Spring Cloud Config一文搞懂
1、简介
传统配置的痛点:
- 在以前的项目中,我们通过配置文件、操作系统变量、Java系统属性等方式配置Java项目;在spring boot爆火之后我们的配置信息都写在application.yml或application.properties文件中,这些配置文件随着项目的打包与应用一起发布;但是当我们需要修改配置文件中的配置信息的时候,需要更新配置文件重新构建、重新发布;如果配置信息配置在操作系统环境变量或者Java系统属性中则需要重启应用。
- 配置文件中往往有一些敏感信息,比如数据库密码、Redis密码、加密秘钥等信息。这些信息如果直接配置在配置文件中,容易泄露。
针对这些问题,Spring Cloud早期发布了Spring Cloud Config进行集中式配置管理,成功解决了这些问题。
Spring Cloud Config分为Server端和Client端。其中Spring Cloud Config Server是Spring Cloud为指定应用中所有服务提供集中式配置的一个服务,借助Spring Cloud Config Server可以实现集中管理所有应用的配置,避免重复配置。
Spring Cloud Config带来了诸多好处:
- 配置文件与应用解耦,可以在不重启应用的前提下随时更新发布、回滚配置文件
- 不同的服务可以共享配置,这在微服务架构系统中非常有用,避免重复配置,大大降低了微服务配置的维护成本
- 配置与应用隔离之后,敏感信息得到保护
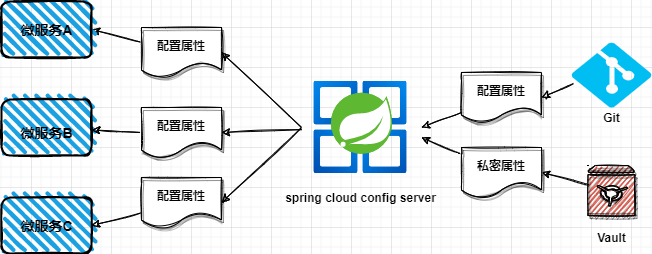
Spring Cloud Config Server通过Git仓库给微服务提供配置属性架构图:
2、正文
正文通过Spring Boot项目展开对Spring Cloud Config的探讨。分别会有以下几个方面来展开:
- Spring Cloud Config + Git手动刷新
- Spring Cloud Config + Git + WebHook实现自动刷新
- Spring Cloud Config + Eureka
- Spring Cloud Bus多端刷新
注意整个项目的搭建是一步一步来的,重复的步骤不会重复出现。
2.1 Spring Cloud Config + 手动刷新
Spring Cloud Config Server
首先需要搭建Spring Cloud Config Server服务,Spring Cloud Config Server服务应该作为一个单独的应用运行和维护,所以我们单独为Spring Cloud Config Server启动一个服务。
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>我这里选择的Spring Boot版本和Spring Cloud版本如下(版本如果不对应会出现异常,大家可以选择自己需要的对应版本):
<!--spring boot 版本 2.3.4.RELEASE-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<!--spring cloud 版本 Hoxton.RELEASE-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>>Hoxton.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>application.yml配置文件:
下面的配置文件中有几个点比较重要,配置错误将无法获取配置信息
a、default-label,配置文件所在分支,默认值为master
b、search-paths,配置文件所在根目录
c、uri ,仓库地址
## 服务名
spring:
application:
name: config-service
## config git相关配置
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://gitee.com/leonplious/config-server-demo.git # 仓库地址
username: xxxx # git 登录账户
password: xxxx # git 登录密码
default-label: master # 分支
search-paths: userservice # 分支下根文件夹名
## 服务端口
server:
port: 28888编写启动类,启动类上需要添加@EnableConfigServer注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}此时我们可以开始测试Spring Cloud Config Server。推送一个配置文件到git仓库中,配置文件的名称为userservice-dev.yml,配置文件的内容如下:
