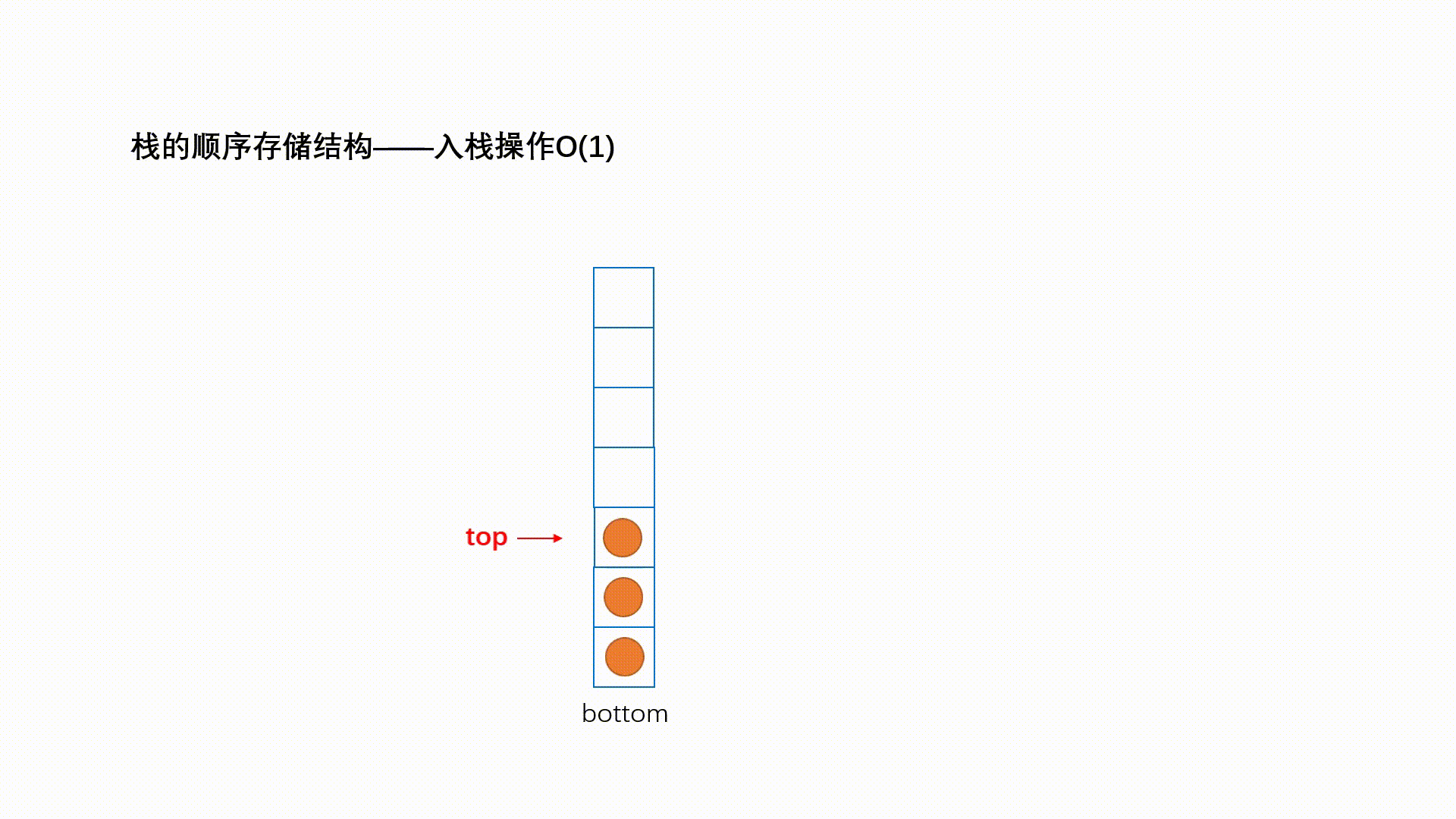
栈是一种插入和删除总在一端的有序列表,最后插入的元素时总是第一个被删除的元素,这种特征也被称为 Last in First out(LIFO)或者 First