数据结构--单向链表
数据结构--单向链表
一、单链表描述
单链表
这是链表中结构最简单的,一个单链表的节点(Node)分为两部分,第一个部分保存或者显示节点的信息,另一个部分存储的是下一个节点的地址,最后一个节点存储的地址的部分指向的是空值。
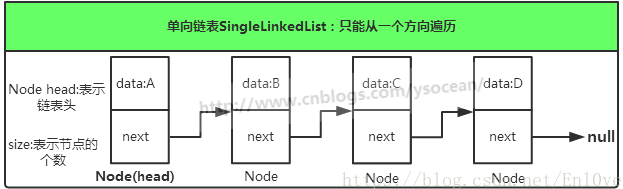
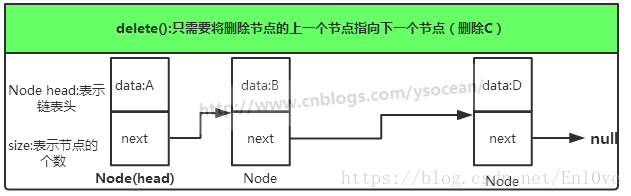
单链表只可向一个方向遍历,一般查找一个节点的时候需要从第一个节点开始访问,一直访问到需要的位置。而插入一个节点,对于单链表,我们只提供在链表头插入,只需要将当前插入的节点设置为头结点,next节点指向原头节点即可,删除一个节点,我们将该节点的前一个节点的next指向该节点的下一个节点。
单链表插入新节点图
删除节点图
二、链表结构优缺点
1、为什么单向链表的增删效率高
因为链表每个元素存储的空间是没有顺序的,删除或者添加某个元素,只需要让该节点指针重新指向下一个节点即可。
数组因为是连续的地址内存,需要移动元素位置,所以数组增伤效率较低。
2、为什么单向链表查询效率较低
单向链表的每个元素在空间的存储位置上没有规律,也没有顺序。那么在查找某个元素的时候必须从头节点挨着往下找,直到找到为止。
三、单向列表实现
-
public class SingleLinkedList {
-
private int size; //链表节点的个数
-
private Node head;
-
-
public SingleLinkedList(){
-
size = 0;
-
head = null;
-
}
-
-
private class Node{
-
private Object data; //每个节点的数据
-
private Node next; //每个节点指向下一个节点的连接
-
-
public Node(Object data){
-
this.data = data;
-
}
-
}
-
-
//在链表头部添加元素
-
public Object addHead(Object obj){
-
Node newhead = new Node(obj);
-
if(size == 0){
-
head = newhead;
-
}else{
-
newhead.next = head;
-
head = newhead;
-
}
-
size++;
-
return obj;
-
}
-
-
//在单链表头部进行删除
-
public Object delHead(){
-
Object obj = head.data;
-
head = head.next;
-
size--;
-
return obj;
-
}
-
-
//查找返回指定节点,找不到,返回Null
-
public Node FindNode(Object obj){
-
Node currnet = head;
-
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
-
if(obj.equals(currnet.data)){
-
return currnet;
-
}else{
-
currnet = currnet.next;
-
}
-
}
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
//删除指定元素,成功返回ture
-
public boolean delete(Object obj){
-
if(size == 0){
-
return false;
-
}
-
-
Node current = head;
-
Node previous = head;
-
while(!current.data.equals(obj)){
-
if(current.next == null){
-
return false;
-
}else{
-
previous = current;
-
current = current.next;
-
}
-
}
-
-
//如果删除的节点是第一个节点
-
if(current == head){
-
head = current.next;
-
size--;
-
}else{
-
//删除的节点不是第一个节点
-
previous.next = current.next;
-
size--;
-
}
-
return true;
-
}
-
-
//判断链表是否为空
-
public boolean isEmpty(){
-
return (size == 0);
-
}
-
-
//显示节点信息
-
public void display(){
-
if(size > 0){
-
Node node = head;
-
int template = size;
-
-
if(template == 1){
-
System.out.println("[" + node.data + "]");
-
return;
-
}
-
-
while(template > 0){
-
if(node.equals(head)){
-
System.out.print("["+node.data + "->");
-
}else if(node.next == null){
-
System.out.print(node.data + "]");
-
}else{
-
System.out.print(node.data + "]");
-
}
-
node = node.next;
-
template--;
-
}
-
System.out.println();
-
}else{//如果聊表一个节点都没有,直接打印【】
-
System.out.println("[]");
-
}
-
}
-
}
2、单向列表实现栈
栈中的pop()方法和push()方法,对应于链表的在头部删除元素deleteHead()以及在头部增加元素addHead()。
-
public class StackSingleLink {
-
private SingleLinkedList link;
-
-
public StackSingleLink(){
-
link = new SingleLinkedList();
-
}
-
-
//移除栈顶元素
-
public Object pop(){//实现栈的pop()方法,返回的是栈移除的元素
-
Object obj = link.delHead();
-
return obj;
-
}
-
-
//添加元素
-
public void push(Object obj){
-
link.addHead(obj);
-
}
-
-
//判断栈中是否为空
-
public boolean isEmpty(){
-
return link.isEmpty();
-
}
-
-
//打印栈中的元素
-
public void print(){
-
link.display();
-
}
-
}
四、双向链表
对于单向链表,如果想在尾部添加一个节点,那么必须从头部一直遍历到尾部,找到尾部的节点,然后在尾节点后面插入一个节点,但是这样的操作很麻烦,但是如果我们在设计链表的时候加上一个对尾节点的引用,那么会简单的很多。
双向链表图

代码实现
-
public class DoublePointLinkedList {