user:
username: "liziba"
password: "hello"启动Spring Cloud Config Server应用,访问http://localhost:28888/userservice/dev/master,可以得到如下信息,证明Spring Cloud Config Server服务启动成功。
{
"name":"userservice",
"profiles":[
"dev"
],
"label":"master",
"version":"285fd1b9f068cec6def6ba14ab787807a9ffecbc",
"state":null,
"propertySources":[
{
"name":"https://gitee.com/leonplious/config-server-demo.git/userservice/userservice-dev.yml",
"source":{
"user.username":"liziba",
"user.password":"hello"
}
}
]
}注意Spring Cloud Config 有它的一套访问规则,通过这套规则可以获取相应数据,数据的响应格式略有不同。
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties- application指应用名称,我们的配置文件名称应该严格按照application-{profile}.yml命名。
- profile指环境信息,比如生产环境【prod】、开发环境【dev】、测试环境【test】
- label指git分支,比如master
我这里使用的是第一种方式,这种方式能够返回详细的配置信息,以及分支信息、profile信息、应用名等,默认的分支名master可以省略。http://localhost:28888/userservice/dev等同于http://localhost:28888/userservice/dev/master
接下来就可以开始配置Spring Cloud Config Client
新建Spring Cloud Config Client服务,该服务会从Spring Cloud Config Server中获取配置信息。
依赖:
<!--config客户端依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--web提供rest访问端点-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--actuator提供端点触发更新-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>配置文件bootstrap.yml:
需要注意使用config获取配置信息时,我们需要将config相关配置提取到优先级最高的bootstrap.yml配置文件中,否则不会生效。spring-cloud-starter-config默认会访问8888端口,如果你的Spring Cloud Config Server并未使用该端口启动,可以在bootstrap.yml文件中指定Spring Cloud Config Server端口信息,这样才能覆盖,否则获取不到Spring Cloud Config Server上的配置信息。
我这里的配置文件演示了多环境dev和prod,注意我的config.uri地址时http://localhost:28888,并不是http://localhost:8888
server:
port: 18888
spring:
application:
name: userservice
profiles:
active: dev
## 加载并暴露所有端点,用于或许刷新端点
management:
endpoints:
refresh:
enabled: true
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
## 配置中心无法访问,返回此数据
user:
username: NaN
password: NaN
---
spring:
profiles: dev
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:28888
label: master
profile: dev
fail-fast: true
---