in Last out(FILO)。
入栈的操作叫做 push ; 动画演示如下:
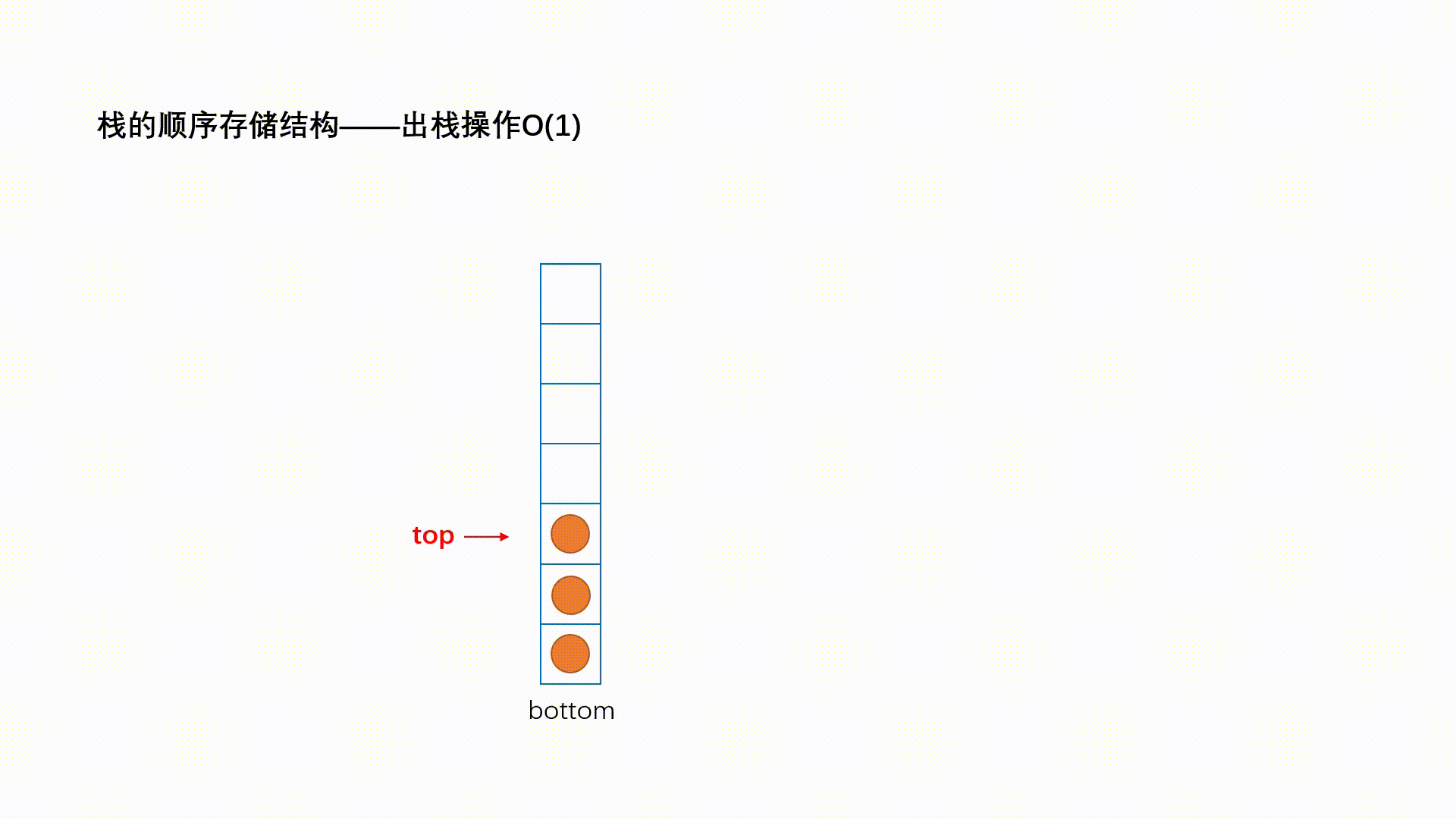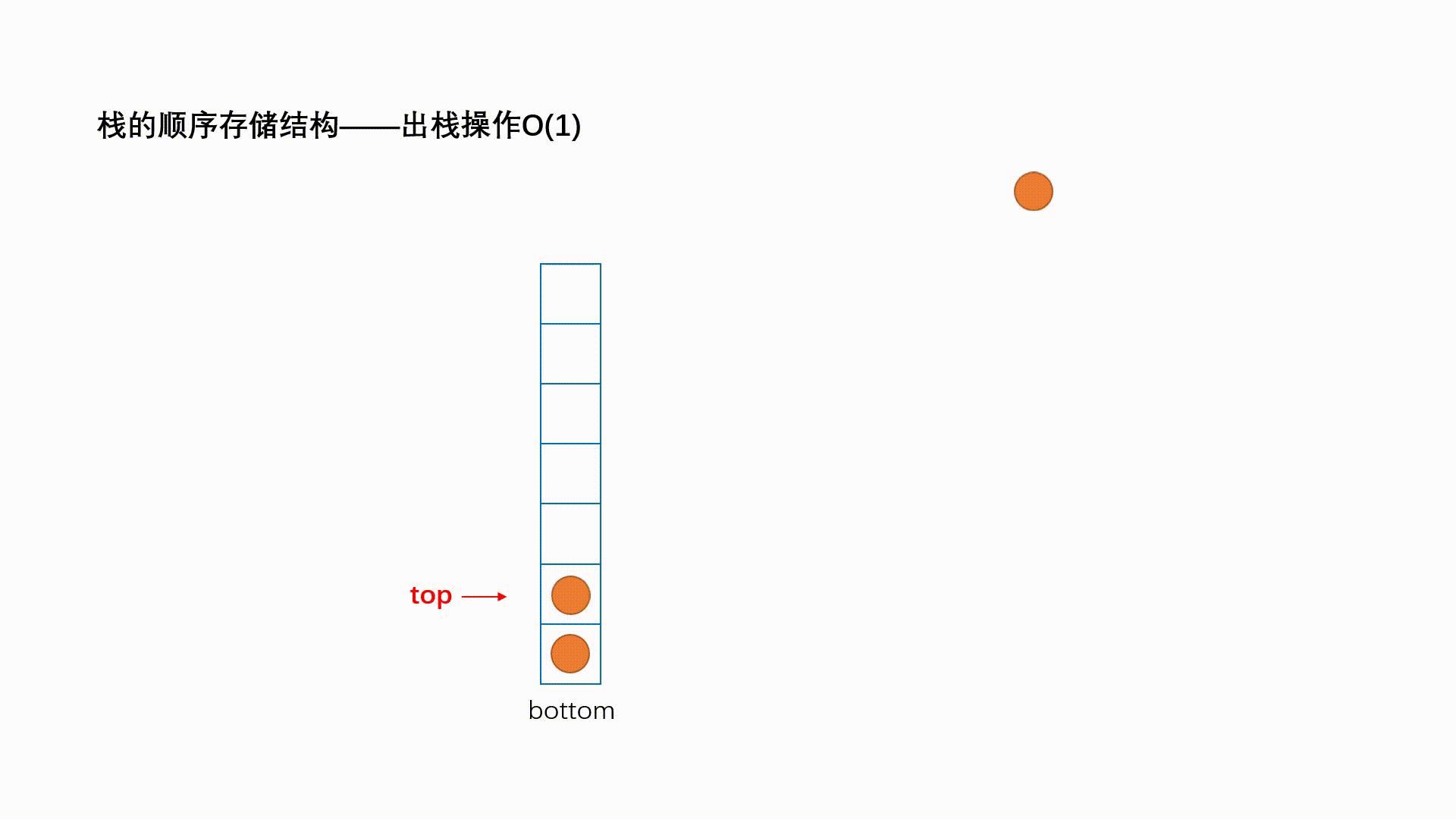