Mybatis学习笔记(四)缓存(一级缓存、二级缓存)
一、Mybatis缓存简介
正如大多数持久层框架一样,MyBatis 同样提供了一级缓存和二级缓存的支持
- 一级缓存: 基于PerpetualCache 的 HashMap本地缓存,其存储作用域为 Session,当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该Session中的所有 Cache 就将清空。
- 二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap存储,不同在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache。
- 对于缓存数据更新机制,当某一个作用域(一级缓存Session/二级缓存Namespaces)的进行了 C/U/D 操作后,默认该作用域下所有 select 中的缓存将被clear。
1. 一级缓存
一级缓存:线程级别的缓存;本地缓存;SqlSession级别的缓存。
Mybatis的一级缓存默认开启。
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//获取和数据库的一次会话:getConnection()
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
//使用SqlSession操作数据库,获取dao接口的实现
TeacherDao mapper = openSession.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
//根据id查询
Teacher teacherById = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById);
System.out.println("-------------------------");
Teacher teacherById2 = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById2);
openSession.commit();
} finally {
//关闭连接
openSession.close();
}
}

只要之前查询过的数据,mybatis就会保存在一个缓存中(Map);下次获取直接从缓存中拿。
2. 一级缓存失效的几种情况
==1.不同的sqlSession,使用不同的一级缓存;只有在同一个SqlSession期间查询到的数据会保存在这个SqlSession的缓存中;下次使用这个sqlSession查询会从缓存中拿。==
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//获取和数据库的一次会话:getConnection()
SqlSession openSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession openSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
//使用SqlSession操作数据库,获取dao接口的实现
TeacherDao mapper = openSession1.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
TeacherDao mapper2 = openSession2.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
Teacher teacherById = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById);
System.out.println("-------------------------");
Teacher teacherById2 = mapper2.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById2);
openSession1.commit();
openSession2.commit();
} finally {
//关闭连接
openSession1.close();
openSession2.close();
}
}

==2.同一个方法,不同参数,由于可能之前没查询过,所有还会发新的sql;==
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//获取和数据库的一次会话:getConnection()
SqlSession openSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
//使用SqlSession操作数据库,获取dao接口的实现
TeacherDao mapper = openSession1.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
Teacher teacherById = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
Teacher teacherById2 = mapper.getTeacherById(2);
System.out.println(teacherById);
System.out.println(teacherById2);
openSession1.commit();
} finally {
//关闭连接
openSession1.close();
}
}

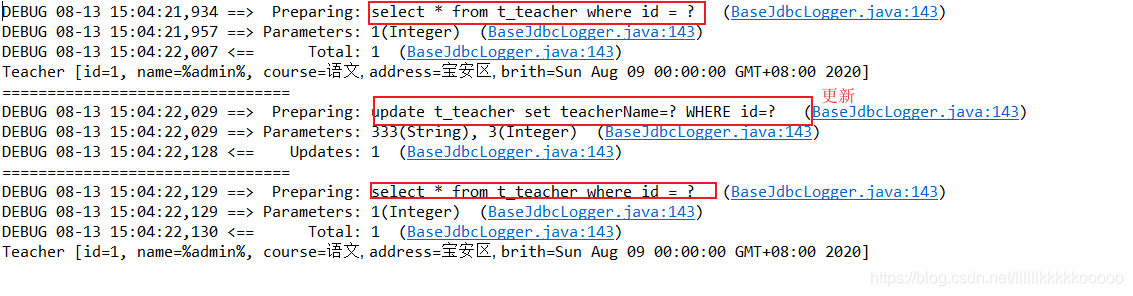
==3.在这个sqlSession期间执行上任何一个增删改操作,增删改操作会把缓存清空。 ==
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//获取和数据库的一次会话:getConnection()
SqlSession openSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
//使用SqlSession操作数据库,获取dao接口的实现
TeacherDao mapper = openSession1.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
Teacher teacherById = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById);
System.out.println("================================");
//执行任何一个增删改方法
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setId(3);
teacher.setName("333");
mapper.updateTeacher(teacher);
System.out.println("================================");
Teacher teacherById2 = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById2);
openSession1.commit();
} finally {
//关闭连接
openSession1.close();
}
}
==4. 手动清空了缓存==
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//获取和数据库的一次会话:getConnection()
SqlSession openSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
//使用SqlSession操作数据库,获取dao接口的实现
TeacherDao mapper = openSession1.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
Teacher teacherById = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById);
System.out.println("================================");
//清空缓存
openSession1.clearCache();
System.out.println("================================");
Teacher teacherById2 = mapper.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById2);
openSession1.commit();
} finally {
//关闭连接
openSession1.close();
}
}

3. 二级缓存
二级缓存:全局范围的缓存;除过当前线程;SqlSession能用其他也可以使用,Mybatis默认没有使用
一级缓存的SqlSession关闭或者提交以后,一级缓存的数据会放在二级缓存中;
==开启二级缓存==
1.在mybatis全局配置文件中开启二级缓存
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
2.在需要使用的Dao的xml添加就可以了
<!--使用二级缓存-->
<cache></cache>
3.对实体类实现序列化接口

测试
@Test
public void test02() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession openSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession openSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
TeacherDao mapper1 = openSession1.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
TeacherDao mapper2 = openSession2.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);
Teacher teacherById1 = mapper1.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById1);
openSession1.close();
System.out.println("--------------------------");
Teacher teacherById2 = mapper2.getTeacherById(1);
System.out.println(teacherById2);
openSession2.close();
}

二、缓存的查询顺序
==1、== 不会出现一级缓存和二级缓存中有同一个数据。
二级缓存中:一级缓存关闭了就有了;
一级缓存中:二级缓存中没有此数据,就会看一级缓存,一级缓存没有就去查询数据库,数据库查询后就会放到一级缓存。
==2、== 任何时候都是先看二级缓存、再看一级缓存,如果大家都没有就去查询数据库;
觉得博主写的不错的读者大大们,可以点赞关注和收藏哦,谢谢各位!
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)