Spring5 - Bean的初始化和销毁的4种方式
【摘要】
文章目录
概述方式一: 自行指定bean的初始化方法和bean的销毁方法方式二: 通过 InitializingBean和DisposableBean 接口实现bean的初始化以及销毁方法方式三:...

概述
- 针对单实例bean的话,容器启动的时候,bean的对象就创建了,而且容器销毁的时候,也会调用Bean的销毁方法
- 针对原型bean的话,容器启动的时候,bean是不会被创建的而是在获取bean的时候被创建,而且bean的销毁不受 IOC容器的管理.
方式一: 自行指定bean的初始化方法和bean的销毁方法
【beans】
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
public class A1 {
public void init(){
System.out.println("A1 init");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("A1 destory");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
public class A2 {
public void init(){
System.out.println("A2 init");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("A2 destory");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
【配置类】
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
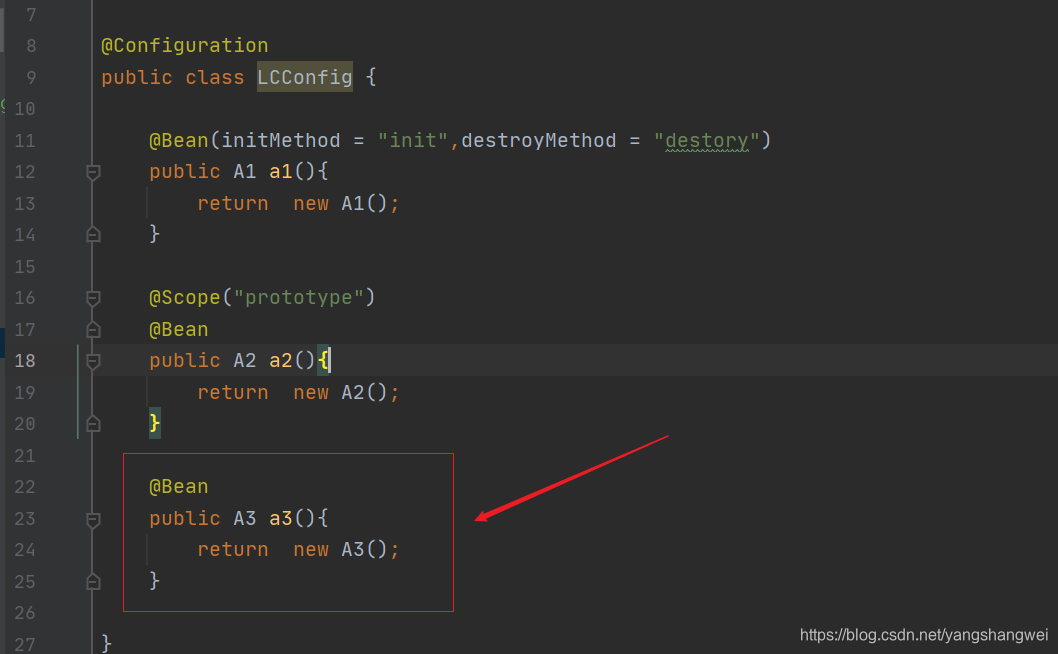
@Configuration
public class LCConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destory")
public A1 a1(){
return new A1();
}
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean
public A2 a2(){
return new A2();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
【测试】
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2020/10/11 22:58
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class LCTest {
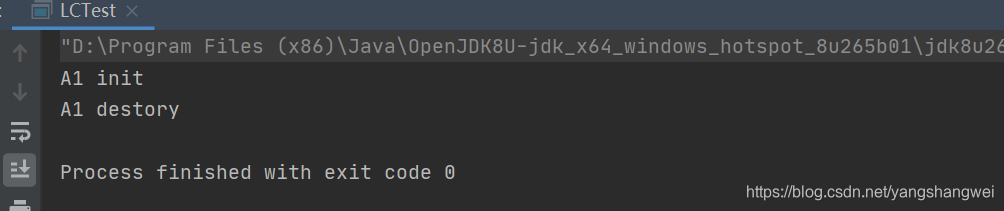
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(LCConfig.class);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
// 容器销毁
ac.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
