各项工具大pk,分组聚合哪家强?
作者简介:小小明,Pandas数据处理专家,致力于帮助无数数据从业者解决数据处理难题。
大家好,我是小小明。
先看一个小需求:
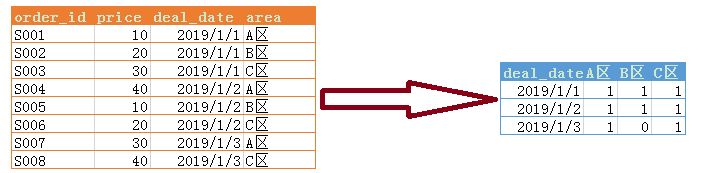
今天呢,我将带大家分别使用MySQL、Excel、Pandas、VBA和Python来实现这个需求,让大家对分组统计代码层面的实现能够更加熟悉。
MySQL实现分组统计
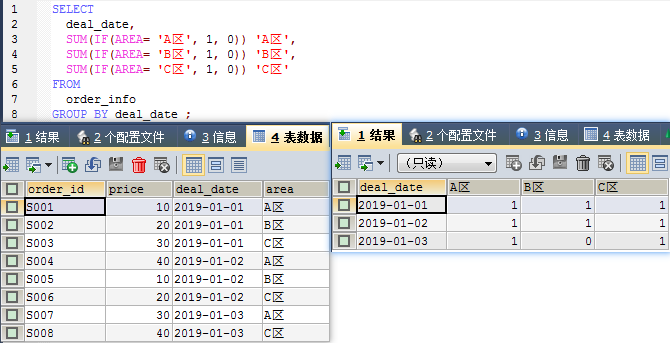
sql语句:
SELECT
deal_date,
SUM(IF(AREA= 'A区', 1, 0)) 'A区',
SUM(IF(AREA= 'B区', 1, 0)) 'B区',
SUM(IF(AREA= 'C区', 1, 0)) 'C区'
FROM
order_info
GROUP BY deal_date ;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
结果:
Excel实现分组统计
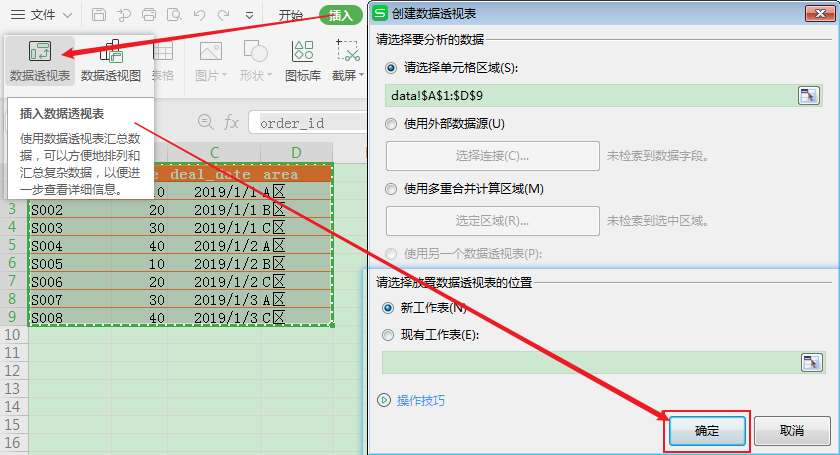
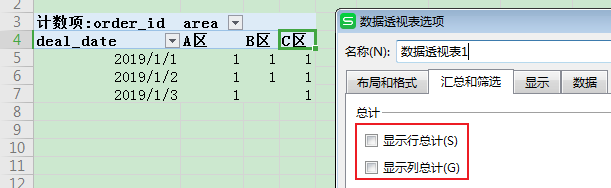
首先创建数据透视表:
然后将对应的字段拖动到正确的位置:
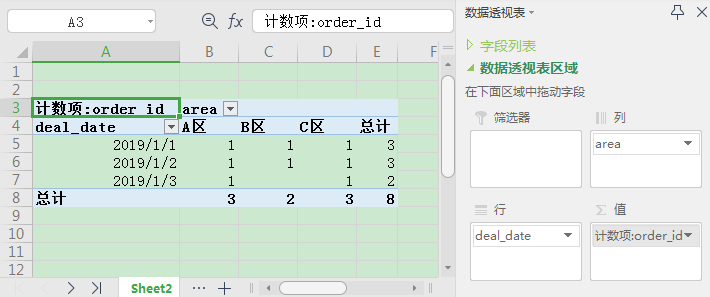
然后打开透视表选项取消这两项勾选即可:
Pandas进行分组统计
读取数据:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv", encoding="gb18030")
df
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
结果:
| order_id | price | deal_date | area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | S001 | 10 | 2019/1/1 | A区 |
| 1 | S002 | 20 | 2019/1/1 | B区 |
| 2 | S003 | 30 | 2019/1/1 | C区 |
| 3 | S004 | 40 | 2019/1/2 | A区 |
| 4 | S005 | 10 | 2019/1/2 | B区 |
| 5 | S006 | 20 | 2019/1/2 | C区 |
| 6 | S007 | 30 | 2019/1/3 | A区 |
| 7 | S008 | 40 | 2019/1/3 | C区 |
使用数据透视表操作:
df.pivot_table(values="order_id", index="deal_date",
columns="area", aggfunc="count", fill_value=0)
- 1
- 2
上述代码相当于groupby操作:
df.groupby(["deal_date", "area"])["order_id"].count().unstack(1, fill_value=0)
- 1
但我一般会这样写:
df.groupby(["deal_date", "area"]).size().unstack(1, fill_value=0)
- 1
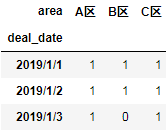
结果均为:
