C++ 二进制文件 & 顺序读写
【摘要】
C++ 二进制文件 & 顺序读写
概述二进制 vs ASCII二进制写入ASCII 写入
read 和 write 读写二进制文件案例一案例二
概述
二进制文件不同于文本文件,...
概述
二进制文件不同于文本文件, 它可以用于任何类型的文件 (包括文本文件).

二进制 vs ASCII
对于数值数据, ASCII 形式与二进制形式不同. ASCII 文件直观, 便于阅读, 但一般占存储空间较多, 而且需要花时间转换. 二进制文件是计算机的内部形式, 节省空间且不需要转换, 但不能直观显示.
对于字符信息, 在内存中是以 ASCII 代码形式存放, 无论用 ASCII 文件输出还是用二进制文件输出, 形式是一样的.
二进制写入
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
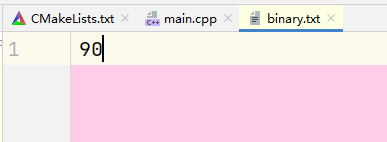
int x = 12345;
ofstream outfile("binary.txt", ios::binary);
outfile.write((char*)&x, 2); // 写入
outfile.close(); // 释放
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
输出结果:
ASCII 写入
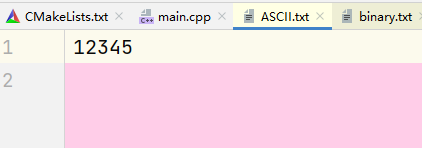
将 int x = 12345 写入文件.
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 12345;
ofstream outfile("ASCII.txt");
outfile << x << endl; // 写入
outfile.close(); // 释放
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
输出结果:
read 和 write 读写二进制文件
打开方式:
ofstream a("file1.dat", ios::out | ios::binary);
ifstream b("file2.dat",ios::in | ios::binary);
- 1
- 2
文件读写方式:
istream& read(char *buffer,int len);
ostream& write(const char * buffer,int len);
- 1
- 2
- char *buffer 指向内存中一段存储空间
- int len 是读写的字节数
例子:
将 p1 指向的空间中 50 个字节存入文件对象 a:
a.write(p1,50)
- 1
从文件对象 b 读出 30 个字节, 存址指向空间:
b.read(p2,30)
- 1
案例一
将数据以二进制的形式存放在磁盘中.
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Student stud[2] = {
{01, "Little White"},
{01, "Big White"}
};
ofstream outfile("student.dat", ios::binary);
if(!outfile){
cerr << "open error" << endl;
exit(1); // 退出程序
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
outfile.write((char*)&stud[i], sizeof(stud[i]));
}
cout << "任务完成, 请查看文件" << endl;
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
案例二
将二进制文件中的数据读入内存.
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Student stud[2];
ifstream infile("student.dat", ios::binary);
if(!infile){
cerr << "open error" << endl;
exit(1); // 退出程序
}
// 读取数据
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
infile.read((char*)&stud[i], sizeof(stud[i]));
}
infile.close();
// 显示数据
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
stud[i].display();
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
文章来源: iamarookie.blog.csdn.net,作者:我是小白呀,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:iamarookie.blog.csdn.net/article/details/117093275
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)