方式二: 通过 InitializingBean和DisposableBean 接口实现bean的初始化以及销毁方法
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2020/10/11 23:06
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
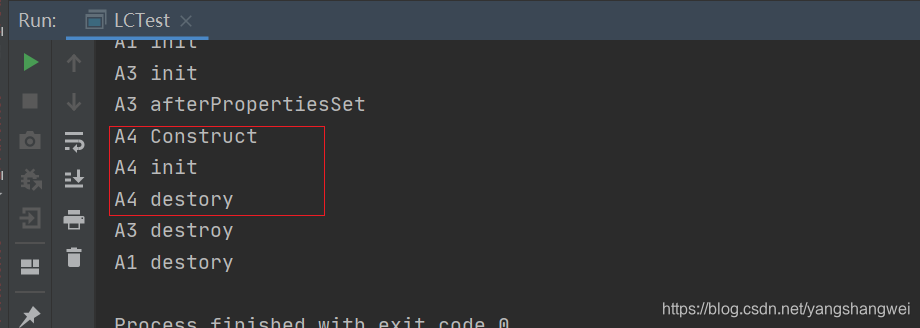
public class A3 implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public A3() {
System.out.println("A3 init");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("A3 destroy");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("A3 afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
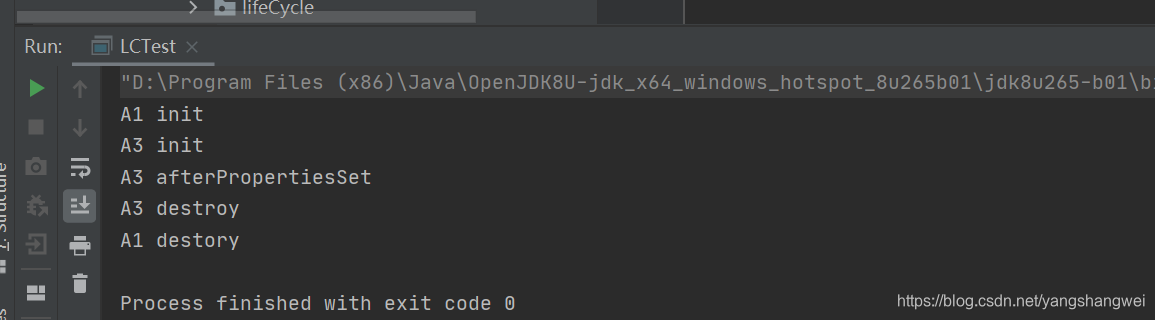
执行上面的测试代码
方式三: 通过JSR250规范 提供的注解@PostConstruct 和@ProDestory标注的方法
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2020/10/11 23:12
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class A4 {