VBA实现分组统计
经过近1小时的痛苦的尝试,终于编写出了下面这段VBA代码,它模拟实现了分组计数的过程:
Option Explicit
Function is_exists(name As String)
Dim sht As Worksheet
For Each sht In Worksheets
If sht.name = name Then
is_exists = True
Exit Function
End If
Next
is_exists = False
End Function
Sub 分组统计()
Dim LastRow, LastCol As Long
Dim Sh As Worksheet
'Sh指代当前活动页
Set Sh = Sheets("data")
'当前活动页的最后一行
LastRow = Sh.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).row
'当前活动页的最后一列
LastCol = Sh.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
'定义D为字典
Dim D As Object
Set D = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
Dim row, i As Integer
Dim key, value As String
For i = 2 To LastRow
key = Sh.Cells(i, 3).value
value = Sh.Cells(i, 4).value
'如果在字典里
If Not D.exists(key) Then
D.Add key, Array(0, 0, 0)
End If
row = D(key)
If value = "A区" Then
row(0) = row(0) + 1
ElseIf value = "B区" Then
row(1) = row(1) + 1
ElseIf value = "C区" Then
row(2) = row(2) + 1
End If
D(key) = row
Next
'调试输出字典存储的内容
For Each key In D.keys()
Debug.Print key & "," & Join(D(key), ",")
Next
Dim sht As Worksheet
If is_exists("result") Then
Sheets("result").Delete
End If
'在最后的位置增加一个sheet作为结果表
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)
Set sht = Sheets(Sheets.Count)
sht.name = "result"
'屏幕刷新=false
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
'下面写出数据到结果表中,首先写出标题行
sht.Range("A1").Resize(1, 4) = Application.Transpose(Array("deal_date", "A区", "B区", "C区"))
sht.Range("A2").Resize(D.Count, 1) = Application.Transpose(D.keys)
i = 2
For Each row In D.items()
