使用卷积神经网络识别手写数字图片——tensorflow部署
【摘要】 识别手写数字图片是深度学习的print(“Hello world!”),是入门级别的小实验,主要是熟悉卷积神经网络的开发流程。本次用到的依然是经典的minist数据集,不过事先分出了训练集和测试集并转换成csv格式。
目的
识别手写数字图片是深度学习的print(“Hello world!”),是入门级别的小实验,主要是熟悉卷积神经网络的开发流程。本次用到的依然是经典的minist数据集,不过事先分出了训练集和测试集并转换成csv格式。
网络结构和流程
1.结构简述
由于数据比较简单,所以用到的模型不是很复杂,使用了两层的卷积层和两层全连接层共四层网络,其中卷积层均采用5x5的卷积核,并带有2x2的池化,训练迭代次数为3000次,学习率为 ,每一次喂进去50张图片,训练集共60000张图片,测试集共40000张图片。
2.流程
由于测试集的大小超过了100M,使用本次的存储配置选择OBS,路径选择训练集测试集所在的OBS路径,规格依然选用CPU,工作环境依然只要能使用tensorflow的1.x版本即可。

创建完完成后进入Notebook新建一个tensorflow的文件,并同步训练集测试集和代码文件(即选中所有需要同步的文件后点击左上角的Sync OBS按钮)
点击进入代码文件输入代码即可开始训练。
代码
#导入相关库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
#参数
LEARN_RATE = 1e-5
TRAIN_ITERATIONS = 3000
DROPOUT = 0.5
BATCHSIZE = 50
DISPLAY = 100
#读入训练集和测试集
train_data = pd.read_csv("mnist_train.csv",header = 0)
test_data = pd.read_csv("mnist_test.csv",header = 0)
train_data = train_data.values
test_data = test_data.values
print(train_data.shape,test_data.shape)
#分出标签集和图片集
train_images = train_data[::,1::]
train_labels = train_data[::,0]
test_images = test_data[::,1::]
test_labels = test_data[::,0]
print(train_labels.shape)
#像素点归一化
train_images = train_images.astype(np.float32)
train_images = np.multiply(train_images,1.0/255.0)
test_images = test_images.astype(np.float32)
test_images = np.multiply(test_images,1.0/255.0)
#标签onehot编码化
def to_onehot(labels,classes):
rows = labels.shape[0]
onehot_labels = np.zeros((rows,classes))
index = np.arange(rows)*classes
onehot_labels.flat[index+labels.ravel()] = 1
return onehot_labels
train_labels = to_onehot(train_labels,10)