public A4() {
System.out.println("A4 Construct ");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("A4 init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("A4 destory");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
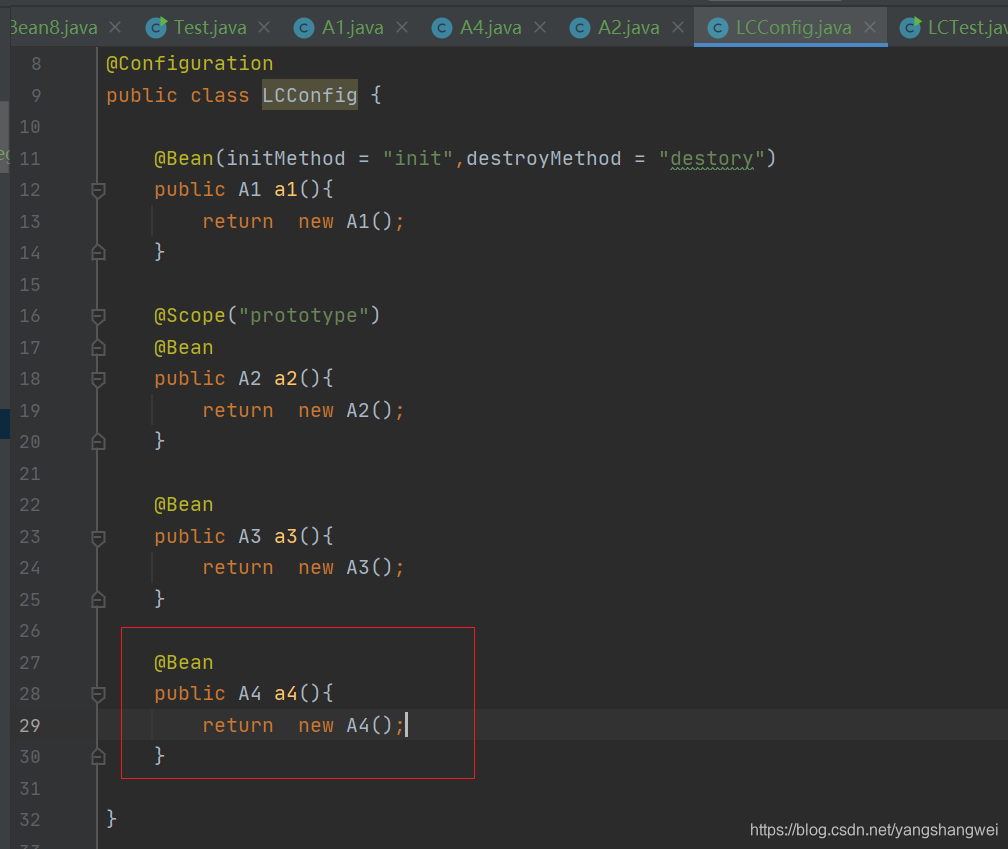
测试结果
方式四:通过Spring的BeanPostProcessor的 bean的后置处理器会拦截所有bean创建过程
public class A5 {
public A5() {
System.out.println("A5 Construct");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("A5 init");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("A5 destory");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
【bean後置處理器】
package com.artisan.base.lifeCycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class A5BeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof A5){
