reduce端join与map端join算法实现
本篇博客小菌为大家带来的是MapReduce中reduce端join与map端join算法的实现。
reduce端join算法实现
先让我们来看下需求,有下面两种表格:
订单数据表 t_order:
| id | date | pid | amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 20150710 | P0001 | 3 |
| 1002 | 20150710 | P0002 | 3 |
商品信息表 t_product:
| id | pname | category_id | price |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0001 | 小米5 | 1000 | 2000 |
| P002 | 锤子T1 | 1000 | 3000 |
假如数据量巨大,两表的数据是以文件的形式存储在HDFS中,需要用mapreduce程序来实现一下。
用SQL查询运算的话,语句如下:
select a.id,a.date,b.pname,b.category_id,b.price from t_order a join t_product b on a.pid = b.id
- 1
但如果现在想用MapReduce实现类似的效果该如何实现呢?
正确的思路是:通过将关联的条件作为map输出的key,将两表满足join条件的数据并携带数据所来源的文件信息,发往同一个reduce task,在reduce中进行数据的串联
我们先表格中的数据整理成文件。
orders.txt
1001,20150710,p0001,2
1002,20150710,p0001,3
1002,20150710,p0002,3
- 1
- 2
- 3
product.txt
p0001,小米5,1000,2000
p0002,锤子T1,1000,3000
- 1
- 2
接下来我们就开始上手代码~~
第一步:定义OrderBean
package demo14_join算法_reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Auther: 传智新星
* @Date: 2019/11/18 10:42
* @Description:
*/
public class JoinBean implements Writable {
private String id;
private String date;
private String pid;
private String amount;
private String pname;
private String category_id;
private String price;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "JoinBean{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", date='" + date + '\'' +
", pid='" + pid + '\'' +
", amount='" + amount + '\'' +
", pname='" + pname + '\'' +
", category_id='" + category_id + '\'' +
", price='" + price + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(String pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
public String getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(String amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getPname() {
return pname;
}
public void setPname(String pname) {
this.pname = pname;
}
public String getCategory_id() {
return category_id;
}
public void setCategory_id(String category_id) {
this.category_id = category_id;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
public JoinBean() {
}
public JoinBean(String id, String date, String pid, String amount, String pname, String category_id, String price) {
this.id = id;
this.date = date;
this.pid = pid;
this.amount = amount;
this.pname = pname;
this.category_id = category_id;
this.price = price;
}
//序列化
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(id+"");
out.writeUTF(date+"");
out.writeUTF(pid+"");
out.writeUTF(amount+"");
out.writeUTF(pname+"");
out.writeUTF(category_id+"");
out.writeUTF(price+"");
}
//反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.id=in.readUTF();
this.date=in.readUTF();
this.pid=in.readUTF();
this.amount=in.readUTF();
this.pname=in.readUTF();
this.category_id=in.readUTF();
this.price=in.readUTF();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
第二步:定义map类
package demo14_join算法_reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Auther: 传智新星
* @Date: 2019/11/18 10:48
* @Description:
*/
public class JoinMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text,JoinBean> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//实例JoinBean
JoinBean joinBean = new JoinBean();
//通过context可以获取这行文本所属的文件名称
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit();
String name = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
String [] split = value.toString().split(",");
//对文件名进行判断
//包含orders的就获取角标为2 的数据
if (name.contains("orders")){
joinBean.setId(split[0]);
joinBean.setDate(split[1]);
joinBean.setPid(split[2]);
joinBean.setAmount(split[3]);
context.write(new Text(split[2]),joinBean);
}else{
//不包含orders的就获取数据内角标为0的数据
joinBean.setPname(split[1]);
joinBean.setCategory_id(split[2]);
joinBean.setPrice(split[3]);
context.write(new Text(split[0]),joinBean);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
第三步:自定义reduce类
package demo14_join算法_reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Auther: 传智新星
* @Date: 2019/11/18 11:00
* @Description:
*/
public class JoinReduce extends Reducer<Text,JoinBean,JoinBean, NullWritable> {
// 遍历values 进将多个一半的joinBean 拼接到一起
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<JoinBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//实例一个最终的bean
JoinBean joinBean = new JoinBean();
for (JoinBean value : values) {
if (value.getId()!=null&&!value.getId().equals("null")){
joinBean.setId(value.getId());
joinBean.setDate(value.getDate());
joinBean.setPid(value.getPid());
joinBean.setAmount(value.getAmount());
}else{
joinBean.setPname(value.getPname());
joinBean.setCategory_id(value.getCategory_id());
joinBean.setPrice(value.getPrice());
}
}
//将赋值完的对象赋值
context.write(joinBean,NullWritable.get());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
第四步:开发main方法入口
package demo14_join算法_reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
/**
* @Auther: 传智新星
* @Date: 2019/11/18 11:08
* @Description:
*/
public class JoinDrive extends Configured implements Tool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int run = ToolRunner.run(new JoinDrive(), args);
System.out.println("运行的状态:"+run);
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.实例化Configuration对象
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//实例化Job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "MoreFile");
job.setJarByClass(JoinDrive.class);
//2.设置输入
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("E:\\2019大数据课程\\DeBug\\测试\\order\\素材\\4\\map端join\\input"));
//3.设置map
job.setMapperClass(JoinMap.class);
//设置key,value的输出类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(JoinBean.class);
//4.设置reduce
job.setReducerClass(JoinReduce.class);
//设置key,value的输出类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(JoinBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
//5.设置输出
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("E:\\2019大数据课程\\DeBug\\测试结果\\join1"));
//返回运行结果
return job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
让我们打开join1目录下生成的文件
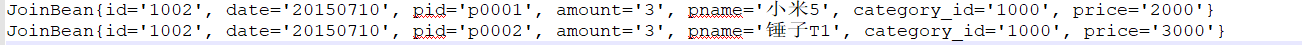
说明我们的程序运行成功!
