Spring Session - 使用Spring Session从零到一构建分布式session

快速入门 Spring Session + Redis
官网指导
https://spring.io/projects/spring-session-data-redis#samples

我们就用spring boot 来演示下吧
Demo

pom 依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>boot2</artifactId>
<groupId>com.artisan</groupId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>springsession</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 Spring MVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis lettuce 需要使用-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Spring Session 使用 Redis 作为数据源的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Spring Data Redis 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
配置文件
server:
port: 8888
spring:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: # Redis密码
timeout: 5000ms
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-wait: -1ms
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
session:
store-type: redis
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
-
max-active: 8 # 连接池最大连接数,默认为 8 。使用负数表示没有限制。
-
max-idle: 8 # 默认连接数最大空闲的连接数,默认为 8 。使用负数表示没有限制。
-
min-idle: 0 # 默认连接池最小空闲的连接数,默认为 0 。允许设置 0 和 正数。
-
max-wait: -1 # 连接池最大阻塞等待时间,单位:毫秒。默认为 -1 ,表示不限制。
-
session: store-type: redis 指定存储类型
配置类RedisHttpSessionConfiguration
package com.artisan.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.EnableRedisHttpSession;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2021/2/16 14:12
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
@Configuration
@EnableRedisHttpSession
public class RedisHttpSessionConfiguration {
@Bean(name = "springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer")
public RedisSerializer springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer() {
return RedisSerializer.json();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
添加 @EnableRedisHttpSession 注解,开启自动化配置 Spring Session 使用 Redis 作为数据 。
我们来下 EnableRedisHttpSession 注解

-
maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds 属性,Session 不活跃后的过期时间,默认为 1800 秒。
-
redisNamespace 属性,在 Redis 的 key 的统一前缀,默认为 “spring:session” 。
-
flushMode 属性,Redis 会话刷新模式(RedisFlushMode)。支持两种,默认为
RedisFlushMode.ON_SAVERedisFlushMode.ON_SAVE ,在请求执行完成时,统一写入 Redis 存储。
RedisFlushMode.IMMEDIATE ,在每次修改 Session 时,立即写入 Redis 存储。 -
cleanupCron 属性,清理 Redis Session 会话过期的任务执行 CRON 表达式,默认为
"0 * * * * *"每分钟执行一次。虽然Redis 自带了 key 的过期,但是惰性删除策略,实际过期的 Session 还在 Redis 中占用内存。所以,Spring Session 通过定时任务,删除 Redis 中过期的 Session ,尽快释放 Redis 的内存。
默认情况下,采用 Java 自带的序列化方式 ,可读性很差。 所以在 springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer() 方法,定义了一个 Bean 名字为 springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer的 RedisSerializer Bean ,采用 JSON 序列化方式 。
好了,截止到目前,核心的框架已经搭建起来了,我们来测试下

package com.artisan.controller;
import com.artisan.common.CommonResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2021/2/16 14:42
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
@RestController
public class ArtisanController extends BaseController {
@GetMapping("/mockSet")
public CommonResult set(@RequestParam("key") String key, @RequestParam("value") String value) {
getHttpSession().setAttribute(key, value);
return CommonResult.success("成功模拟登录");
}
@GetMapping("/mockGet")
public CommonResult get(@RequestParam("key") String key) {
return CommonResult.success( getHttpSession().getAttribute(key));
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
启动测试类,走一波
package com.artisan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringSeesionDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringSeesionDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
访问 http://localhost:8888/mockSet?key=artisan &value=avalue
http://localhost:8888/mockGet?key=artisan

Redis中的session数据解析
127.0.0.1:0>keys *
1) "spring:session:sessions:expires:e0dd90b9-9551-4e8a-9609-cde0758b88c2"
2) "spring:session:sessions:e0dd90b9-9551-4e8a-9609-cde0758b88c2"
3) "spring:session:expirations:1613470560000"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
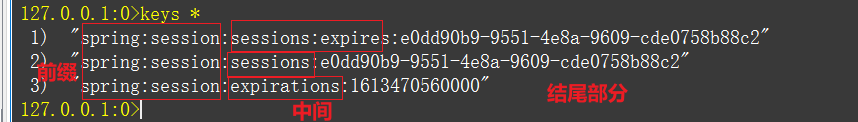
每一个 Session 对应 Redis 二个 key-value 键值对
- 开头:以 spring:session 开头,可以通过 @EnableRedisHttpSession 注解的 redisNamespace 属性配置。
- 结尾:以对应 Session 的 sessionid 结尾。
- 中间:中间分别是
"session"、"expirations"、sessions:expires
一般情况下,只需要关注中间为 session 的 key-value 键值对即可,它负责真正存储 Session 数据