System.out.println("A5BeanPostProcessor...postProcessBeforeInitialization:"+beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof A5){
System.out.println("A5BeanPostProcessor...postProcessAfterInitialization:"+beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
【config】
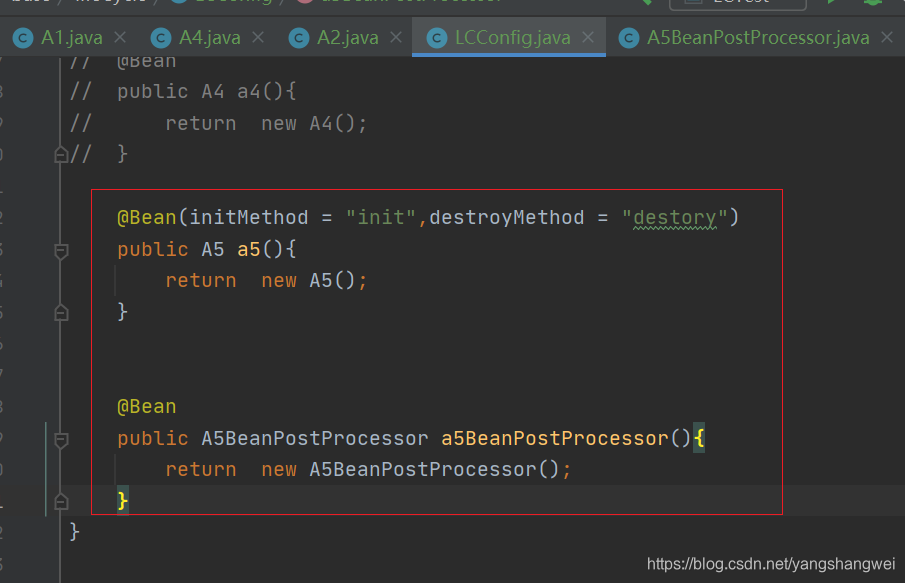
【test】
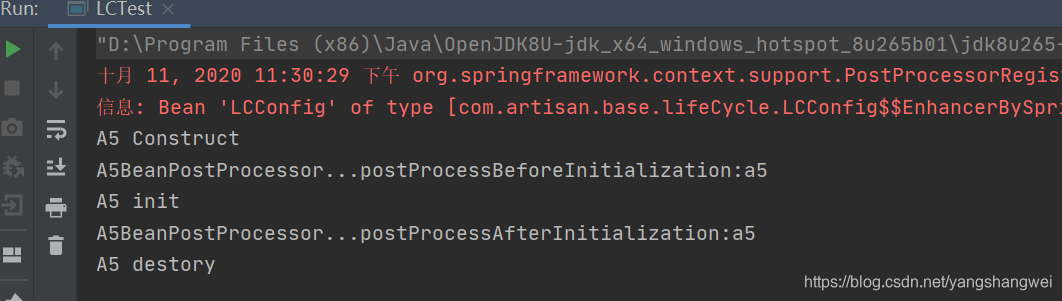
简单说一下 BeanPostProcessor的执行时机
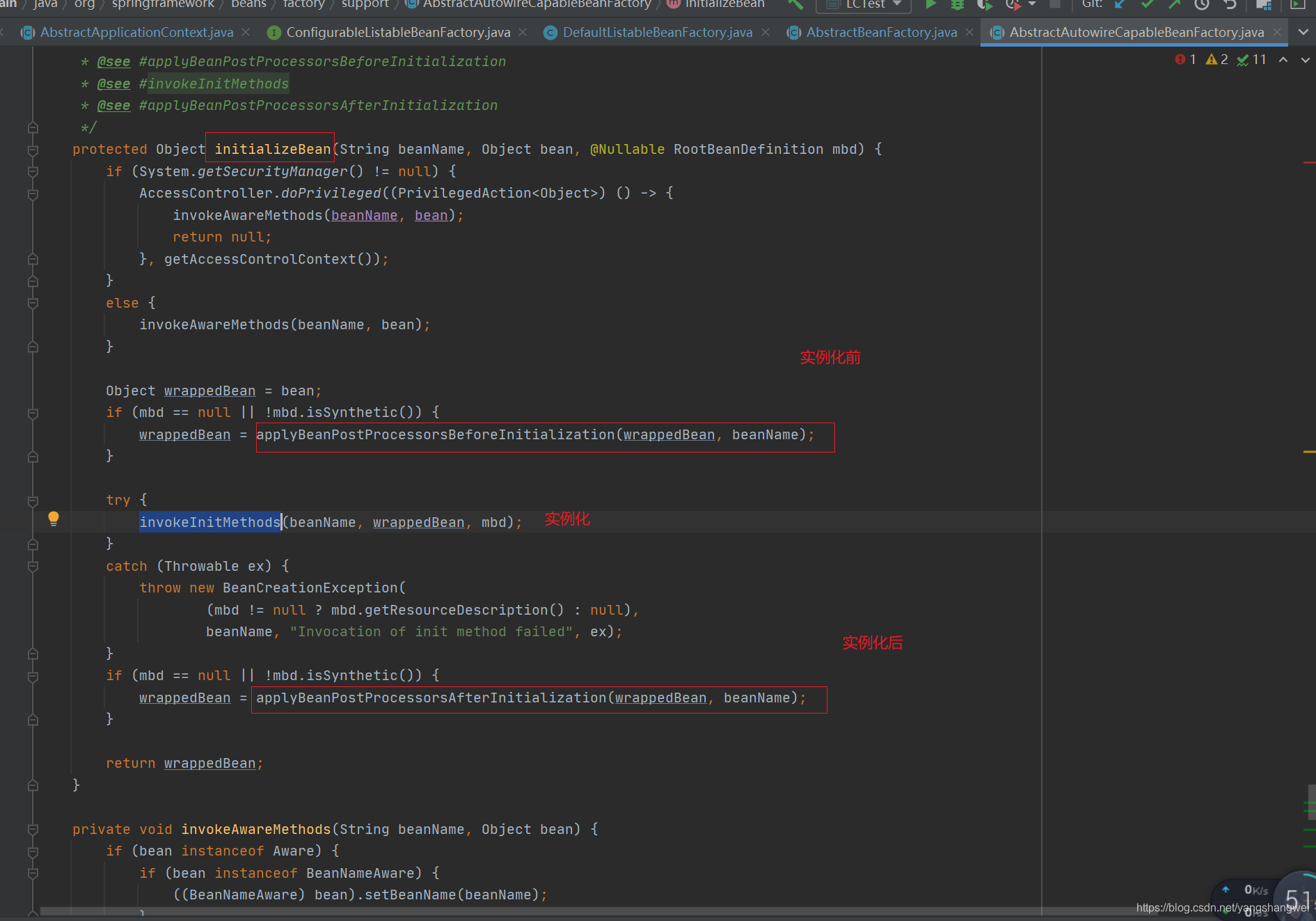
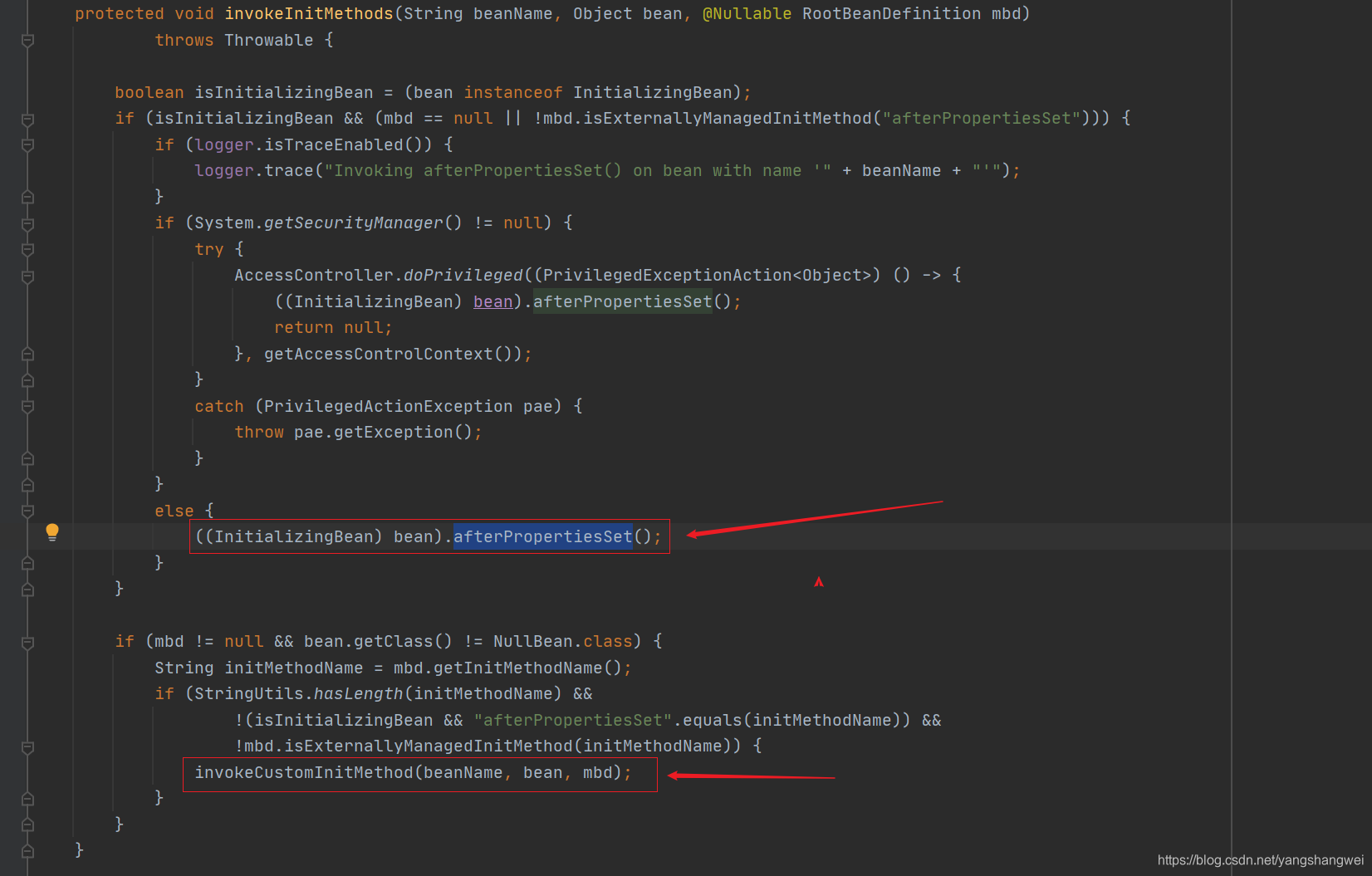
看看invokeInitMethods
文章来源: artisan.blog.csdn.net,作者:小小工匠,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:artisan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/109018923
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)