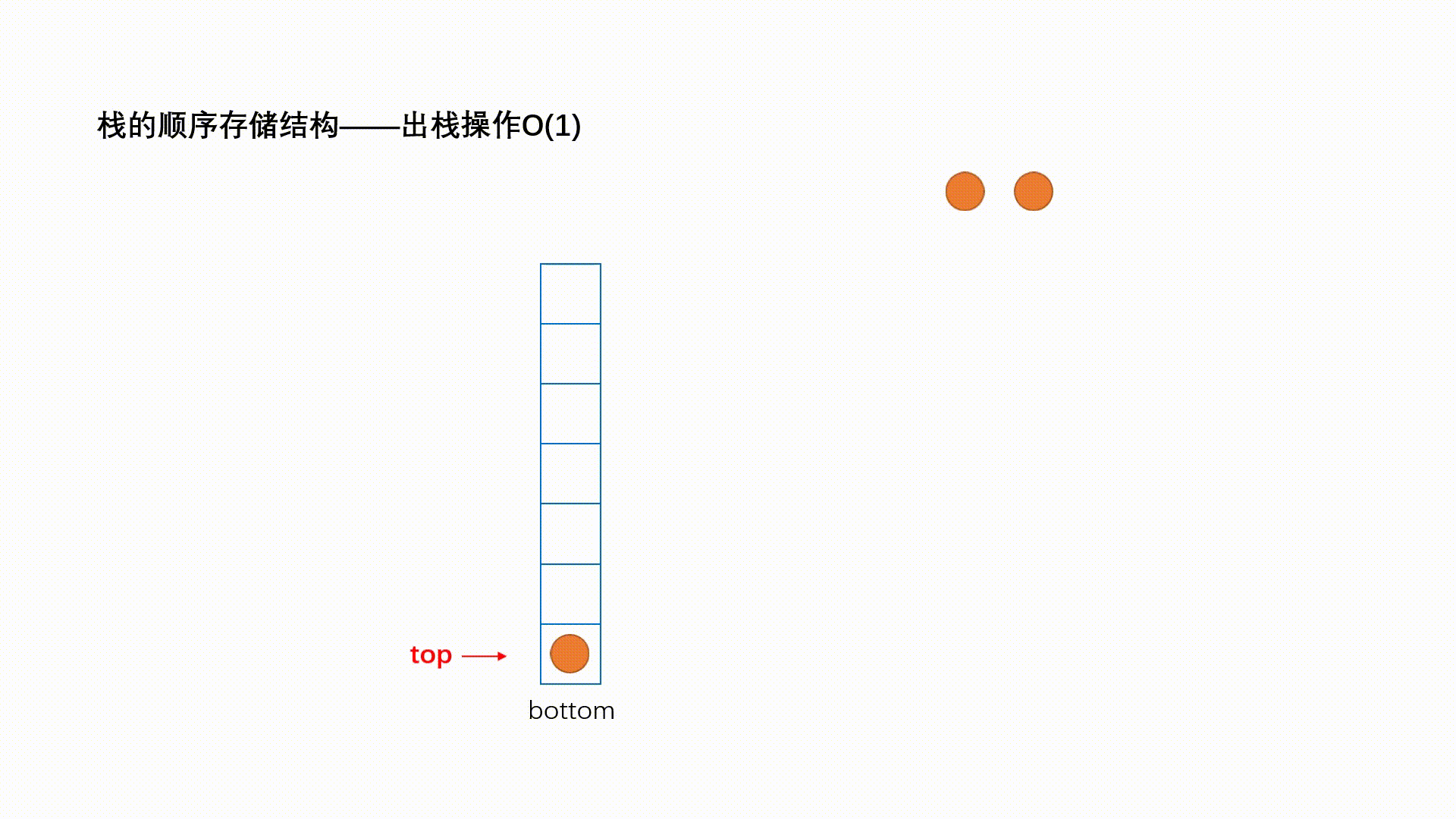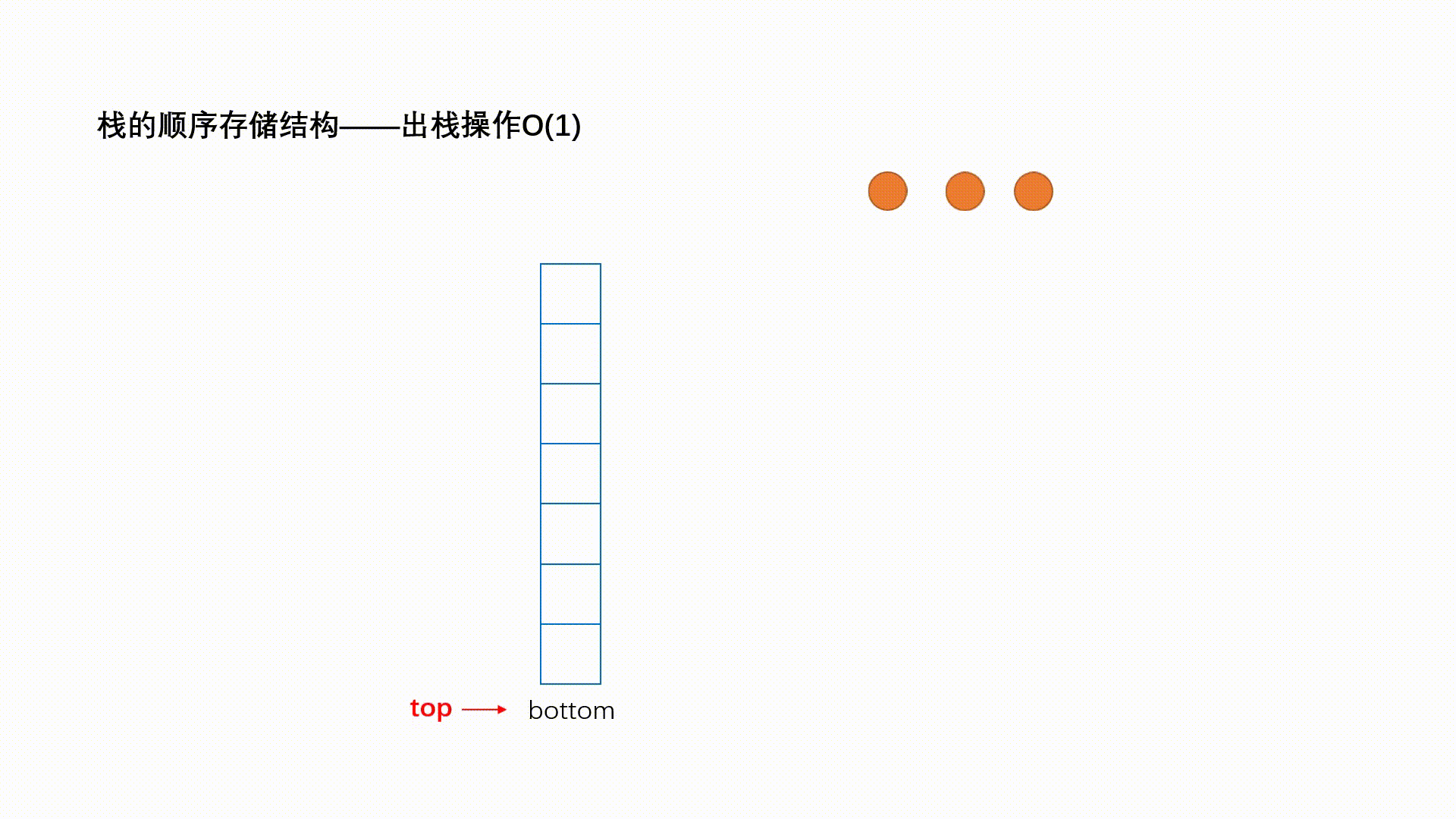
出栈的操作叫做 pop,动画演示如下:
往一个满栈里插入元素叫做 栈溢出;
栈的方法
push(e): Add e at the top of the (implicit) stackpop(): Remove and return the top element of the stackempty(): Return the Boolean value true just in case the stack is empty.top(): Return the top element of that stack without removing it.