spring:
profiles: prod
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:28888
label: master
profile: prod
fail-fast: true编写两个User和User2用于获取配置信息,两个类获取配置的方式不一样,分别通过 @Value 或和@ConfigurationProperties 来获取:
@Data
@ToString
@Component
public class User {
@Value("${user.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${user.password}")
private String password;
}@Data
@ToString
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
public class User2 {
private String username;
private String password;
}编写rest访问端点,获取两个User的配置信息:
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
private final User user;
private final User2 user2;
@GetMapping("/user1")
public String user() {
return user.toString();
}
@GetMapping("/user2")
public String user2() {
return user2.toString();
}
}启动服务,分别访问两个rest端点,此时可以分别获取到如下信息,说明我们配置信息已经获取到了。
http://localhost:18888/user/user1
User(username=liziba, password=hello)http://localhost:18888/user/user2
User2(username=liziba, password=hello)此时我们将username修改成中文‘李子捌’,并推送到Gitee;修改后的配置文件如下:
user:
username: "李子捌"
password: "hello"再次访问两个rest端点,发现两个请求返回的都是旧数据,并没有获取到最新的配置。别慌,没人通知他更新它肯定是旧数据呀!这个时候我们引入的actuator依赖和management.endpoints配置就派上用场了。
我们可以借助postman、curl等http工具向http://localhost:18888/actuator/refresh端点发起post请求。
再次访问两个rest端点,分别返回如下数据
http://localhost:18888/user/user1
User(username=liziba, password=hello)http://localhost:18888/user/user2
User2(username=李子捌, password=hello)@Value 获取配置信息的方式并未获取到最新数据,而@ConfigurationProperties 获取配置信息获取到了更新后的数据,所以我们在开发的时候记得使用@ConfigurationProperties来结合config获取配置信息。
2.2 Spring Cloud Config + Git + WebHook实现自动刷新
实现自动刷新的功能,我们需要借助两个东西;第一个是GitHub、Gitee、GitLab提供的WebHook功能,第二个是@RefreshScope注解。
第一步:配置WebHook(我这里采用的是Gitee)
进入你的配置文件所在仓库地址,选择管理页签之后选择WebHooks,点击添加WebHook
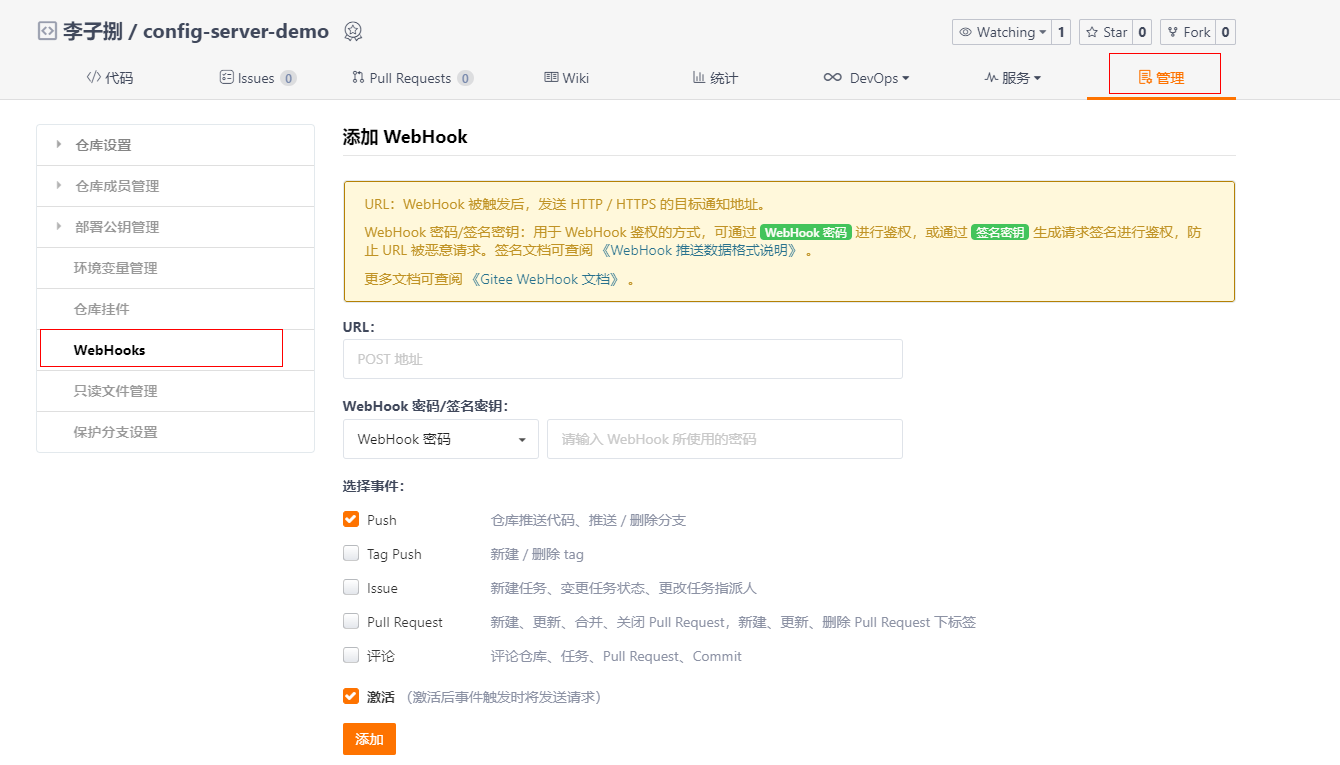
注意URL中填写的是actuator提供的refresh端点,也就是我们上面用postman请求的地址,你可以选择你需要触发调用该地址的事件,一般选择Push。特别需要注意的是,你是要Gitee或GitHub需要提供一个公网地址,一般公司内部都会搭建GitLab代码仓库,公司内部可以使用内网地址。
第二步:添加@RefreshScope注解
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@RefreshScope
public class UserController {
// ...