127.0.0.1:0>hgetall spring:session:sessions:ab7d40d8-cd3d-49d7-8b3a-d1ae71d40935
1) "lastAccessedTime" # 最后访问时间
2) "1613469344975"
3) "maxInactiveInterval" # Session 允许最大不活跃时长,单位:秒。
4) "1800"
5) "creationTime" # 创建时间
6) "1613469342207"
7) "sessionAttr:artisan" # 设置的属性值
8) ""avalue""
127.0.0.1:0>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
对于中间为 sessions:expires和 expirations的两个来说,主要为了实现主动删除 Redis 过期的 Session 会话,解决 Redis 惰性删除的问题。
spring:session:expirations:{时间戳},是为了获得每分钟需要过期的 sessionid 集合,即 {时间戳} 是每分钟的时间戳
附 其他相关类
BaseController
package com.artisan.controller;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
public class BaseController {
public HttpServletRequest getRequest(){
return ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
}
public HttpServletResponse getResponse(){
return ((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse();
}
public HttpSession getHttpSession(){
return getRequest().getSession();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
统一返回结果相关的Code
【IErrorCode 】
package com.artisan.common;
public interface IErrorCode {
long getCode();
String getMessage();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
【ResultCode 】
package com.artisan.common;
public enum ResultCode implements IErrorCode {
SUCCESS(200, "操作成功"),
FAILED(500, "操作失败"),
VALIDATE_FAILED(404, "参数检验失败"),
UNAUTHORIZED(401, "暂未登录或token已经过期"),
FORBIDDEN(403, "没有相关权限");
private long code;
private String message;
private ResultCode(long code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public long getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
【CommonResult】
package com.artisan.common;
public class CommonResult<T> {
private long code;
private String message;
private T data;
protected CommonResult() {
}
protected CommonResult(long code, String message, T data) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 成功返回结果
*
* @param data 获取的数据
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> success(T data) {
return new CommonResult<T>(ResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), ResultCode.SUCCESS.getMessage(), data);
}
/**
* 成功返回结果
*
* @param data 获取的数据
* @param message 提示信息
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> success(T data, String message) {
return new CommonResult<T>(ResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), message, data);
}
/**
* 失败返回结果
* @param errorCode 错误码
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> failed(IErrorCode errorCode) {
return new CommonResult<T>(errorCode.getCode(), errorCode.getMessage(), null);
}
/**
* 失败返回结果
* @param message 提示信息
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> failed(String message) {
return new CommonResult<T>(ResultCode.FAILED.getCode(), message, null);
}
/**
* 失败返回结果
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> failed() {
return failed(ResultCode.FAILED);
}
/**
* 参数验证失败返回结果
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> validateFailed() {
return failed(ResultCode.VALIDATE_FAILED);
}
/**
* 参数验证失败返回结果
* @param message 提示信息
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> validateFailed(String message) {
return new CommonResult<T>(ResultCode.VALIDATE_FAILED.getCode(), message, null);
}
/**
* 未登录返回结果
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> unauthorized(T data) {
return new CommonResult<T>(ResultCode.UNAUTHORIZED.getCode(), ResultCode.UNAUTHORIZED.getMessage(), data);
}
/**
* 未授权返回结果
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> forbidden(T data) {
return new CommonResult<T>(ResultCode.FORBIDDEN.getCode(), ResultCode.FORBIDDEN.getMessage(), data);
}
/**
* 请求异常返回结果#add by yangguo
*/
public static <T> CommonResult<T> badResponse(IErrorCode errorCode) {
return new CommonResult<T>(errorCode.getCode(), errorCode.getMessage(), null);
}
public long getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(long code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
Jedis的POM依赖及配置
Spring Boot 2 以上默认使用lettuce作为redis的客户端,如果想要用jedis ,我这里也给大家准备了一份,请参考
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!-- 去掉对 Lettuce 的依赖, Spring Boot 优先使用 Lettuce 作为 Redis 客户端 -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 Jedis 的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
spring:
# 对应 RedisProperties 类
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: # Redis 服务器密码,默认为空。生产中,一定要设置 Redis 密码!
database: 0 # Redis 数据库号,默认为 0 。
timeout: 0 # Redis 连接超时时间,单位:毫秒。
# 对应 RedisProperties.Jedis 内部类
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 8 # 连接池最大连接数,默认为 8 。使用负数表示没有限制。
max-idle: 8 # 默认连接数最大空闲的连接数,默认为 8 。使用负数表示没有限制。
min-idle: 0 # 默认连接池最小空闲的连接数,默认为 0 。允许设置 0 和 正数。
max-wait: -1 # 连接池最大阻塞等待时间,单位:毫秒。默认为 -1 ,表示不限制。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16

文章来源: artisan.blog.csdn.net,作者:小小工匠,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:artisan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/113820856
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)