但我们这个程序也有一个很明显的缺点:join算法是在reduce阶段完成的,reduce端的处理压力太大,map节点的运算负载则很低,资源利用率不高,且在reduce阶段极易产生数据倾斜!
具体的解决方案是什么?这自然而然地引出了我们后面的"主角"——map端的join算法!
map端join算法实现
先让我们来看下map的join算法的原理阐述
- 适用于关联表中有小表的情形
- 可以将小表分发到所有的map节点。这样,map节点就可以在本地对自己所读到的大表数据进行join并输出最终结果,可以大大提高join操作的并发度,加快处理速度
先让我们准备一下数据
pdts.txt(作为"小表"存在的文件必须位于Hadoop集群上)
p0001,xiaomi,1000,2
p0002,appale,1000,3
p0003,samsung,1000,4
- 1
- 2
- 3
orders.txt(map_join_iput文件夹下)
1001,20150710,p0001,2
1002,20150710,p0002,3
1003,20150710,p0003,3
- 1
- 2
- 3
终于可以开始上手代码了~
第一步:定义mapJoin
package demo14_join算法_reducejoin.mapjoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.filecache.DistributedCache;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class JoinMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text,Text> {
HashMap<String,String> b_tab = new HashMap<String, String>();
String line = null;
/*
map端的初始化方法当中获取缓存文件,一次性加载到map当中来
*/
@Override
public void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//这种方式获取所有的缓存文件
// URI[] cacheFiles1 = DistributedCache.getCacheFiles(context.getConfiguration());
URI[] cacheFiles = DistributedCache.getCacheFiles(context.getConfiguration());
// 获取map的缓存文件
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(cacheFiles[0], context.getConfiguration());
//打开缓存文件
FSDataInputStream open = fileSystem.open(new Path(cacheFiles[0]));
//创建缓冲流对象进行读取
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(open));
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
String[] split = line.split(",");
b_tab.put(split[0],split[1]+"\t"+split[2]+"\t"+split[3]);
}
fileSystem.close();
IOUtils.closeStream(bufferedReader);
}
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//这里读的是这个map task所负责的那一个切片数据(在hdfs上)
String[] fields = value.toString().split(",");
String orderId = fields[0];
String date = fields[1];
String pdId = fields[2];
String amount = fields[3];
//获取map当中的商品详细信息
String productInfo = b_tab.get(pdId);
context.write(new Text(orderId), new Text(date + "\t" + productInfo+"\t"+amount));
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
第二步:定义程序运行main方法
package demo14_join算法_reducejoin.mapjoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.filecache.DistributedCache;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.net.URI;
/**
* @Auther: 传智新星
* @Date: 2019/11/18 11:46
* @Description:
*/
public class MapJoinDriver extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//设置缓存文件
DistributedCache.addCacheFile(new URI("hdfs://192.168.100.100/tmp/pdts.txt"),conf);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "MapJoin");
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("E:\\2019大数据课程\\DeBug\\测试\\order\\素材\\4\\map端join\\map_join_iput"));
job.setMapperClass(JoinMap.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("E:\\2019大数据课程\\DeBug\\测试结果\\mapjoin2"));
return job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int run = ToolRunner.run(new MapJoinDriver(), args);
System.out.println("运行状态:"+run);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
程序运行完后,我们进入写入的目录,打开文件

同样结果正确,说明我们的map端的join算法算是成功实现了!!!
那么本次的分享就到这里了,后续小菌还会为大家带来更多Hadoop的内容,喜欢的朋友们不要忘了关注小菌吖٩(๑>◡<๑)۶ 。

文章来源: alice.blog.csdn.net,作者:大数据梦想家,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:alice.blog.csdn.net/article/details/103133868
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)