sklearn中分类器的比较
【摘要】 简 介: 运行对比了 分类器的比较? 中的sklearn中的分类的性能对比。这为我们理解机器学习中的特性提供了理解基础。关键词: sklearn,python 分类器比较 在 分类器的比较? 给出了在sklearn的python包中的几类分类器性能的比较。 1.1 sklearn分类器 在人工数据集上比较scikit-learn中的几种分类器。这个例子的重点是说明不同分类器的决策边界...

简 介: 运行对比了 分类器的比较? 中的sklearn中的分类的性能对比。这为我们理解机器学习中的特性提供了理解基础。
关键词: sklearn,python
分类器比较
在 分类器的比较? 给出了在sklearn的python包中的几类分类器性能的比较。
1.1 sklearn分类器
在人工数据集上比较scikit-learn中的几种分类器。这个例子的重点是说明不同分类器的决策边界的性质。这些例子所传达的直觉不一定会传递给真实的数据集,因此,这一点应该有所把握。
特别是在高维空间中,数据更容易被线性分离,而朴素贝叶斯和线性支持向量机等分类器的简单性可能导致比其他分类器更好的泛化。
1.1.1 分类器
测试的分类器总共十个:
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Gaussian Process",
"Decision Tree", "Random Forest", "Neural Net", "AdaBoost",
"Naive Bayes", "QDA"]
* Nearest Neighbors
* Linear SVM
* RBF SVM
* Gaussian Process
* Decision Tree
* Random Forest
* Neural Net
* AdaBoost
* Naive Bayes
* QDA
1.2 数据集合
图中显示实色训练点和半透明的测试点。右下角显示测试集的分类准确率。
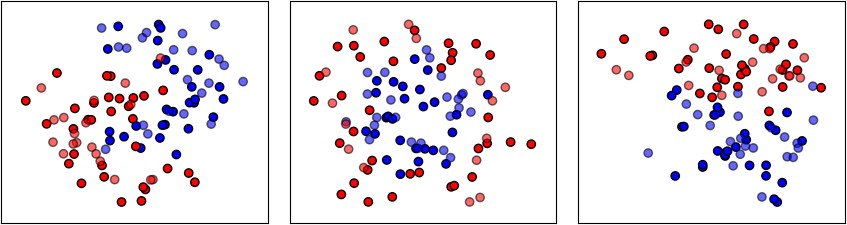
▲ 图1.1.1 训练数据集合
左:弯月数据集合;中:圆环数据集合;右:线性可分数据集合
左:弯月数据集合;中:圆环数据集合;右:线性可分数据集合
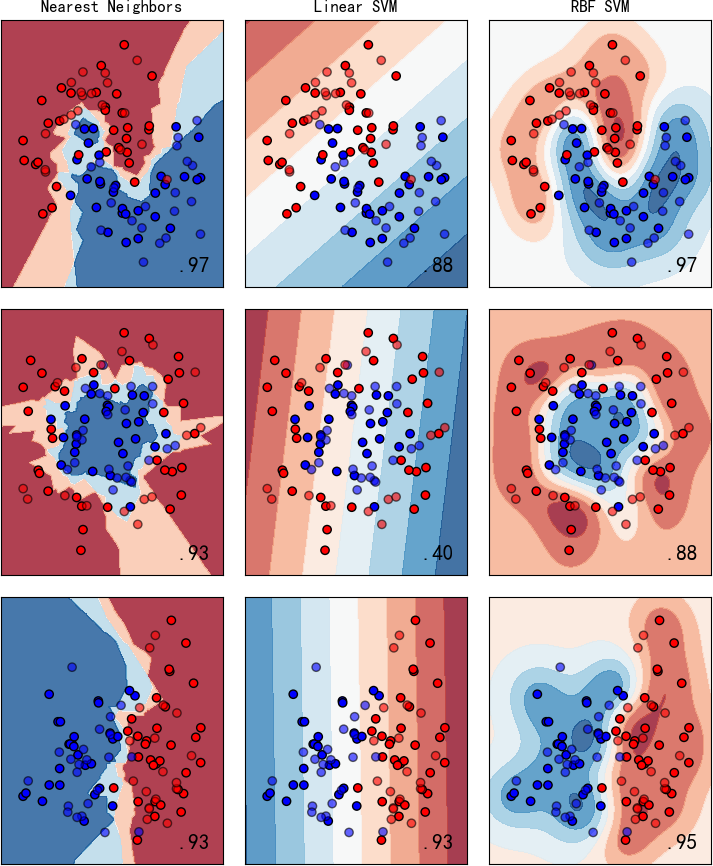
▲ 图1.2.2 左:Nearest Neighbors;中:Linear SVM; 右:RBF SVM
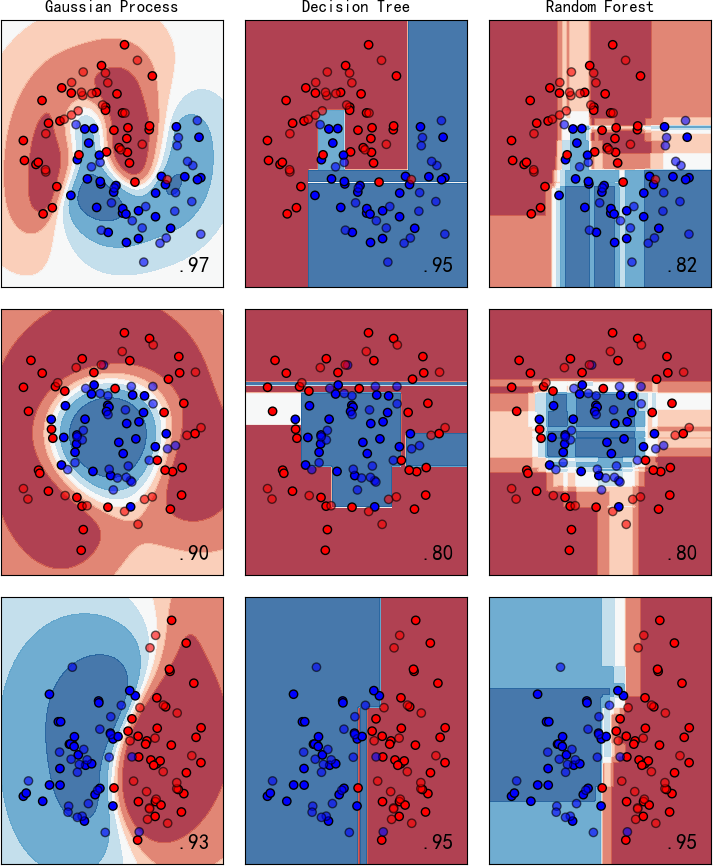
▲ 图1.2.3 左:Gaussion Process;中:Decision Tree; 右:Random Forest
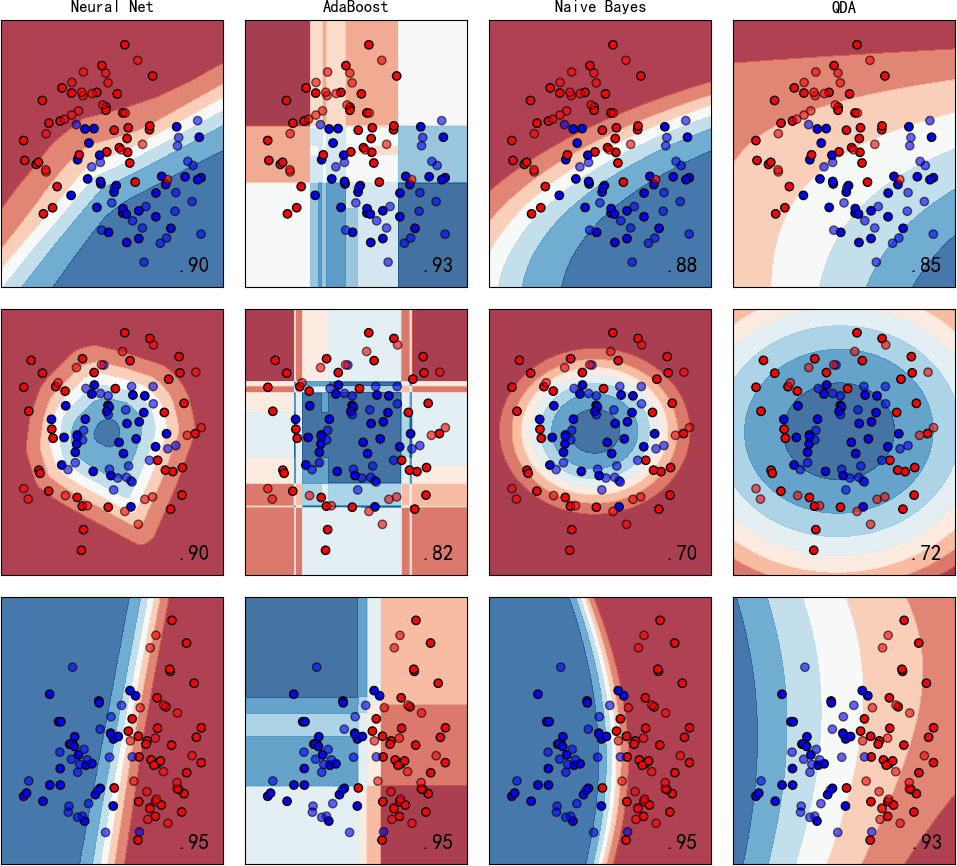
▲ 图1.2.4 左:Neural Net;左中:Adaboost; 右中:Naive Bayes;右:QDA
1.3 测试代码
#!/usr/local/bin/python
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
#============================================================
# TEST2.PY -- by Dr. ZhuoQing 2021-12-24
#
# Note:
#============================================================
from headm import * # =
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
#------------------------------------------------------------
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Gaussian Process",
"Decision Tree", "Random Forest", "Neural Net", "AdaBoost",
"Naive Bayes", "QDA"]
#------------------------------------------------------------
classifiers = [
KNeighborsClassifier(3),
SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025),
SVC(gamma=2, C=1),
GaussianProcessClassifier(1.0 * RBF(1.0)),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5),
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1),
MLPClassifier(alpha=1, max_iter=1000),
AdaBoostClassifier(),
GaussianNB(),
QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis()]
#------------------------------------------------------------
X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2,
random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable
]
#------------------------------------------------------------
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(27, 9))
i = 1
#------------------------------------------------------------
# iterate over datasets
for ds_cnt, ds in enumerate(datasets):
# preprocess dataset, split into training and test part
X, y = ds
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4, random_state=42)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF'])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title("Input data")
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors='k')
# Plot the testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6,
edgecolors='k')
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors='k')
# Plot the testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors='k', alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title(name)
ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'),
size=15, horizontalalignment='right')
i += 1
#------------------------------------------------------------
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
#------------------------------------------------------------
# END OF FILE : TEST2.PY
#============================================================
※ 总结 ※
运行对比了 分类器的比较? 中的sklearn中的分类的性能对比。这为我们理解机器学习中的特性提供了理解基础。
■ 相关文献链接:
□ 分类器的比较?
● 相关图表链接:
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)