}2.3 Spring Cloud Config + Eureka
大部分情况下,在微服环境中我们都会使用配置中心,这里采用Eureka配置中心,结合Spring Cloud Config实现配置动态刷新。实现这个功能我们需要引入Eureka的依赖,启动一个注册中心服务,并修改Spring Cloud Config Server相关配置和Spring Cloud Config Client相关配置。
依赖:
<!--Eureka Server依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>配置文件:
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}修改Spring Cloud Config Server
增加依赖:
<!--Eureka Client依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>修改配置文件(增加eureka 客户端配置):
spring:
application:
name: config-service
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://gitee.com/leonplious/config-server-demo.git
username: xxxx
password: xxxx
default-label: master
search-paths: userservice
server:
port: 28888
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: true
register-with-eureka: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true修改启动类(增加@EnableEurekaClient注解):
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
@EnableEurekaClient
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}此时启动EurekaServer和Spring Cloud Config Server,可以在Eureka上看到Spring Cloud Config Server注册信息。
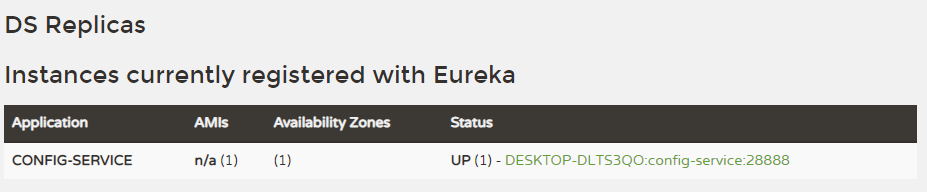
修改Spring Cloud Config Client
增加依赖:
<!--Eureka Client依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>修改配置文件(增加eureka 客户端配置,修改Config配置信息):
未使用注册中心我们指定uri,使用注册中心之后我们可以直接使用服务名。
server:
port: 18888
spring:
application:
name: userservice
profiles:
active: dev
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
## 加载所有端点
management:
endpoints:
refresh:
enabled: true
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
## 配置中心无法访问,返回此数据
user:
username: NaN
password: NaN
---
spring:
profiles: dev
cloud:
config:
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: config-service # 配置Config Server服务名
# uri: http://localhost:28888
label: master
profile: dev
fail-fast: true
---
spring:
profiles: prod
cloud:
config:
discovery:
enabled: true
service-id: config-service
# uri: http://localhost:28888
label: master
profile: prod
fail-fast: true修改启动类(增加@EnableEurekaClient注解):
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}重新访问两个rest端点,可以效果一致。如果需要配置Eureka的高可用集群,在我的《Spring Cloud系列专栏》中有文章可以参考。
2.4 Spring Cloud Bus多端刷新
在生产环境中,我们往往会集群部署,此时我使用WebHook来刷新单个端点就显得很鸡肋了。这个时候我们可以使用Spring Cloud Bus来实现多端刷新。它是通过Message Queue来广播配置更新通知来实现的。
官方介绍地址:
我们先安装RabbitMQ来使用Spring Cloud Bus(官方支持rabbit和kafka)
修改Spring Cloud Config Client应用中的相关配置和依赖
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>修改配置文件(引用rabbit配置,其他配置不变):
server:
port: 18888
spring:
application:
name: userservice
profiles:
active: dev
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
password: guest
username: guest
virtual-host: /此时我们使用IDEA将Spring Cloud Config Client应用使用不同端口启动两个服务
选中服务后点击Edit Configurations...
