【Java 数据结构 & 算法】宁可累死自己, 也要卷死别人 6 循环队列
【摘要】
【Java 数据结构 & 算法】⚠️宁可累死自己, 也要卷死别人 6⚠️ 循环队列
概述循环队列循环队列实现改变队列大小enqueue 方法dequeue 方法main
完整代码
...
概述
从今天开始, 小白我将带大家开启 Jave 数据结构 & 算法的新篇章.

循环队列
循环队列 (Circular Queue) 是一种特殊的队列. 循环队列解决了队列出队时需要将所有数据前移一位 (复杂度为 O(n)) 的问题.
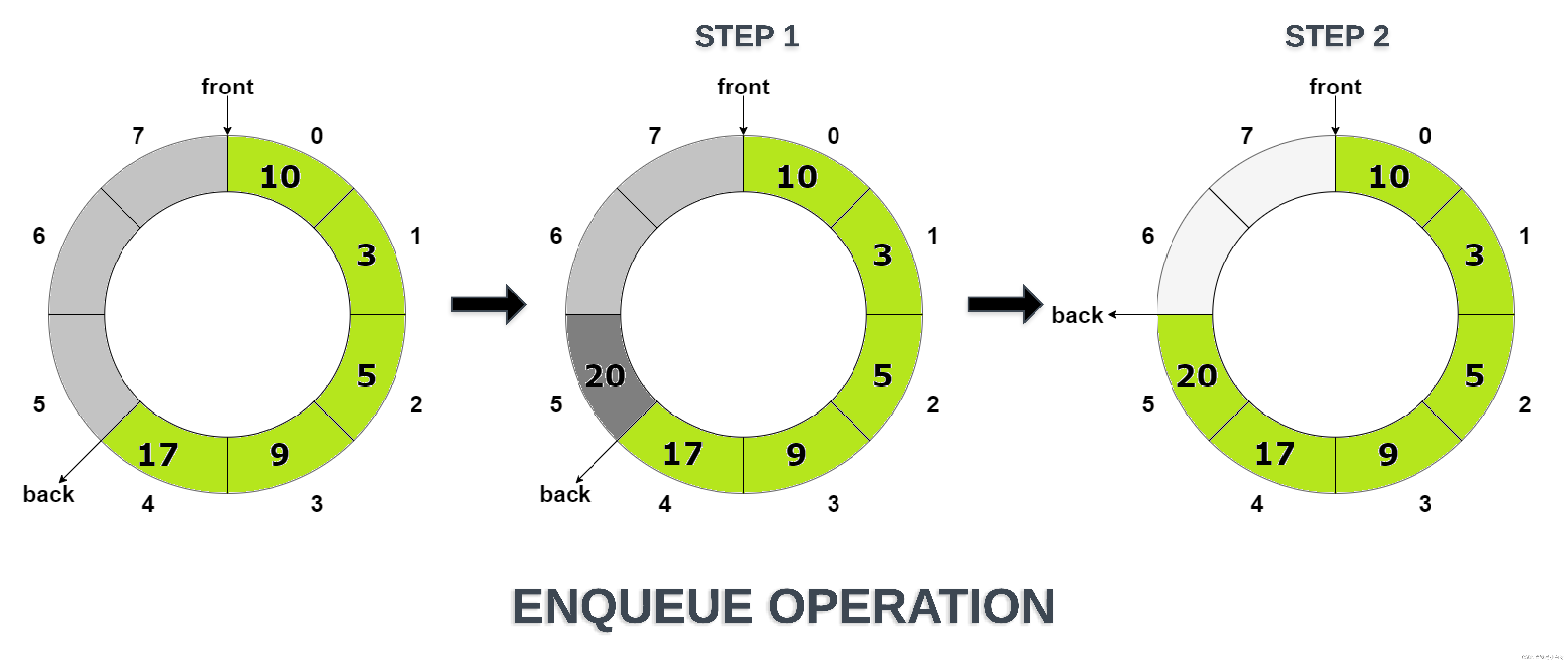
循环队列的底层依然是数组, 不过增加了指向头和尾的指针.