sht.Cells(i, 2).Resize(1, 3) = row
i = i + 1
Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
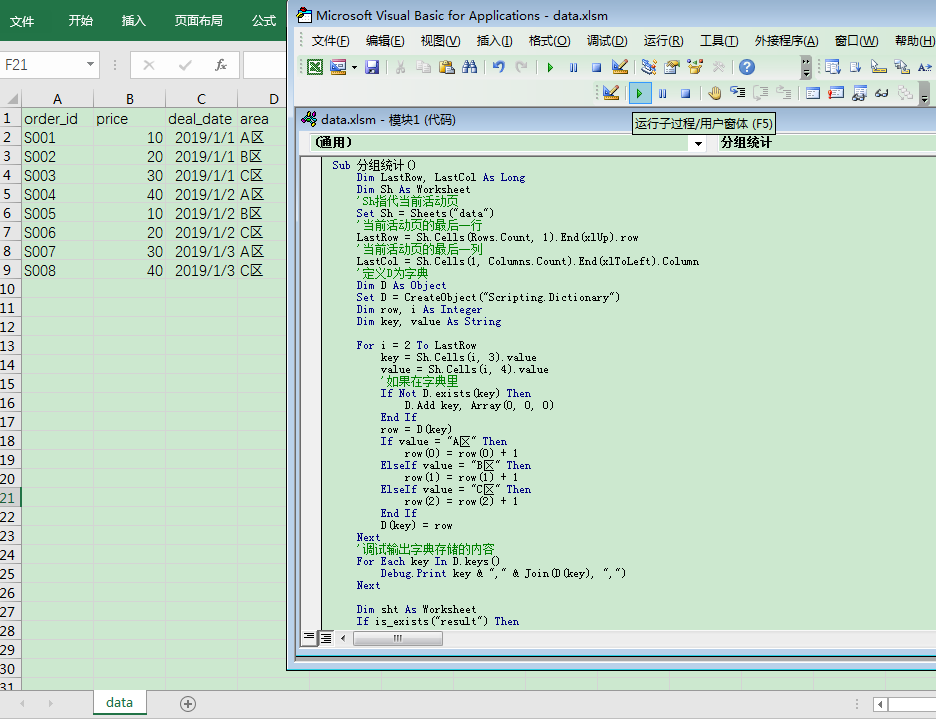
运行前:
点击按钮运行后:
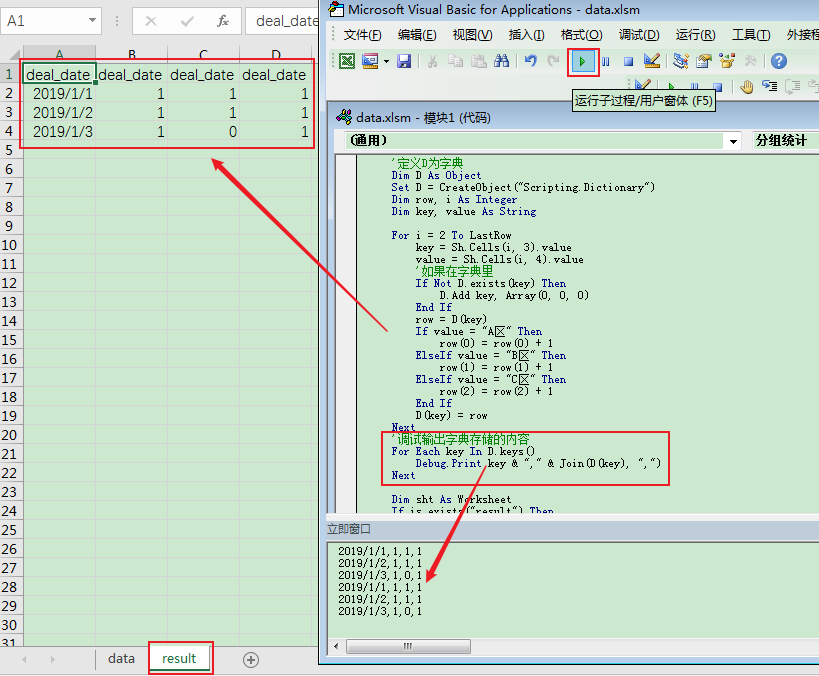
立即窗口和工作表都看到了正确的结果输出,立即窗口看到重复2次的输出是因为我连续运行了两次。
Python实现分组计数
实现代码:
import csv
from collections import namedtuple
result = {}
columns = ["A区", "B区", "C区"]
areas_map = dict(zip(columns, range(len(columns))))
with open("data.csv", encoding="gb18030") as f:
f_csv = csv.reader(f)
headers = next(f_csv)
resultSet = namedtuple("resultSet", headers)
for r in f_csv:
row = resultSet(*r)
areas = result.setdefault(row.deal_date, [0, 0, 0])
areas[areas_map[row.area]] += 1
result
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
结果:
{'2019/1/1': [1, 1, 1], '2019/1/2': [1, 1, 1], '2019/1/3': [1, 0, 1]}
- 1
借助Pandas转换为表结构方便查看:
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(result, 'index', columns=["A区", "B区", "C区"])
- 1
结果:
| A区 | B区 | C区 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/1/1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019/1/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019/1/3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
下面用Python模拟一下Pandas数据透视表实现分组统计的过程:
import csv
from collections import namedtuple, Counter
result = Counter()
with open("data.csv", encoding="gb18030") as f:
f_csv = csv.reader(f)
headers = next(f_csv)
resultSet = namedtuple("resultSet", headers)
for r in f_csv:
row = resultSet(*r)
result[(row.deal_date, row.area)] += 1
result