栈的结构
type Stack interface { containers.Container Push(e interface{}) Pop() (interface{}, error) Top() (interface{}, error) }
栈的数组实现
package mainimport ( "errors" "fmt")// ArrayStack is an implementation of a stack.type ArrayStack struct { elements []interface{}}// New creates a new array stack.func New() *ArrayStack { return &ArrayStack{}}// Size returns the number of elements in the stack.func (s *ArrayStack) Size() int { return len(s.elements)}// Empty returns true or false whether the stack has zero elements or not.func (s *ArrayStack) Empty() bool { return len(s.elements) == 0}// Clear clears the stack.func (s *ArrayStack) Clear() { s.elements = make([]interface{}, 0, 10)}// Push adds an element to the stack.func (s *ArrayStack) Push(e interface{}) { s.elements = append(s.elements, e)}// Pop fetches the top element of the stack and removes it.func (s *ArrayStack) Pop() (interface{}, error) { if s.Empty() { return nil, errors.New("Pop: the stack cannot be empty") } result := s.elements[len(s.elements)-1] s.elements = s.elements[:len(s.elements)-1] return result, nil}// Top returns the top of element from the stack, but does not remove it.func (s *ArrayStack) Top() (interface{}, error) { if s.Empty() { return nil, errors.New("Top: stack cannot be empty") } return s.elements[len(s.elements)-1], nil}func main() { s := New() s.Push(1) s.Push(2) s.Push(3) fmt.Println(s) fmt.Println(s.Pop()) fmt.Println(s) fmt.Println(s.Top()) fmt.Println("栈的长度:", s.Size()) fmt.Println("栈是否为空:", s.Empty()) s.Clear() if s.Empty() { fmt.Println("栈为空") }}
运行结果:
&{[1 2 3]}3 <nil>&{[1 2]}2 <nil>栈的长度: 2栈是否为空: false栈为空
栈的链表实现
package linkedliststackimport "errors"type LinkedStack struct{ topPtr *node count int}func (s *LinkedStack) Size() int { return s.count}func (s *LinkedStack) Empty() bool { return s.count == 0}func (s *LinkedStack) Clear() { s.count = 0 s.topPtr = nil}func (s *LinkedStack) Push(e interface{}) { s.topPtr = &node{e, s.topPtr} s.count++}func (s *LinkedStack) Pop() (interface{}, error) { if s.count == 0 { return nil, errors.New("Pop: the stack cannot be empty") } result := s.topPtr.item s.topPtr = s.topPtr.next s.count-- return result, nil}func (s *LinkedStack) Top() (interface{}, error) { if s.count == 0 { return nil, errors.New("Pop: the stack cannot be empty") } result s.topPtr.item, nil}
读者可以试着自己尝试去写 main 函数验证链表实现的栈。
总结
利用栈这种数据结构,我们可以方便的去实现一些比较实用的功能:比如,浏览器的前后跳转、表达式求值、括号匹配,还可以实现二叉树的中序遍历等。


评论(0)