你真的知道C语言里extern "C" 的作用吗?
【摘要】
经常在C语言的头文件中看到下面的代码:
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
// all of your legacy C code here
#ifdef...
经常在C语言的头文件中看到下面的代码:
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
// all of your legacy C code here
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这通常用于C++和C混合编程的时候,为了防止C++的编译器在编译C文件的时候出现错误;
众所周知,C++可以进行函数名重载,但是C则没有这种功能,那这和extern "C"又有什么关系呢?
先看下面这个表格,如下所示;
| 语言 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| C | 函数名可以作为唯一ID和代码段的程序建立联系 |
| C++ | 因为重载的关系,函数名符号会被破坏,从而会更加函数的参数不同而重新生成函数符号 |
未添加 extern “C”
test.h
#ifndef TEST_H
#define TEST_H
void foo1(void);
void foo2(void);
void foo3(int i);
#endif
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
test.c
void foo1(void){}
void foo2(void) {}
void foo3(int i){}
int main(int argc,char** argv){
foo1();
foo2();
foo3(1);
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
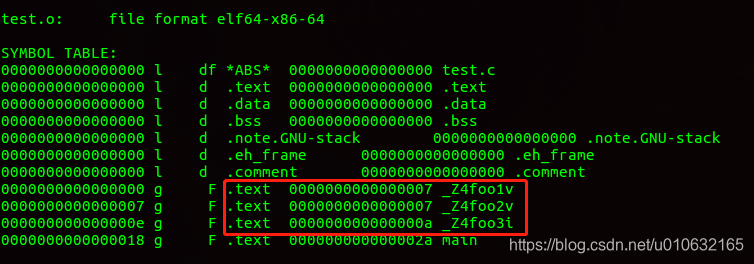
编译这两个文件,生成test.o文件,通过objdump查看函数符号;
g++ -c test.c test.h
objdump -t test.o
- 1
- 2
可以看到函数符号已经被编译器修改了;
添加extern “C”
test.h
#ifndef TEST_H
#define TEST_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void foo1(void);
void foo2(void);
void foo3(int i);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
test.c
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void foo1(void){}
void foo2(void) {}
void foo3(int i){}
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
int main(int argc,char** argv){
foo1();
foo2();
foo3(1);
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
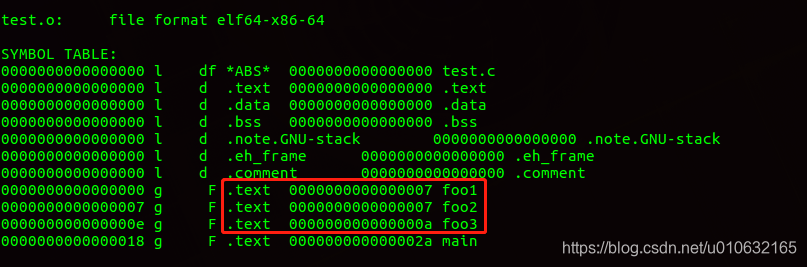
编译这两个文件,生成test.o文件,通过objdump查看函数符号;
g++ -c test.c test.h
objdump -t test.o
- 1
- 2
这时候函数符号是正确的;
extern “C” 是告诉C++的编译器不要打我这些C函数的主意;参考这篇文章会更加详细。
文章来源: great.blog.csdn.net,作者:小麦大叔,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:great.blog.csdn.net/article/details/95976533
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)