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
结果:
Counter({('2019/1/1', 'A区'): 1,
('2019/1/1', 'B区'): 1,
('2019/1/1', 'C区'): 1,
('2019/1/2', 'A区'): 1,
('2019/1/2', 'B区'): 1,
('2019/1/2', 'C区'): 1,
('2019/1/3', 'A区'): 1,
('2019/1/3', 'C区'): 1})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
第二步Pandas还需再对这个结果进行重塑才得到最终所需要的结果,具体重塑的过程实际实现较为复杂,但可以借助category的Series模拟实现一下:
indexs = result.keys()
index = pd.Series(map(lambda x: x[0], indexs), dtype='category')
columns = pd.Series(map(lambda x: x[1], indexs), dtype='category')
values = result.values()
data = np.zeros((len(index.cat.categories), len(columns.cat.categories)))
for x, y, v in zip(index.cat.codes, columns.cat.codes, values):
data[x, y] = v
result = pd.DataFrame(data, index=index.cat.categories,
columns=columns.cat.categories, dtype='int8')
result
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
结果:
| A区 | B区 | C区 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/1/1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019/1/2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019/1/3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
总结
其实不管用什么语言和工具,分组聚合统计的核心原理都是:
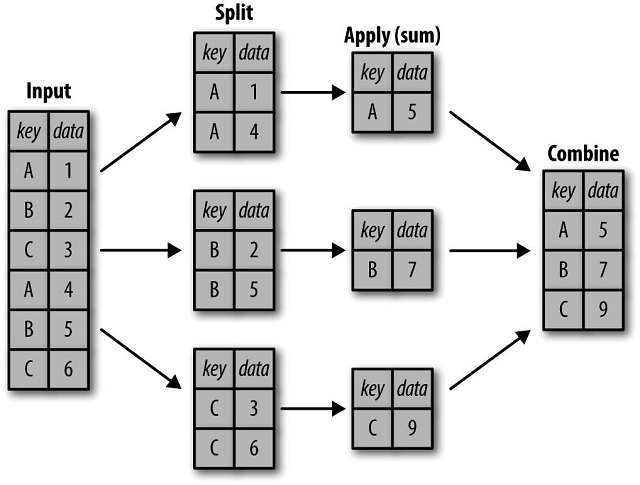
今天我给大家同时演示了MySQL、Excel、Pandas、VBA和Python实现分组聚合,通过对比,或许读者能自己总结出各项工具的优劣和适用场景,欢迎你在下方评论区留言或评论,发表你的看法,给大家分享和互动。
文章来源: xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net,作者:小小明-代码实体,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net/article/details/112384143
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)