test_labels = to_onehot(test_labels,10)
train_labels = train_labels.astype(np.uint8)
test_labels = test_labels.astype(np.uint8)
#定义卷积,偏置项,池化
def weight(shape):
w0 = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(w0)
def bias(shape):
b0 = tf.constant(0.1,shape = shape)
return tf.Variable(b0)
def conv2d(x,W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding = 'SAME')
def max_pooling2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding = 'SAME')
#定义输入格式
x = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,784])
y_ = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,10])
#第一层卷积
w_conv1 = weight([5,5,1,32])
b_conv1 = bias([32])
image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1])
#第一层池化
output1 = max_pooling2x2(tf.nn.relu(conv2d(image,w_conv1)+b_conv1))
#第二层卷积
w_conv2 = weight([5,5,32,64])
b_conv2 = bias([64])
#第二层池化
output2 = max_pooling2x2(tf.nn.relu(conv2d(output1,w_conv2)+b_conv2))
#第一层全连接
w_fc1 = weight([7*7*64,1024])
b_fc1 = bias([1024])
input_fc1 = tf.reshape(output2,[-1,7*7*64])
output_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(input_fc1,w_fc1)+b_fc1)
#dropout
keep_rate = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32)
fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(output_fc1,keep_rate)
#第二层全连接(输出层)
w_fc2 = weight([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias([10])
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(fc1_drop,w_fc2)+b_fc2)
#损失函数(交叉熵)
cross_entroy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y))
#优化器,普通的梯度下降
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LEARN_RATE).minimize(cross_entroy)