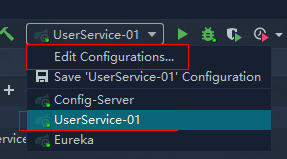
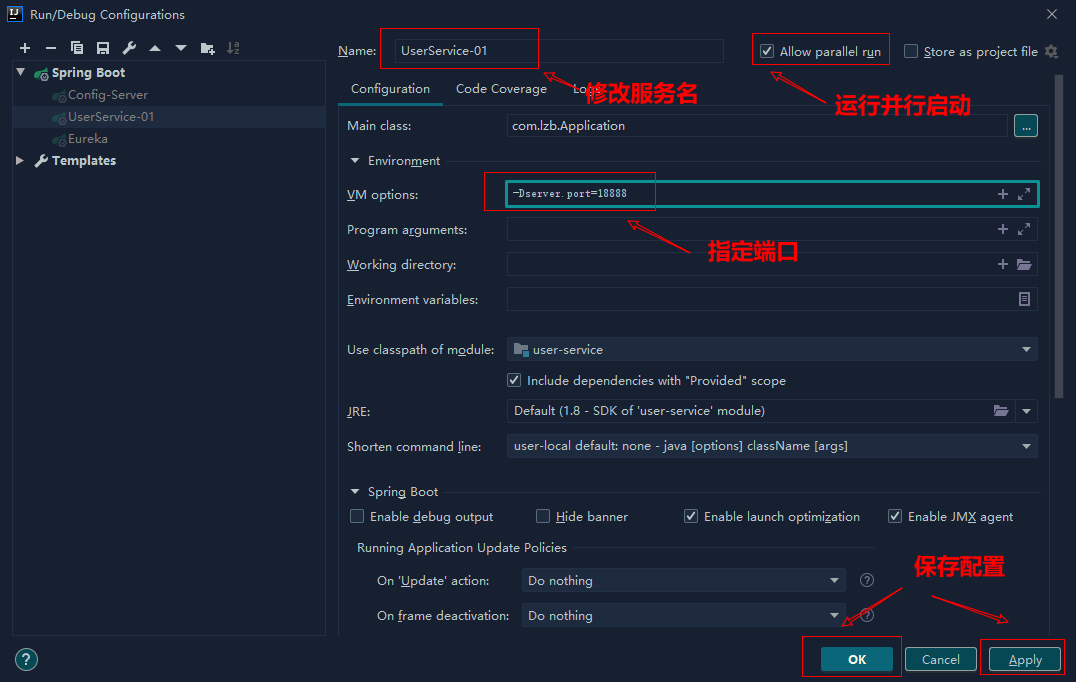
修改配置,指定端口和服务名,并勾选Allow parallel run
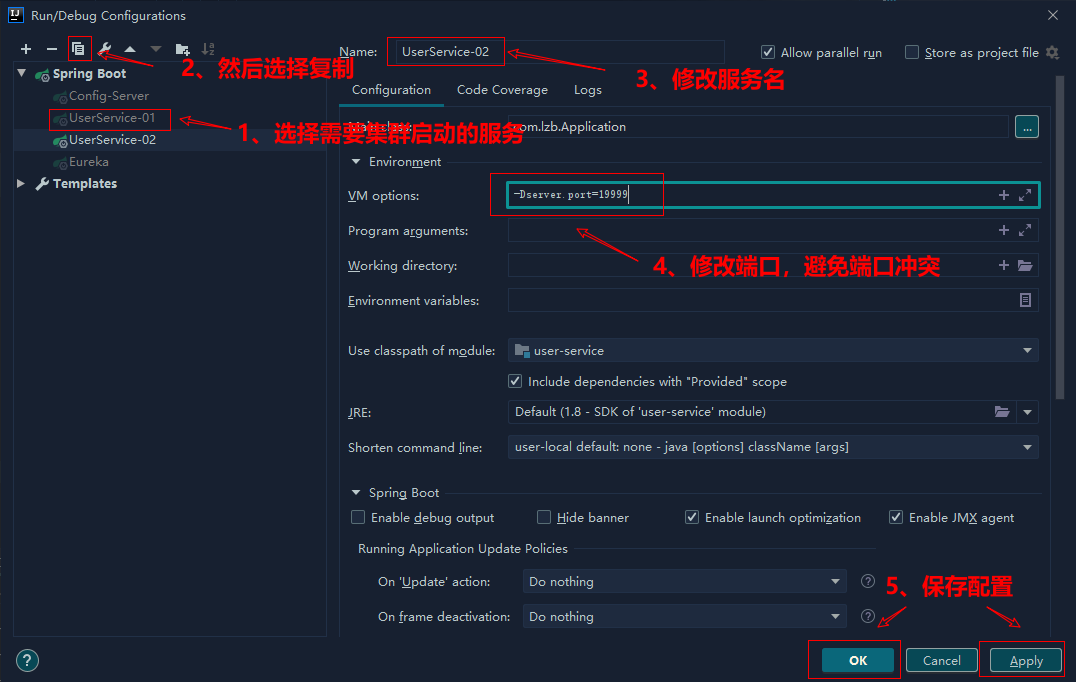
复制一份配置,使用另一端口启动
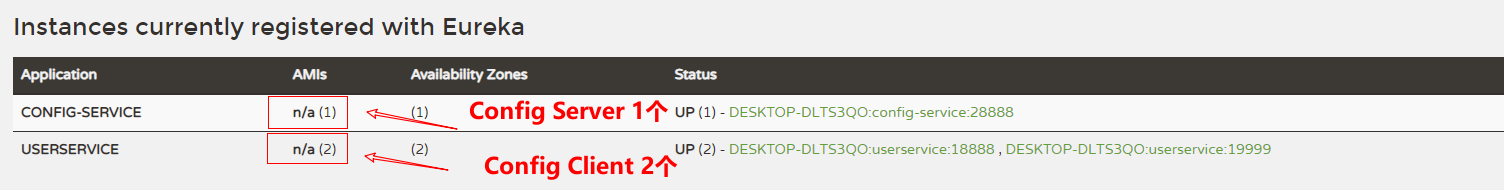
此时可以访问单点Eureka,查看注册信息
RabbitMQ上有两个匿名队列
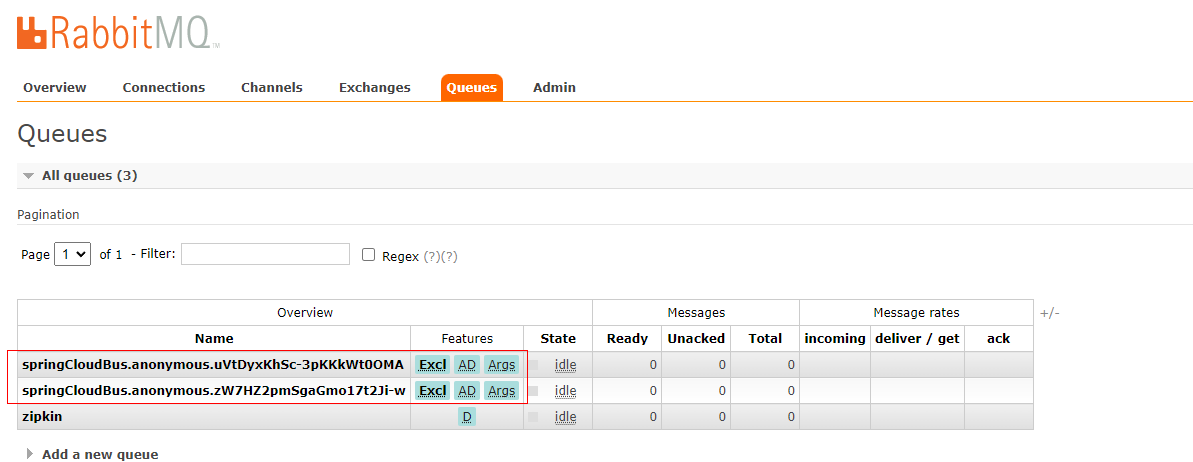
此时我们根据不同的端口访问rest端口
http://localhost:19999/user/user2
http://localhost:18888/user/user2
User2(username=liziba, password=123456)修改Gitee上的配置文件
user:
username: "Edg"
password: "champion"如果没有配置WebHook则使用postman发起一个post请求到http://localhost:18888/actuator/bus-refresh端点,注意这里是bus-refresh。重新访问两个rest端点,此时配置信息已刷新:
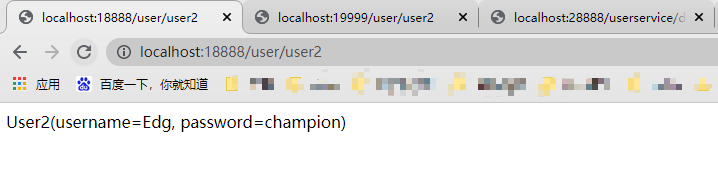
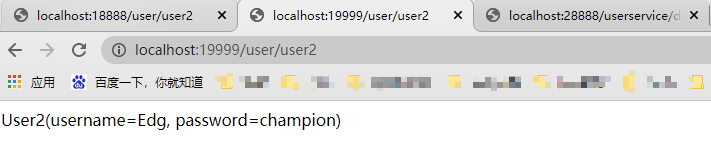
👇🏻 关注公众号 获取更多资料👇🏻

- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)