Java类方法
【摘要】
文章目录
Java 类方法静态与非静态使用对象访问方法使用多个类
Java 类方法
方法是在类中声明的,并且它们用于执行某些操作。举个例子: 创建一个myMethod()在test1 ...
Java 类方法
方法是在类中声明的,并且它们用于执行某些操作。举个例子:
创建一个myMethod()在test1 中命名的方法:
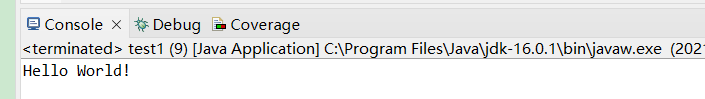
public class test1 {
static void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
当它被 调用时,myMethod()打印文本(动作)。
调用 myMethod():
package test15;
public class test1 {
static void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
myMethod();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
运行:
静态与非静态
你应该经常会看到具有static或public 属性和方法的Java 程序。在上面的例子中,我们创建了一个static 方法,这意味着它可以在不创建类的对象的情况下被访问,不像public,它只能被对象访问。
演示static和public 方法之间差异的示例:
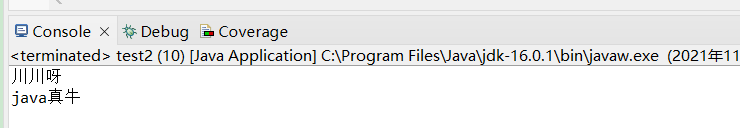
package test15;
public class test2 {
// Static method
static void myStaticMethod() {
System.out.println("川川呀");
}
// Public method
public void myPublicMethod() {
System.out.println("java真牛");
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
myStaticMethod(); // Call the static method
// myPublicMethod(); This would compile an error
test2 myObj = new test2(); // Create an object of Main
myObj.myPublicMethod(); // Call the public method on the object
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
运行:
使用对象访问方法
举个例子:创建一个名为 的 Car 对象myCar。调用对象 上的fullThrottle()和speed()方法myCar,并运行程序
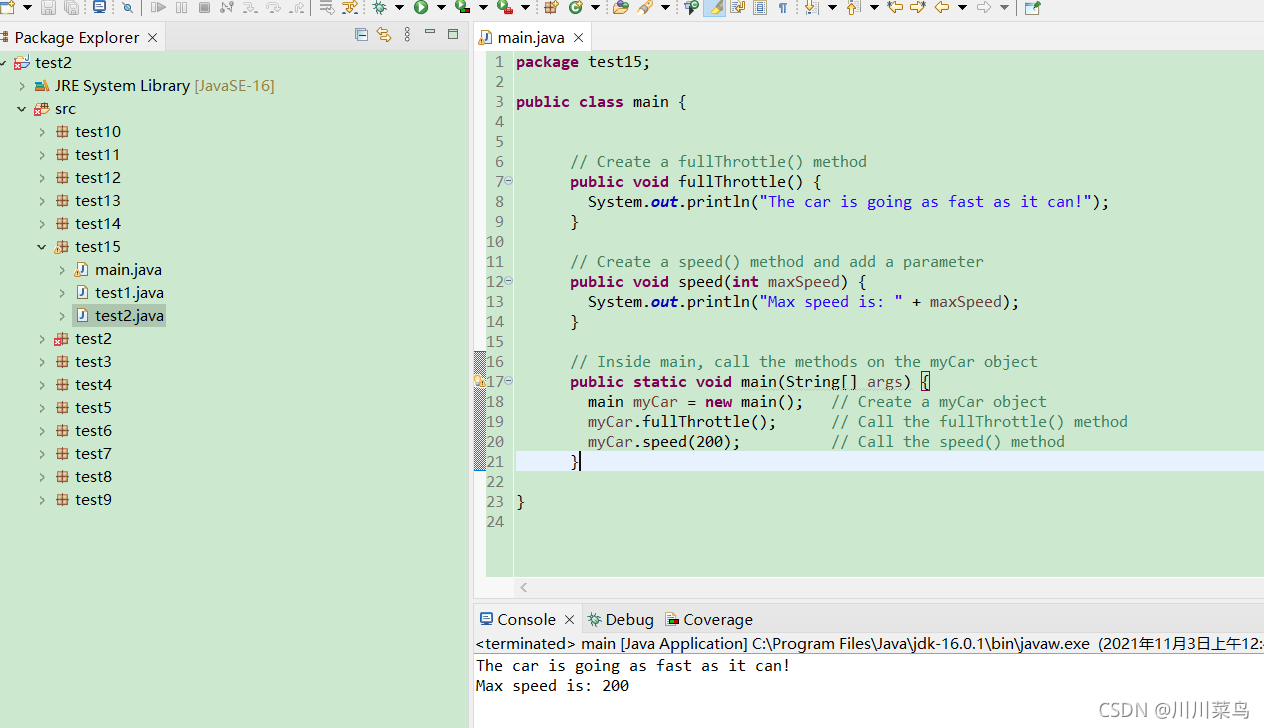
package test15;
public class main {
// Create a fullThrottle() method
public void fullThrottle() {
System.out.println("The car is going as fast as it can!");
}
// Create a speed() method and add a parameter
public void speed(int maxSpeed) {
System.out.println("Max speed is: " + maxSpeed);
}
// Inside main, call the methods on the myCar object
public static void main(String[] args) {
main myCar = new main(); // Create a myCar object
myCar.fullThrottle(); // Call the fullThrottle() method
myCar.speed(200); // Call the speed() method
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
运行:
使用多个类
请记住,java 文件的名称应与类名称匹配。在本例中,我们在同一目录中创建了两个文件
- test3.java
- test4.java
test3.java:
package test15;
public class test3 {
public void fullThrottle() {
System.out.println("小车飞快!");
}
public void speed(int maxSpeed) {
System.out.println("最大速度: " + maxSpeed);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
test4.java:
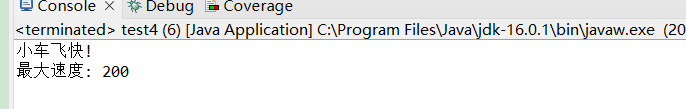
package test15;
public class test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test3 myCar = new test3 (); // Create a myCar object
myCar.fullThrottle(); // Call the fullThrottle() method
myCar.speed(200); // Call the speed() method
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
运行:
文章来源: chuanchuan.blog.csdn.net,作者:川川菜鸟,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:chuanchuan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121112177
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)