循环队列实现
- 判断队列是否为空: 当头指针 Q.front == 尾指针 Q.rear, 队列为空
- 判断队列是否为满: 当头指针 Q.front == 尾指针 Q.rear + 1) % Maxsize, 队列为满
改变队列大小
// 改变队列大小
private void resize(int capacity) {
// 定义新数组
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[capacity + 1];
// 转移数组元素
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
newData[i] = data[(i +front) % data.length];
}
// 更新
data = newData;
front = 0;
rear = size;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
enqueue 方法
// 入队
public void enqueue(E e) {
// 判断是否为满
if((rear + 1) % data.length == front) {
resize(getCapacity() * 2);
}
// 队伍加入
data[rear] = e;
rear = (rear + 1) % data.length;
size++;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
dequeue 方法
// 出队
public E dequeue() {
// 判断是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
}
// 取出第一个元素
E element = data[front];
data[front] = null;
// 移动头指针
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
// 数组大小-1
size--;
// 判断是否需要缩小
if(size==getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0) {
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
}
return element;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
main
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建循环队列
CircularQueue<Integer> queue = new CircularQueue<>(5);
// 入队
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
}
// 出队
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
输出结果:
CircularQueue{data=[0, null, null, null, null, null], front=0, rear=1, size=1}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, null, null, null, null], front=0, rear=2, size=2}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, 2, null, null, null], front=0, rear=3, size=3}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, 2, 3, null, null], front=0, rear=4, size=4}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, null], front=0, rear=5, size=5}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, null, null, null, null, null], front=0, rear=6, size=6}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, null, null, null, null], front=0, rear=7, size=7}
CircularQueue{data=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null], front=0, rear=8, size=8}
CircularQueue{data=[null, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null], front=1, rear=8, size=7}
CircularQueue{data=[null, null, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null], front=2, rear=8, size=6}
CircularQueue{data=[null, null, null, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null], front=3, rear=8, size=5}
CircularQueue{data=[null, null, null, null, 4, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null], front=4, rear=8, size=4}
CircularQueue{data=[null, null, null, null, null, 5, 6, 7, null, null, null], front=5, rear=8, size=3}
CircularQueue{data=[6, 7, null, null, null, null], front=0, rear=2, size=2}
CircularQueue{data=[7, null, null], front=0, rear=1, size=1}
CircularQueue{data=[null, null], front=0, rear=0, size=0}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
完整代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CircularQueue<E> {
private E[] data;
private int front, rear;
private int size;
// 无参构造
public CircularQueue() {
this(10);
}
// 有参构造
public CircularQueue(int capacity) {
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity + 1];
front = rear = size = 0;
}
// 入队
public void enqueue(E e) {
// 判断是否为满
if((rear + 1) % data.length == front) {
resize(getCapacity() * 2);
}
// 队伍加入
data[rear] = e;
rear = (rear + 1) % data.length;
size++;
}
// 出队
public E dequeue() {
// 判断是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
}
// 取出第一个元素
E element = data[front];
data[front] = null;
// 移动头指针
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
// 数组大小-1
size--;
// 判断是否需要缩小
if(size==getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0) {
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
}
return element;
}
// 获取队列大小
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
// 获取队列容量
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length - 1;
}
// 队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
// 改变队列大小
private void resize(int capacity) {
// 创建新数组
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[capacity + 1];
// 转移数组元素
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
newData[i] = data[(i +front) % data.length];
}
// 更新
data = newData;
front = 0;
rear = size;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CircularQueue{" +
"data=" + Arrays.toString(data) +
", front=" + front +
", rear=" + rear +
", size=" + size +
'}';
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建循环队列
CircularQueue<Integer> queue = new CircularQueue<>(5);
// 入队
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
}
// 出队
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121

文章来源: iamarookie.blog.csdn.net,作者:我是小白呀,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:iamarookie.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121882681
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)