【JavaSE】多态数组的使用
【摘要】 【JavaSE】多态数组的使用
1. 多态数组
-
数组的定义类型为父类类型,里面保存的实际元素类型为子类类型
-
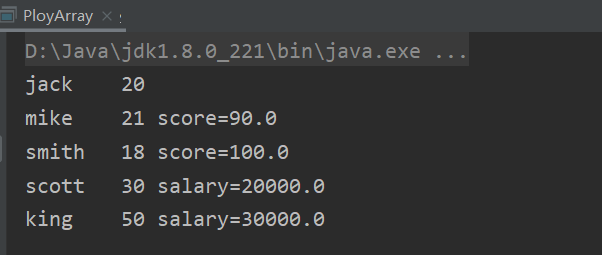
应用实例:现有一个继承结构如下:要求创建 1 个 Person 对象、2 个 Student 对象和 2 个 Teacher 对象, 统一放在数组中,并调用每个对象say方法。

public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String say(){
return name + "\t" + age;
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
private double score;
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
//重写父类say方法
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + " score=" + score;
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person {
private double salary;
public Teacher(String name, int age, double salary) {
super(name, age);
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
//重写父类 say 方法
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + " salary=" + salary;
}
}
public class PloyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] person = new Person[5];
person[0] = new Person("jack", 20);
person[1] = new Student("mike", 21, 90);
person[2] = new Student("smith", 18, 100);
person[3] = new Teacher("scott", 30, 20000);
person[4] = new Teacher("king", 50, 30000);
//循环遍历多态数组,调用 say() 方法
for (int i = 0; i < person.length; i++) {
//提示:Person[i]编译类型是 person,运行类型是根据实际情况JVM来判断
System.out.println(person[i].say()); //动态绑定机制
}
}
}
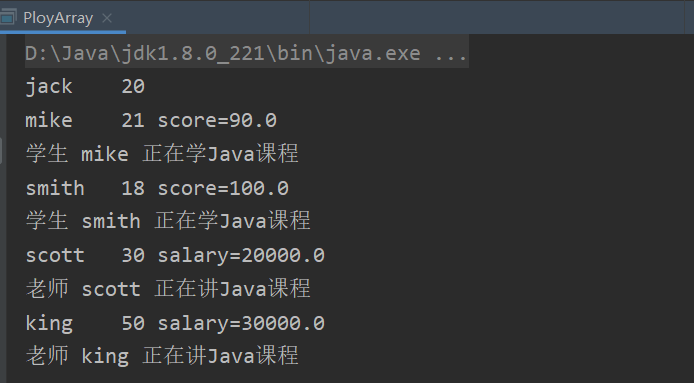
- 应用实例升级:如何调用子类特有的方法,比如:Teacher 有一个
teach()方法, Student 有一个study()方法,怎么调用?
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String say(){
return name + "\t" + age;
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
private double score;
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
//重写父类say方法
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + " score=" + score;
}
//特有方法
public void study(){
System.out.println("学生 " + getName() + " 正在学Java课程");
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person {
private double salary;
public Teacher(String name, int age, double salary) {
super(name, age);
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
//重写父类 say 方法
@Override
public String say() {
return super.say() + " salary=" + salary;
}
//特有方法
public void teach(){
System.out.println("老师 " + getName() + " 正在讲Java课程");
}
}
public class PloyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] person = new Person[5];
person[0] = new Person("jack", 20);
person[1] = new Student("mike", 21, 90);
person[2] = new Student("smith", 18, 100);
person[3] = new Teacher("scott", 30, 20000);
person[4] = new Teacher("king", 50, 30000);
//循环遍历多态数组,调用 say() 方法
for (int i = 0; i < person.length; i++) {
//提示:Person[i]编译类型是 person,运行类型是根据实际情况JVM来判断
System.out.println(person[i].say()); //动态绑定机制
//使用类型判断 + 向下转型
if (person[i] instanceof Student){//判断 person[i]运行类型是不是Student
Student student = (Student) person[i];//向下转型
student.study();
//也可以使用 (Student) person[i].study();
}else if (person[i] instanceof Teacher) {
Teacher teacher = (Teacher) person[i];
teacher.teach();
}else if (person[i] instanceof Person){
}else{
System.out.println("你的类型有误,请自行检查");
}
}
}
}
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)