-
private int size;//节点个数
-
private Node head;//头节点
-
private Node tail;//尾节点
-
-
public class Node{
-
private Object data;
-
private Node next;
-
-
public Node(Object obj){
-
this.data = obj;
-
}
-
}
-
-
public DoublePointLinkedList(){
-
size = 0;
-
head = null;
-
tail = null;
-
}
-
-
//链表头部新增节点
-
public void addHead(Object obj){
-
Node node = new Node(obj);
-
if(size == 0){ //判断链表是否为空
-
head = node;
-
tail = node;
-
size++;
-
}else{
-
node.next = head;
-
head = node;
-
size++;
-
}
-
}
-
-
//链表尾增加节点
-
public void addTail(Object obj){
-
Node node = new Node(obj);
-
if(size == 0){
-
head = node;
-
tail = node;
-
size++;
-
}else{
-
tail.next = node;
-
tail = node;
-
size++;
-
}
-
}
-
-
//删除头部节点,成功返回true,失败返回false
-
public boolean delHead(){
-
if(size == 0){
-
return false;
-
}
-
if(head.next == null){//表明链表中有一个节点
-
head = null;
-
tail = null;
-
}else{
-
head = head.next;
-
}
-
size--;
-
return true;
-
}
-
-
//判断是否为空
-
public boolean isEmpty(){
-
return (size == 0);
-
}
-
-
//获得链表的节点个数
-
public int getSize(){
-
return size;
-
}
-
-
//显示节点信息
-
public void display(){
-
if(size > 0){
-
Node node = head;
-
int template = size;
-
-
if(template > 0){
-
if(node.equals(head)){
-
System.out.print("[" + head.data + "->");
-
}else if(node.next == null){
-
System.out.print(tail.data + "]");
-
}else{
-
System.out.print( node.data + "->");
-
}
-
node = node.next;
-
template--;
-
}
-
System.out.println();
-
}else{//如果链表一个节点都没有,直接打印[]
-
System.out.println("[]");
-
}
-
}
-
}
队列(Queue)
队列可以用双端链表来实现。
-
public class Queue {
-
private DoublePointLinkedList list;
-
-
private Queue(){
-
list = new DoublePointLinkedList();
-
}
-
-
//向队列中插入一个对象(只能插入到尾部)
-
public void insert(Object obj){
-
list.addTail(obj);
-
}
-
-
//向队列中插入一个对象(只能从头部去除)
-
public void remove(){
-
list.delHead();
-
}
-
-
//判断队列中是否为空
-
public boolean isEmpty(){
-
return list.isEmpty();
-
}
-
-
//打印队列中的元素
-
public void print(){
-
list.display();
-
}
-
}
有序链表
前面的链表实现插入都是无序的,在有些应用中需要链表中的数据有序,这称之为有序链表。在有序链表中,数据是按照关键值有序排列的。一般在大多数需要使用有序数组的场合也可以使用有序链表。有序链表优于有序数组的地方是插入的速度(因为元素不需要移动),另外链表可以扩展到全部有效的使用内存,而数组只能局限于一个固定的大小中。
-
public class OrderLinkedList {
-
private Node head;
-
-
public class Node{
-
private int data;
-
private Node next;
-
-
public Node(int data){
-
this.data = data;
-
}
-
}
-
-
public OrderLinkedList(){
-
head =null;
-
}
-
-
//插入节点,并且按照从小到大的顺序排列
-
public void insert(int data){
-
Node node = new Node(data);
-
Node pre = null;
-
Node current = head;
-
while(current != null && current.data < node.data){
-
pre = current;
-
current = current.next;
-
}
-
if(pre == null){
-
head = current;
-
head.next = current;
-
}else{
-
pre.next = node;
-
node.next = current;
-
}
-
}
-
-
//删除节点
-
public void delete(){
-
head = head.next;
-
}
-
-
//打印节点
-
public void display(){
-
Node current = head;
-
while(current != null){
-
System.out.println(current.data + " ");
-
current.next = current;
-
}
-
System.out.println("");
-
}
-
}
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/enl0ve/article/details/80890225
文章来源: brucelong.blog.csdn.net,作者:Bruce小鬼,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:brucelong.blog.csdn.net/article/details/94589584
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)