#精度计算
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
#定义nextbatch
totalnum = 0
index_num = 0
image_num = train_images.shape[0]
def next_batch(batch_size):
global totalnum
global index_num
global train_images
global train_labels
start = index_num
index_num+=batch_size
if index_num>image_num:
totalnum+=1
new_index = np.arange(image_num)
np.random.shuffle(new_index)
train_images = train_images[new_index]
train_labels = train_labels[new_index]
start = 0
index_num = batch_size
assert batch_size<=image_num
end = index_num
return train_images[start:end],train_labels[start:end]
#初始化
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
#迭代训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
train_accuracies = []
test_accuracies = []
x_range = []
display_step = 1
for i in range(TRAIN_ITERATIONS):
xs, ys = next_batch(BATCHSIZE)
if(i%DISPLAY==0 or i == TRAIN_ITERATIONS):
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:xs,
y_:ys,
keep_rate:1.0})
test_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:test_images[0:BATCHSIZE],
y_:test_labels[0:BATCHSIZE],
keep_rate:1.0})
print("step:%d,train accuracy:%.2f,test accuracy:%.2f"%(i,train_accuracy,test_accuracy))
train_accuracies.append(train_accuracy)
test_accuracies.append(test_accuracy)
x_range.append(i)
if i%(display_step*10)==0 or i:
display_step*=10
sess.run(train,feed_dict={x:xs,y_:ys,keep_rate:DROPOUT})
训练过程的精度变化:
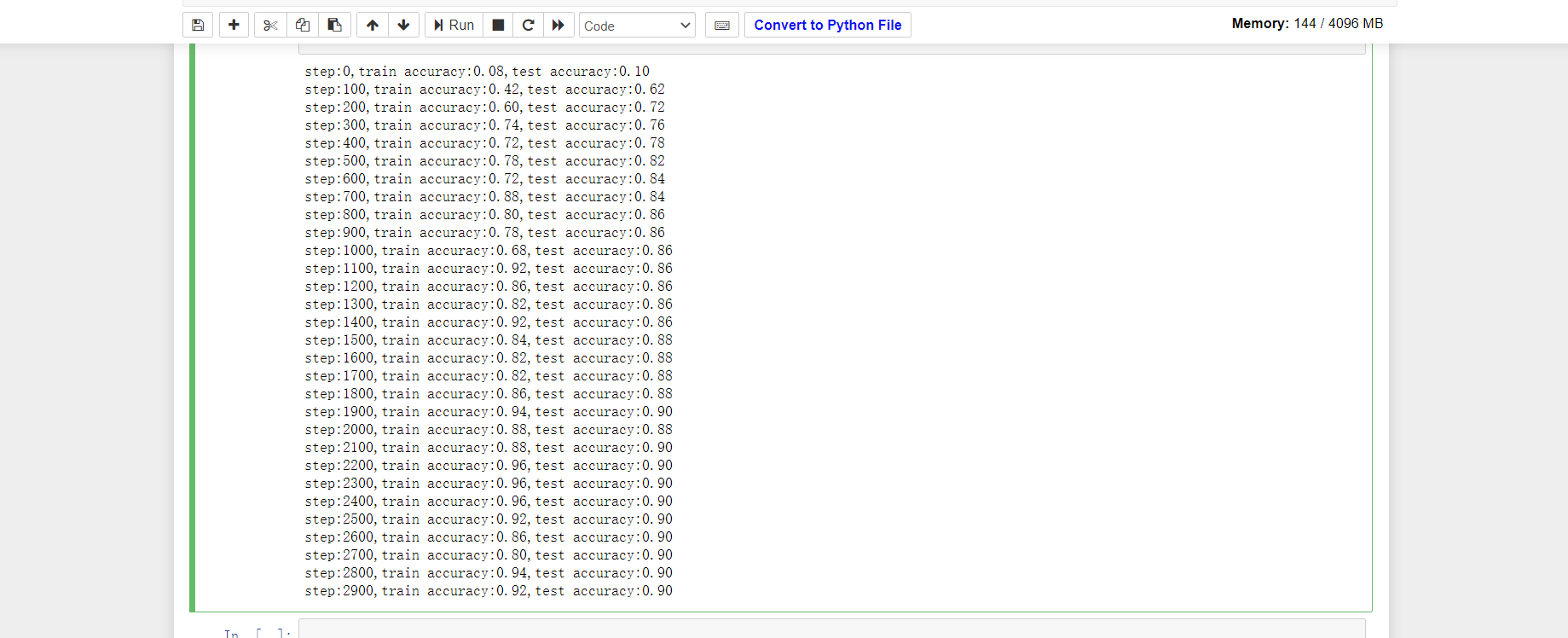
最终对测试集的预测准确率能达到90%左右。
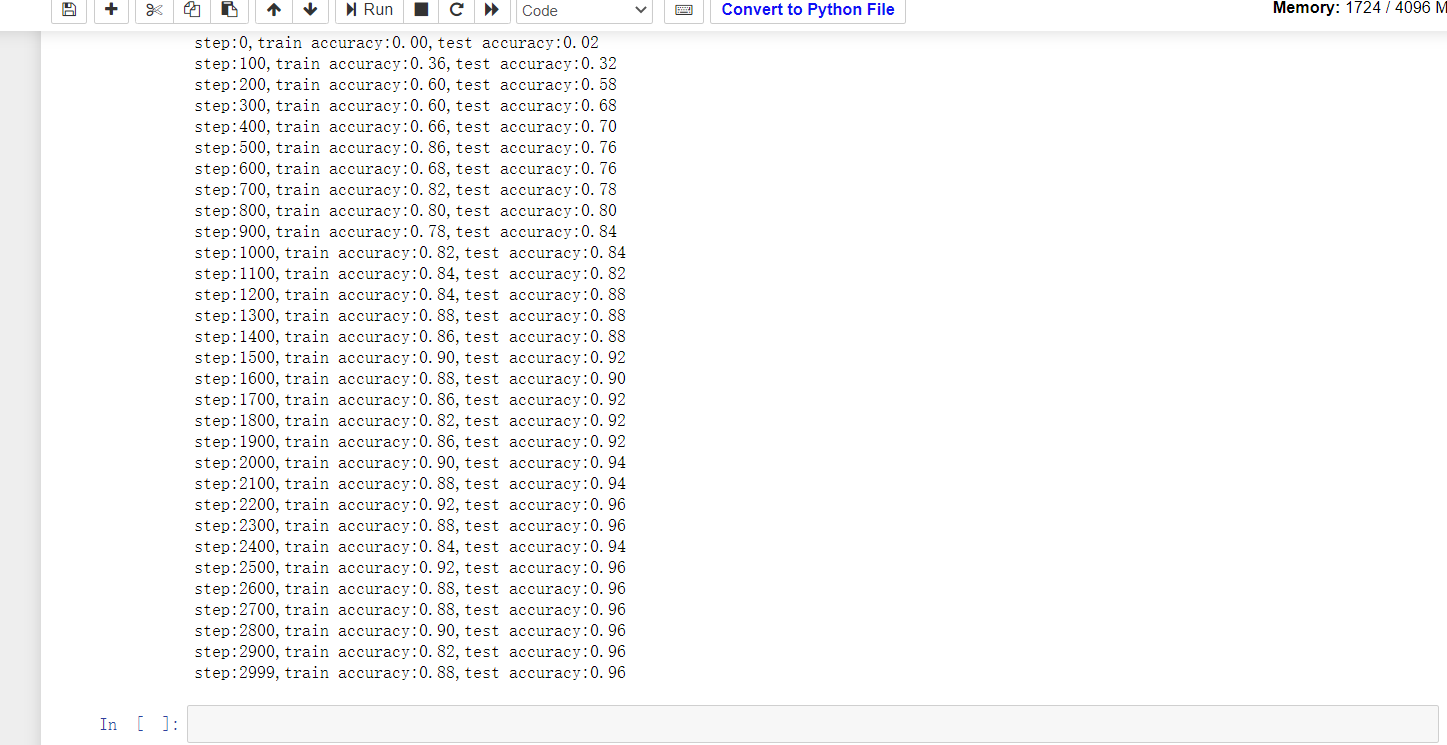
最好的一次训练:
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)